Bumble bee
| Bumble bee | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Bumble bee, ♀ |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Chaetocercus bombus | ||||||||||||
| Gould , 1871 |
The bumble bee ( Chaetocercus bombus ) is a species of bird in the hummingbird family (Trochilidae) found in Colombia , Ecuador and Peru . The stock is on the IUCN as endangered ( Vulnerable estimated). The species is considered to be monotypical .
features
The bumble bee reaches a body length of 6 to 7 cm. The male has a straight black beak. The plumage is generally bronze-blue-green. The eye stripe is yellow-brown-white, a color that merges into the ring collar and the chest band. The throat is pink-red, the rest of the underside bronze blue-green. The tail is forked, the outer control springs are reduced to fork prongs. Males in resting plumage have a cinnamon to fox-red throat. The cheeks are dark. The female is bronze-green on the top and cinnamon-colored on the underside. The sides and cesspool are dark yellow. The dark yellow rounded tail has a black subterminal band. Young animals resemble the females.
Behavior and nutrition
The bumble bee gets its nectar from agaves , daisy family , Cavendishia , Inga , Muntingia , Palicourea , Psammisia and other heather plants . Also include arthropods to their food. It is believed that, like the white-bellied elf ( Chaetocercus mulsant ), it subordinates itself to other hummingbirds. With its slow bumblebee-like flight, it often goes unnoticed by territory owners . Their own feeding territories are not part of their feeding strategy.
Reproduction
All that is known about the reproductive biology of the bumble bee is that a male was observed at courtship in March.
Vocalizations
The bumblebee elf's singing probably consists of a mixture of chills, twittering and humming tsitsitsi..tssi-tssi..tschitschip tones. During food intake and in the hovering flight, it emits single chip - or double chip chip - sounds. When communicating with other hummingbirds or when hunting, you can also hear squeaky xwi-xwi-ti-ti-ti sounds. The flapping of the wings sounds like a bee in the hovering flight, the tail feathers can produce a rattling sound.
distribution and habitat
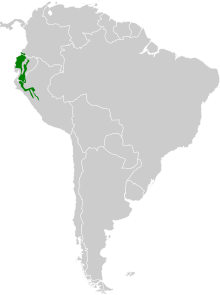
The bumble bee prefers deciduous forests in the transition zone from humid to semi-humid areas at altitudes from sea level to 2300 meters in western Ecuador and 900 to 3000 meters in eastern Ecuador and Peru. It gets its food from the lower to the middle strata .
migration
The bumble bee is probably a resident bird that, as a seasonal line bird, may also migrate at high altitudes.
Etymology and history of research
The first description of the bumble bee was in 1871 by John Gould under the scientific name Chaetocercus bombus . The type specimen was collected by W. Buckley on the Río Citado. In 1855, George Robert Gray introduced the new genus Chaetocercus . This name is made up of the Greek words "chaitē χαιτη " for "long, flying hair" and "kerkos κερκος " for "tail". The species name "bombus" is the Latin word for "humming, humming" or can also be derived from the Greek "bombos βομβος ".
literature
- Thomas Züchner, Eduardo de Juana, Peter Boesman in: Josep del Hoyo , Andrew Elliott, Jordi Sargatal , David Andrew Christie , Eduardo de Juana: Little Woodstar (Chaetocercus bombus) In: Handbook of the Birds of the World Alive . Lynx Edicions, Barcelona.
- James A. Jobling: Helm Dictionary of Scientific Bird Names . Christopher Helm, London 2010, ISBN 978-1-4081-2501-4 .
- John Gould: Mr. Gould brought under the Notice of the meeting two new species of Humming-birds, which he believed to be new to science, and for which he proposed the names of Chaetocerus bombus and Thalurania hypochlora . In: Proceedings of the Scientific Meetings of the Zoological Society of London for the Year 1870 . tape 3 , 1870, p. 803-804 ( biodiversitylibrary.org ).
- George Robert Gray: Catalog of the genera and subgenera of birds contained in the British Museum . Printed by order of the Trustees, London 1855 ( biodiversitylibrary.org ).
Web links
- Chaetocercus bombus inthe IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019.1. Listed by: BirdLife International, 2016. Retrieved June 5, 2019.
- BirdLife International: Species Factsheet - Little Woodstar ( Chaetocercus bombus ) . Retrieved June 5, 2019.
- Videos, photos and sound recordings for Little Woodstar (Chaetocercus bombus) in the Internet Bird Collection
- Bumble bee ( Chaetocercus bombus ) at Avibase; accessed on June 5, 2019.
- Chaetocercus bombus in the Integrated Taxonomic Information System (ITIS). Retrieved June 5, 2019.
- xeno-canto: sound recordings - bumble bee ( Chaetocercus bombus )
- Little Woodstar (Chaetocercus bombus) in the Encyclopedia of Life . Accessed June 5, 2019.
Individual evidence
Remarks
- ↑ Even if the volume shows the year 1870, the article did not appear until 1871.
- ↑ The Río Citado is located south of Pallatanga and northwest of Alausi . It is rarely found in maps. It is shown on the Mapa Base de la Provincia de Chimborazo map.
- ↑ After consulting The Royal Entomological Society, there appears to be an error in A Guide to the Archives of the Royal Entomological Society (2002). With William Buckley (1814–1888) named in the publication, the artist and entomologist William Buckler (1814–1884) should be meant from the data . Possibly the original article is a typo by Gould and he meant the collector Clarence Buckley (1832–? 1885), who was traveling in Ecuador at this time.
- ↑ Gray proposed the red flag elf ( Chaetocercus jourdanii ( Bourcier , 1839)) to the species.