Gallium hydroxide
| Crystal structure | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
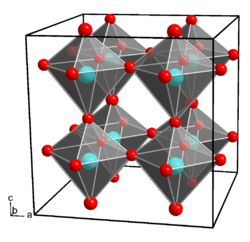
| __ Ga 3+ __ OH - | ||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Gallium hydroxide | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | Ga (OH) 3 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless amorphous mass or crystalline substance |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 120.74 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
3.84 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
soluble in dilute mineral acids |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Gallium hydroxide is a chemical compound of gallium from the group of hydroxides .
Occurrence
Gallium hydroxide occurs naturally as the mineral söhngeit .
Extraction and presentation
Gallium hydroxide is formed during the neutralization of gallium (III) salt solutions . Gallium hydroxide hydrate is a by- product of aluminum production .
properties
Gallium hydroxide occurs either as a colorless amorphous mass or as a colorless orthorhombic and pseudocubic crystalline substance. In addition to gallium hydroxide, gallium (III) oxide monohydrate (GaO (OH) or Ga 2 O 3 • H 2 O) can also be regarded as a further hydroxide of gallium ( gallium oxide hydroxide ), which occurs when gallium hydroxide is heated for a long time at around 170 ° C , by heating to 900 ° C at 50 kbar under hydrothermal conditions or slowly by aging . When heated above 500 ° C it decomposes with the formation of gallium (III) oxide.
Gallium hydroxide crystallizes in the orthorhombic crystal system , space group Pmn 2 1 (space group no. 31) , with the lattice parameters a = 7.487 Å , b = 7.438 Å and c = 7.496 Å. Each gallium atom is coordinated octahedral by six hydroxide ions, each hydroxide ion binds to two gallium ions.
use
By reaction with hydrogen sulfide can gallium (III) sulfide are obtained.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology: Gallium and Gallium Compounds ( Memento of April 27, 2012 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ a b Handbookofmineralogy: Söhngeit (PDF; 70 kB)
- ↑ Jean D'Ans, Ellen Lax; Paperback for chemists and physicists: Volume 3, p. 464; ISBN 978-3540600350
- ↑ a b Georg Brauer (Ed.), With the collaboration of Marianne Baudler u a .: Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry. 3rd, revised edition. Volume II, Ferdinand Enke, Stuttgart 1978, ISBN 3-432-87813-3 , p. 855.
- ↑ There is not yet a harmonized classification for this substance . A labeling of gallium trihydroxide in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), which was accessed on May 26, 2020, is reproduced from a self-classification by the distributor .
- ^ Mineralienatlas: Söhngeit
- ^ A b A. F. Holleman , E. Wiberg , N. Wiberg : Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry . 102nd edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 2007, ISBN 978-3-11-017770-1 , p. 1196.
- ↑ JD Scott: Crystal structure of a new mineral, sohngeite. In: American Mineralogist , 56, 1871, p. 355.
- ↑ Georg Brauer , with the collaboration of Marianne Baudler a . a. (Ed.): Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry . 3rd, revised edition. tape I . Ferdinand Enke, Stuttgart 1975, ISBN 3-432-02328-6 , pp. 857 .


