Fenazaquin
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
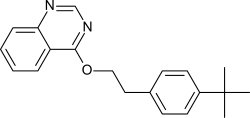
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Fenazaquin | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
4- {2- [4- (1,1-dimethylethyl) phenyl] ethoxy} quinazoline |
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 20 H 22 N 2 O | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless solid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 306.41 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
78.5 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Fenazaquin is a chemical compound from the group of quinazoline derivatives and alkyl aryl ethers .
Extraction and presentation
Fenazaquin can be obtained by reacting 4-quinazolinol with triphenyl phosphite and chlorine and then reacting the intermediate product 4-chloroquinazoline with 4- tert- butylphenylethanol .
properties
Fenazaquin is a colorless solid that is insoluble in water. It hydrolyzes under acidic conditions, but is almost stable under neutral or basic conditions.
use
Fenazaquin has been used as an acaricide since it was first introduced in 1992 . It works by blocking the mitochondrial electron transport in complex I.
Admission status
Fenazaquin is approved as an active ingredient in the EU countries, but pesticides that contain fenazaquin as an active ingredient are not commercially available in Germany, Austria or Switzerland.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e Entry on 4- (2- (4- (1,1-Dimethylethyl) phenyl) ethoxy) quinazoline in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 6, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d Ullmann's Agrochemicals, Volume 1 . Wiley-VCH, 2007, ISBN 978-3-527-31604-5 ( page 558 in the Google book search).
- ↑ Entry on Fenazaquin (ISO) in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on March 15, 2017. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ^ Terence Robert Roberts, DH Hutson: Metabolic pathways of agrochemicals . Royal Soc of Chemistry, 1999, ISBN 978-0-85404-499-3 ( page 224 in Google book search).
- ^ Horst Börner: Plant diseases and plant protection . Springer, 2009, ISBN 978-3-540-49067-8 ( page 588 in the Google book search).
- ↑ Directorate-General for Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on fenazaquin in the EU pesticide database ; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; accessed on December 6, 2019.

