Isobutylamine
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
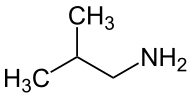
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Isobutylamine | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 4 H 11 N | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
Highly flammable, volatile, colorless liquid with an amine-like odor |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 73.14 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
0.73 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−85 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
66 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
|
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.397 |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
DFG / Switzerland: 2 ml m −3 or 6.1 mg m −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
Isobutylamine is a chemical compound from the group of aliphatic amines .
It is a primary amine and one of the four isomeric amines (besides tert -butylamine , n -butylamine and sec -butylamine ) of butane .
Occurrence
Isobutylamine occurs naturally in some algae and plants.
Extraction and presentation
Isobutylamine can be prepared by reacting isobutyraldehyde with ammonia in the presence of hydrogen .
properties
Physical Properties
Isobutylamine is a colorless liquid that boils at 66 ° C under normal pressure . According to Antoine, the vapor pressure function results from log 10 (P) = A− (B / (T + C)) (P in Pa, T in K) with A = 5.9, B = 1051 and C = −70 in the temperature range from 248 to 347 K.
The aqueous solution of isobutylamine has a strongly alkaline reaction .
Safety-related parameters
The compound forms highly flammable vapor-air mixtures. It has a flash point of −13 ° C. The explosion range is between 1.9% by volume (57 g / m 3 ) as the lower explosion limit (LEL) and 10.8% by volume (330 g / m 3 ) as the upper explosion limit (UEL). The limit gap width was determined to be 1.15 mm. This results in an assignment to explosion group IIA. The ignition temperature is 370 ° C. The substance therefore falls into temperature class T2.
use
Isobutylamine is used to a small extent for organic synthesis and in insecticides .
safety instructions
Carcinogenic substances can form with nitrosating agents.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o Entry on isobutylamine in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on April 8, 2019(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b Isobutylamine data sheet (PDF) from Merck , accessed on February 23, 2010 .
- ↑ Isobutylamine data sheet from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on February 23, 2010 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Swiss Accident Insurance Fund (Suva): Limit values - current MAK and BAT values (search for 78-81-9 or isobutylamine ), accessed on November 2, 2015.
- ^ A b Philip Hall Howard, Handbook of Environmental Fate and Exposure Data for Organic Chemicals, ISBN 0-87371-204-8 .
- ↑ XVII. METHYLAMINE (fischer-tropsch) ( Memento of the original from September 17, 2010 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ^ A b c d E. Brandes, W. Möller: Safety-related parameters - Volume 1: Flammable liquids and gases , Wirtschaftsverlag NW - Verlag für neue Wissenschaft GmbH, Bremerhaven 2003.


