Guangzhouwan
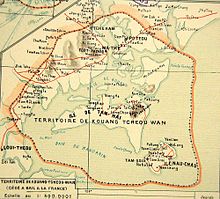
Guangzhouwan ( Chinese 廣州 灣 / 广州 湾 , Pinyin Guǎngzhōu wān , W.-G. Kuang-chou-wan , Jyutping Gwong 2 zau 1 waan 1 - " Guangzhou Bay"; outdated from: Lessing Guang-dschou-wan, Post Kwang -chow-wan , Stange , Kuang-tschou-wan , Vissière Kouang-Tchéou-Wan , Yale Gwang-jou-wan) was a territory in the area of a coastal bay on the southern Chinese peninsula of Leizhou north of the island of Hainan .
The area of Guangzhouwan was from 1899 to (de facto) 1943 French lease area with the administrative seat Fort Bayard (today: Zhanjiang ). It had a size of 842 km 2 and a population of 250,000 (1935).
history
On May 27, 1898, French troops occupied the territory of the later leased area in the south of Guangdong .
In the year after the occupation of the territory France forced the French-Chinese Convention of 16 November 1898 from Imperial China a lease for a period of 99 years (see also the British colony Hong Kong or the German leasehold Jiaozhou Bay ).
The main purpose of leasing the area was to develop southern China, especially Guangdong and Yunnan as far as Sichuan , and to build railways. Furthermore, the area of French influence planned in this area should be controlled from there. The cherished economic hopes for France were never fulfilled due to the poverty of this region.
Guangzhouwan was not an independent colonial area and therefore did not have its own governor . As Territoire de Kouang-Tchéou-Wan, it was under the governor of French Indochina .
After France's defeat in June 1940, the Republic of China, ruled by Chiang Kai-shek , diplomatically recognized " Free France " under Charles de Gaulle and declared it sovereign over the enclave . As a result, the Guangzhouwan administration declared itself loyal to "Free France" and thus refused allegiance to the Vichy government , in contrast to, for example, French Indochina .
After the occupation of the area by Japan following the Second Sino-Japanese War in February 1943, the leased territory by the Vichy government was on 30 July 1943, the collaborating with Japan Chinese puppet government under Wang Jingwei ceded what neither the government of the "Free France “was still recognized by the Republic of China .
The area was formally returned to China by France on February 28, 1946 after the Provisional Government of the French Republic concluded a contract with the Republic of China in the then Chinese capital Chongqing , which officially annulled the agreements on the French concession areas in China that had been in effect until then .
literature
- Office of Strategic Services , Research and Analysis Branch: Survey of China. (1943) In: Editor (Ed.): China and India. (= OSS / State Department. Intelligence and Research Reports. Part III). University Publications of America, Washington, DC 1977, ISBN 0-89093-119-4 , Appendix 2.
Web links
Individual evidence
- ^ Jean Charpentier: Pratique française du droit international public . In: Annuaire français de droit international . tape 5 , 1959, pp. 8886 (French, online bie persée - "Le territoire de Kouang-Tchéou-Wan était rattaché administrativement à l'Indochine, mais il restait soumis, en vertu de la convention franco-chinoise du 16 November 1898, à la souveraineté chinoise.") .