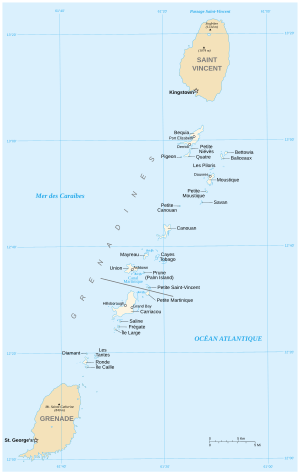
Grenadines
| Grenadines | ||
|---|---|---|
| Waters | Caribbean Sea | |
| archipelago | Leeward Islands | |
| Geographical location | 12 ° 31 ′ N , 61 ° 27 ′ W | |
|
|
||
| Number of islands | 32 | |
| Main island | Carriacou | |
| Total land area | 79 km² | |
| Residents | 17,000 | |
The Grenadines (English Grenadines ) are a cross-border chain of islands between the islands of St. Vincent , Ronde Island and Grenada and geographically belong to the islands above the wind and thus to the Lesser Antilles . They are located between the Caribbean Sea in the west and the Atlantic Ocean in the east. Politically, her northern islands belong to St. Vincent and the Grenadines , her southern islands to Grenada.
The Grenadines include the following inhabited islands: Bequia , Canouan , Mayreau , Mustique , Palm Island , Petit St. Vincent , Rabbit Island , Union Island , Young Island (all part of the state of St. Vincent and the Grenadines ) as well as Petite Martinique and Carriacou (both to the state of Grenada ).
In addition to these islands, there are a number of smaller, uninhabited islands (including Petite Nevis , Isle à Quatre , Battowia, Baliceaux , Petite Mustique , Pigeon Island , Samples Cay , Savan Island , Petit Canouan and Tobago Cays ).
literature
- The Europa World Year Book 2004 . 45th edition, Routledge, ISBN 1-85743-253-3 , pp. 3616-3624.
- Jill Bobrow, Jana Jinkins: St. Vincent and the Grenadines. Gems of the Caribbean. 4th edition, Concepts Pub., Stockbridge (Mass.) 1985, ISBN 0-393-03309-0 .