Isobutanal
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Isobutanal | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 4 H 8 O | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless liquid with a pungent odor |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 72.11 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
0.79 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−65 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
64 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
|
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
moderate in water (75 g l −1 at 20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.374 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Thermodynamic properties | ||||||||||||||||
| ΔH f 0 |
−247.3 kJ / mol |
|||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
Isobutanal (according to IUPAC nomenclature: 2-methylpropanal , also known as isobutyraldehyde ) is an organic-chemical compound from the group of aldehydes . In addition to the branched isobutanal, there is also the isomeric compound butanal (butyraldehyde). Isobutanal is an intermediate in the chemical industry .
Extraction and presentation
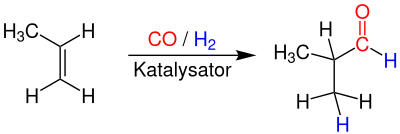
Industrially isobutyraldehyde by hydroformylation of propene by means of organometallic cobalt - or rhodium as the catalyst prepared bar 200 - at temperatures of 130 - 160 ° C and pressures of from 100th
In addition, it can be synthesized by the oxidation of isobutanol (2-methylpropan-1-ol). However, this method is not used because isobutanol is technically only produced by reducing ( hydrogenating ) isobutanal. Isobutanal is also formed during the thermal decomposition of isobutylidenediurea .
properties
Physical Properties
Isobutanal is a volatile, light-sensitive, air-sensitive, highly flammable, colorless liquid with a pungent odor, which is moderately soluble in water. It boils at 64 ° C under normal pressure . The heat of vaporization at the boiling point is 33.4 kJ mol −1 . According to Antoine, the vapor pressure function results from log 10 (P) = A− (B / (T + C)) (P in bar, T in K) with A = 3.87395, B = 1060.141 and C = −63.196 in the temperature range from 286 to 336 K. It has a dynamic viscosity of 0.5 mPa · s.
Safety-related parameters
Isobutanal forms highly flammable vapor-air mixtures. The compound has a flash point of −24 ° C. The explosion range is between 1.6% by volume (47 g / m 3 ) as the lower explosion limit (LEL) and 11% by volume (330 g / m 3 ) as the upper explosion limit (UEL).) The limit gap width was 0 , 92 mm determined. This results in an assignment to explosion group IIA. The ignition temperature is 165 ° C. The substance therefore falls into temperature class T4.
use
Isobutanal is a starting material for the production of valine by the Strecker synthesis :
-
- Isobutanal reacts with ammonia and hydrogen cyanide to form valine and water.
and neopentyl glycol via a Cannizzaro reaction . It can also be used in the Knoevenagel reaction .
It is also an intermediate product for medicinal substances (e.g. D - penicillamine ) and for pesticides.
A large part is also processed further to isobutanol by catalytic hydrogenation .
Biological importance
Isobutanal occurs as a flavoring substance in honey .
Derived connections
- Isobutyraldehyde di (2-ethylhexyl) acetal , additive for drilling fluids
- 2,2,4-trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol monoisobutyrate , coalescing agent
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t Entry on isobutyraldehyde in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on December 15, 2018(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Isobutyraldehyde data sheet from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on September 29, 2010 ( PDF ).
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Standard Thermodynamic Properties of Chemical Substances, pp. 5-26.
- ↑ a b Entry on butyraldehyde. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on November 25, 2018.
- ↑ Entry on isobutyraldehyde in the Hazardous Substances Data Bank , accessed February 7, 2019.
- ↑ Wojtasinski, JG: Measurement of Total Pressures for Determining Liquid-Vapor Equilibrium Relations of the Binary System Isobutyraldehyde n-Butyraldehyde in J. Chem. Eng. Data 8 (1963) 381-385, doi : 10.1021 / je60018a028 .
- ↑ Seprakova, M .; Paulech, J .; Dykyj, J .: Vapor pressure of butyraldehydes in Chem. Zvesti 13 (1959) 313-316.
- ↑ a b c E. Brandes, W. Möller: Safety-related parameters. Volume 1: Flammable Liquids and Gases. Wirtschaftsverlag NW - Verlag für neue Wissenschaft, Bremerhaven 2003.
- ^ Wolfgang M. Weigert, Heribert Offermanns and Paul Scherberich: D -Penicillamine - Production and Properties. In: Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English. 14, 1975, pp. 330-336, doi : 10.1002 / anie.197503301 . PMID 808979 .