Fluvalinate
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Basic structural formula (stereocenters are marked with an * ) | |||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Fluvalinate | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 26 H 22 ClF 3 N 2 O 3 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
oily amber liquid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 502.92 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point | |||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
1.0 · 10 −7 Torr (25 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Fluvalinate is a mixture of four diastereomeric chemical compounds from the group of pyrethroids , it is synthesized from ( RS ) -valine. Tau fluvalinate (τ-fluvalinate) is the common name of a mixture of two diastereomers. This mixture is also called (2 RS-D ) -fluvalinate because it is synthesized from ( R ) -valine ( D- valine).
Extraction and presentation
Fluvalinate can be obtained from 4-trifluoromethylaniline or 2-chloro-4-trifluoromethylaniline .
Stereoisomers
| Fluvalinate (4 stereoisomers) |
|
|---|---|
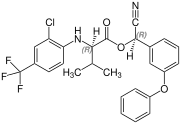 ( R, R ) configuration |
 ( S, S ) configuration |
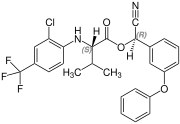 ( S, R ) configuration |
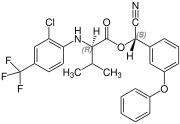 ( R, S ) configuration |
Fluvalinate is synthesized from ( RS ) valine (= racemic valine). The resulting four stereoisomers of fluvalinate are each about 25% in the mixture. The ( R, S ) -configured isomer has the greatest toxic effect against insects.
| τ-fluvalinate (2 diastereomers) trade names: Apistan, Fluvarol, Fluwarol, Klartan, Mavrik |
|
|---|---|
 ( R, R ) configuration |
 ( R, S ) configuration |
Tau fluvalinate is synthesized from ( R ) valine. Therefore, tau fluvalinate is a mixture of the two diastereomers with ( R, R ) - and ( R, S ) -configuration.
properties
Tau fluvalinate is an oily, yellow liquid. It degrades quickly under aerobic conditions, but is stable under anaerobic conditions. It is not bioaccumulative , non-volatile and has a low solubility in water. She is very sensitive to light . The half-life in the soil is 12–92 days, depending on the type of soil.
use
Tau fluvalinate is a broad spectrum insecticide and acaricide belonging to the pyrethroid class. It is approved in the USA against the varroa mite in beehives and for several other uses, for example in ornamental plants and in the seed propagation of carrots and cabbage species. Tau fluvalinate was first registered in 1983 for the Zoecon Corporation as fluvalinate (mixture of four stereoisomers).
Admission
In the European Union, tau fluvalinate has been a permitted crop protection agent for applications as an insecticide and acaricide since June 1, 2011 . In Austria, a product with the active ingredient tau fluvalinate is approved against aphids in cereals, some biting insects in oilseed rape and the rapeseed beetle on various types of cabbage. In Germany and Switzerland there is currently no plant protection product with this active ingredient on the market. Tau fluvalinate is also used in Europe to combat the varroa mite.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e Entry on fluvalinate. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on August 13, 2016.
- ↑ EPA: Reregistration Eligibility Decision for Tau-fluvalinate (PDF; 1.3 MB), September 2005.
- ^ Robert Irving Krieger: Handbook of Pesticide Toxicology . Academic Press, 2001, ISBN 0-12-426260-0 , pp. 1276 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ a b c Entry on N- (2-chloro-4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl) -D-valincyno (3-phenoxyphenyl) methyl ester in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on December 30, 2019(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Entry on cyano- (3-phenoxyphenyl) methyl N- [2-chloro-4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl] -D-valinate in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on December 30, 2019. Manufacturer or . marketer can use the harmonized classification and labeling expand .
- ↑ Extoxnet pip - fluvalinate. extoxnet.orst.edu, accessed July 31, 2017 .
- ↑ Bruce E. Smart, JC Tatlow: Organofluorine Chemistry: Principles and Commercial Applications . Springer, 1994, ISBN 0-306-44610-3 , pp. 250 ( limited preview in Google Book Search).
- ^ David M. Whitacre: Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology . Springer, 2012, ISBN 978-1-4614-3280-7 , pp. 125 ( limited preview in Google Book Search).
- ↑ Shebl M. Sherby, Amira T. Eldefrawi, Sharad S. Deshpande, Edson X. Albuquerque, Mohyee E. Eldefrawi: Effects of pyrethroids on nicotinic acetylcholine receptor binding and function . In: Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology . tape 26 , no. 2 , 1986, p. 107-115 , doi : 10.1016 / 0048-3575 (86) 90082-9 .
- ^ Terence Robert Roberts: Metabolic Pathways of Agrochemicals: Insecticides and fungicides . Royal Society of Chemistry, 1999, ISBN 0-85404-499-X , pp. 670 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ EPA: Tau-fluvalinate Summary Document Registration Review: Initial Docket December 2010 ( Memento of April 12, 2013 in the Internet Archive ) (PDF).
- ↑ Implementing Regulation (EU) No. 540/2011 of the Commission of 25 May 2011 for the implementation of Regulation (EC) No. 1107/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council with regard to the list of approved active substances (PDF) .
- ↑ General Directorate Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on tau-Fluvalinate in the EU pesticide database; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; accessed on March 13, 2016.

