Formanilide
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
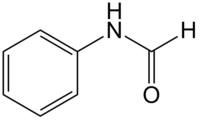
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Formanilide | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
N -phenylformamide |
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 7 H 7 NO | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white solid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 121.14 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.144 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
46.6-47.5 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
271 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
slightly soluble in water (25.4 g l −1 at 20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Formanilide is a chemical compound from the group of carboxamides .
Extraction and presentation
Formanilide can by rapid distillation of aniline and oxalic acid are obtained. It can also be prepared by reaction of aniline with pentafluorophenyl format or by reaction of aryl azides with the enolate of acetaldehyde .
properties
Formanilide is a flammable, hardly inflammable, crystalline, white solid that is sparingly soluble in water. The compound occurs in two isomeric forms ( cis and trans ) at room temperature , which can be distinguished in the NMR spectrum. Reason: The amide bond (more precisely: the CN bond of the carboxamide) is mesomeric stabilized - thus has a partial double bond character - and is therefore not freely rotatable.
use
Formanilide is used as an intermediate in the production of other chemical compounds (for example, mepanipyrim ).
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i Entry on formanilide in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on November 28, 2018(JavaScript required) .
- ^ H. Altenburg, I. Bang, K. Bartelt, Fr. Baum, C. Brahm, W. Cramer, K. Dieterich, R. Ditmar, M. Dohrn, H. Einbeck, H. Euler, E. St. Faust , C. Funk, O. v. Fürth, O. Gerngross, V. Grafe, O. Hesse, K. Kautzsch, Ms. Knoop, R. Kobert, R. Leimbach, J. Lundberg, O. Neubauer, C. Neuberg, M. Kidneystein, OA Oesterle, Th B. Osborne, L. Pincussohn, H. Pringsheim, K. Raske, B. v. Reibold, Br. Rewald, A. Rollett, P. Rona, H. Rupe, Fr. Samuely, H. Scheibler, J. Schmid, J. Schmidt, E. Schmitz, M. Siegfried, E. Strauss, A. Thiele, G. Trier, W. Weichardt, R. Willstätter, A. Windaus, E. Winterstein, E. Witte, G. Zemplén, E. Zunz, Emil Abderhalden: Biochemisches Handlexikon I. Volume, 2nd half . Springer-Verlag, 2013, ISBN 978-3-642-51421-0 , pp. 921 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Malcolm Sainsbury: Aromatic Compounds A Modern Comprehensive Treatise . Elsevier, 1995, ISBN 0-08-088098-3 , pp. 84 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ AJR Bourn, DG Gillies, EW Randall: Cis-trans isomerism in formanilide. In: Tetrahedron . 20, 1964, p. 1811, doi : 10.1016 / S0040-4020 (01) 98450-9 .
- ↑ Ilya I. Marochkin, Olga V. Dorofeeva: Molecular structure and relative stability of trans and cis isomers of formanilides: gas-phase electron diffraction and quantum chemical studies. In: Structural Chemistry . 24, 2013, pp. 233-242, doi : 10.1007 / s11224-012-0071-6 .
- ↑ Thomas A. Unger: Pesticide Synthesis Handbook . William Andrew, 1996, ISBN 978-0-8155-1853-2 , pp. 559 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Eberhard Breitmaier, Günther Jung: Organic chemistry basics, substance classes, reactions, concepts, molecular structures; 129 tables . Georg Thieme Verlag, 2005, ISBN 978-3-13-541505-5 , p. 313 ( limited preview in Google Book search).