Heptasulfurimide
| Structural formula | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
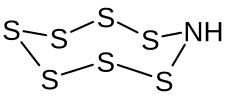
|
||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||
| Surname | Heptasulfurimide | |||||||||
| Molecular formula | NHS 7 | |||||||||
| Brief description |
pale yellow solid |
|||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||
| Molar mass | 239.77 g mol −1 | |||||||||
| density |
2.01 g cm −3 |
|||||||||
| Melting point |
113.5 ° C |
|||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||
Heptasulfurimide is an inorganic chemical compound of sulfur . It belongs to the group of sulfur imides . The structure of the sulfur- nitrogen compound corresponds formally to that of the cyclooctasulfur S 8 .
Presentation and extraction
The heptasulfurimide can be prepared by reacting sulfur with sodium azide in hexamethylphosphoric acid triamide . This initially results in a sodium salt, the protolysis of which leads to the free imide.
properties
Heptasulfurimide is a pale yellow solid that melts at 113.5 ° C. The compound crystallizes in a rhombic crystal system.
It has the properties of a weak acid, as corresponding salts such as S 7 NNa or S 7 N-Hg-NS 7 are known. The reaction of heptasulfurimide with the corresponding sulfur dichlorides S n Cl 2 with n = 1, 2, 3, 5 results in the oligosulfur dinitrides S x N 2 with x = 15, 16, 17, 19. A basic structure S 7 N-S results n –NS 7 , where two S 7 N-ring structures are connected via one, two, three and five sulfur atoms, respectively.
Similar substitution reactions are also possible with other halogen compounds. The bis (heptasulfurimido) sulfoxide is obtained with thionyl chloride .
Analogously, compounds such as boron tribromide , boron tribromide or acetyl chloride are substituted on the NH structure.
The reaction with trimethylsilyldimethylamine gives the corresponding substitution with the trimethylsilyl group .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Wiberg, E .; Wiberg, N .; Holleman, AF : Inorganische Chemie , 103rd edition, 2017 Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co. KG, Berlin / Boston, ISBN 978-3-11-026932-1 , pp. 679-680, (accessed via De Gruyter Online).
- ↑ Goehring, M .; Herb, H .; Koch, W .: About the heptasulfurimide, S 7 NH in Z. Anorg. Chem. 264 (1951) 137-143, doi : 10.1002 / zaac.19512640207 .
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ Wang, Chih-Chieh; Hong, Ying-Ying; Ueng, Chun-Her; Wang, Yu: Charge-density distribution of heptasulfur imide (S 7 NH) in J. Chem. Soc. , Dalton Trans .: Inorg. Chem. (1972-1999), 23 (1992) 3331-3336, doi : 10.1039 / DT9920003331 .
- ↑ Becke-Goehring, M .; Jenne, H .; Rekalic, V .: About the sulfur nitrides S 15 N 2 and S 16 N 2 in Chem. Ber. 92 (1959) 855-857, doi : 10.1002 / cber.19590920413 .
- ↑ Entry on sulfur-nitrogen compounds. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on March 2, 2017.






