Etzelwerk
| Etzelwerk | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Machine room of the headquarters in Altendorf SZ | |||
| location | |||
|
|
|||
| Coordinates | 704 012 / 227963 | ||
| country |
|
||
| place | Altendorf SZ | ||
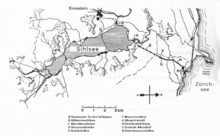
| Waters | Sihlsee | ||
| Data | |||
| Type | pumped storage power plant | ||
| Primary energy | water | ||
| power | 121 MW | ||
| owner | SBB | ||
| Project start | 1899 | ||
| Construction time: | 1932-1937 | ||
| Energy fed in per year | 250 GWh | ||
| Website | company.sbb.ch | ||
| was standing | 2020 | ||
| Etzelwerk AG | |
|---|---|
| legal form | Corporation |
| founding | August 12, 1931 |
| Seat | Einsiedeln SZ |
| management | Markus Geyer |
| Branch | Power generation |
The Etzel Werk AG , headquartered in Einsiedeln is a Swiss power plant company , the traction power (16.7 hertz produced).
history
A first project to build a power plant with a storage lake in the high valley east of Einsiedeln was presented in the Swiss construction newspaper as early as 1899 . It was developed by L. Kürsteiner in collaboration with the Maschinenfabrik Oerlikon (MFO) and was intended to collect the unused water that drains off at night and make it available during the day. Even then it was recognized that electricity is an easily transportable form of energy that makes Switzerland independent from abroad. In 1900, MFO concluded concession agreements with the districts of Einsiedeln and Höfe . The project also aroused the interest of the canton of Zurich in 1902 , which in 1904 proposed to the Federal Council that the power station should be used for the electrification of the SBB , but at the same time subjected it to a detailed examination, which was published in 1906. The SBB bought the project including the concessions from the MFO in 1909, but found that the concessions for the construction of the plant were insufficient and could not be taken over by the SBB for legal reasons, so that they lapsed unused in October 1910.
During the First World War , the concession negotiations were suspended, which were then resumed and in 1919 led to the conclusion of contracts with the cantons of Zurich and Zug . The cantons of Schwyz followed in 1929 , after additional agreements had been concluded in 1926 for the directly affected districts of Einsiedeln and Höfe and it was clarified that the districts of Schwyz and March were not entitled to a license.
The concession gave the Swiss Federal Railways (SBB) and the Northeast Swiss Power Plants (NOK) the right to generate electricity with water from the Sihl . The situation is unusual in that the license is not granted by one but by five licensees. These are the cantons of Schwyz, Zurich and Zug, as well as the districts of Einsiedeln and Höfe. In 1932 work began on creating the future Sihlsee and building the headquarters of the pumped storage power plant in Altendorf on the upper Lake Zurich ; the construction work was completed in 1937.
The power plant went into operation with six Pelton turbines - three sets of machines produced three-phase alternating current for the national grid, three single-phase alternating current for the SBB. Ten years after commissioning, the two storage pumps were installed in 1947 . In the years 1969 to 1973 the power plant was expanded by a seventh machine set, which is equipped with a single-phase alternating current generator-motor and can be used both for power generation and for pumping.
Until September 30, 1987, NOK supplied the canton of Schwyz with electricity (50 Hertz) from the joint venture. In the run-up to the upcoming renewal of the concession, NOK sold its 50% stake in Etzelwerk to SBB, which applied for the renewal of the concession as the sole shareholder. The power plant has been granted a transitional license that is valid until December 2022. With the withdrawal of the NOK, two high-voltage lines were broken off and the three three-phase alternating current generators were replaced by single-phase alternating current generators.
technology
The Sihl is dammed up to the Sihlsee by the heavyweight dam In den Schlagen . The catchment area of the 11 km² reservoir measures 156 km². The reservoir target of the lake is 889 m above sea level. M., the machine house in Altendorf SZ at 416 m, so that the turbines can use a gradient of over 483 m. In the nacelle there are seven large machine sets and two small Pelton turbines set up to cover internal requirements . All machine sets are operated with single-phase alternating current from the traction current network, which has a frequency of 16.7 Hz. The traction power lines to Gossau SG , Steinen and Ziegelbrücke – Sargans go from the substation .
In 1964, the following machine sets were installed in the power plant:
| Manufacturer | power | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | turbine | pump | generator | Type of current | turbine | pump |
| 1 | Escher Wyss | (no) | BBC | Single-phase current 16 2 ⁄ 3 Hz | 16 MW | - |
| 2 | Bell | (no) | BBC | Single-phase current 16 2 ⁄ 3 Hz | 16 MW | - |
| 3 | Escher Wyss | Escher Wyss | BBC | Single-phase current 16 2 ⁄ 3 Hz | 16 MW | 14 MW |
| 4th | Escher Wyss | Escher Wyss | MFO | Three-phase current 50 Hz | 16 MW | 18 MW |
| 5 | Bell | (no) | MFO | Three-phase current 50 Hz | 16 MW | - |
| 6th | Escher Wyss | (no) | MFO | Three-phase current 50 Hz | 16 MW | - |
In addition to the machine sets listed above, two small vertical-axis Pelton turbines deliver three-phase alternating current for the power plant's own use . Each turbine has an output of 220 kW.
The vertical-axis machine sets work at 500 revolutions per minute. They consist of a two-nozzle Pelton turbine with a screen generator . In machine sets 3 and 4, a five-stage centrifugal pump is arranged below the turbine wheel . The first installed pump from machine set 4 had a delivery rate 10% above expectations, which is why a smaller impeller was installed in the pump from machine set 3, which in turn led to a performance that was 10% too low. When the pumps are started up, they are first filled with water, then run up to operating speed with the Pelton turbine before the generator is synchronized as a motor with the mains.
Between 1969 and 1973 the machine house was lengthened by 25 m and a seventh machine set was put into operation. It consists of a six-nozzle Pelton turbine, a single-phase alternating current motor generator and a five-stage centrifugal pump. The arrangement of this much larger machine set is similar to the existing machine sets. The turbine has an output of 44 MW, the pump 22 MW. The machine set is also operated at 500 revolutions per minute.
literature
- The Etzelwerk 2006. Folded brochure. (No longer available online.) Archived from the original on July 23, 2018 ; accessed on June 3, 2020 .
- H. Eggenberger: The projected Etzelwerk . 1929, doi : 10.5169 / SEALS-43472 ( e-periodica.ch [accessed on June 3, 2020]).
See also
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Federal Office of Energy SFOE: Statistics on hydropower plants. Retrieved June 3, 2020 .
- ↑ a b c d The projected power plants in Wäggithal and Etzel . 1899, doi : 10.5169 / SEALS-21328 .
- ↑ Etzelwerk hydroelectric power station. In: company.sbb.ch. SBB
- ↑ J. Stössel: Report of the Government Council to the Cantonal Council regarding the examination of the Etzelwerk project . In: Official Journal of the Canton of Zurich . JJ Ulrich, 1906, p. 523 ff . ( archive.org [accessed June 4, 2020]).
- ↑ a b 3. Granting of a transitional license to the SBB for the use of the water power of the Sihl near Etzel for the period from May 13, 2017 to December 31, 2022 . ( Einsiedeln.ch [PDF]).
- ↑ Renewal of the Etzelwerk license: FAQ . February 3, 2020, Why did the negotiations take so long? ( sz.ch [PDF]).
- ↑ a b Tehachapi Crossing design studies . In: Department of Water Resources, State of California (Ed.): Bulletin . No. 164 . [Sacramento], 1965, p. 303, 309 (English, archive.org [accessed June 5, 2020]).
- ↑ a b c d The Etzelwerk 2006