Mastadenovirus
| Mastadenovirus | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
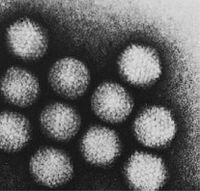
Mastadenovirus |
||||||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Taxonomic characteristics | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||||||
| Mastadenovirus | ||||||||||||||||
| Left | ||||||||||||||||
|
The genus Mastadenovirus includes viruses of the family Adenoviridae , which are found exclusively in mammals . The name of the genus is derived from this property (gr. Μαστός: female breast ). Mastadenoviruses have so far been found in cattle , horses , sheep , goats and pigs , as well as in rodents such as mice , squirrels and guinea pigs . Also in humans and closely related primates Mastadenoviruses were found (see Human adenoviruses ). Mastadenoviruses usually cause infections of the respiratory tract , the conjunctiva and the urinary bladder .
morphology
The approximately 70-90 nm wide non-enveloped virus particles (virions) consist of an icosahedral capsid consisting of 240 hexon proteins ( Triangulationszahl T = 4) and at the corners additional 12 penton proteins is formed. In some species of mastadenoviruses, one or two protein processes (fibers) are found on the pentons . Typical of the genus mastadenovirus is the additional presence of two proteins in the capsid, proteins V and IX. In addition to the structural stabilization of the hexons, protein IX is also active as a functional protein that is involved as a transcription factor in the replication of the virus. Protein V is also responsible for transporting the viral DNA into the cell nucleus . The viral DNA is located inside the capsid.
The surface of the virion, especially the fibers, determine the serological reaction and induction of antibodies . The species and different isolates of the mastadenoviruses can be distinguished serologically, especially by the proteins E3 and E4; however, there are considerable deviations from species of other genera of the Adenoviridae .
Genome
The genome of mastadenoviruses consists of a single, linear molecule of double-stranded DNA with a length of 30,288 to 36,521 bp . At the 5 'end of the DNA, a viral protein (VPg) is non- covalently bound. The sequence motifs typical of adenoviruses ( inverted terminal repetitions , ITRs) are particularly long in mastadenoviruses with 93–371 bp; they contain binding sites for cellular proteins that are adapted to the mammalian cell and serve to control DNA replication.
The species of mastadenoviruses can be associated with dependent viruses (satellite viruses) of the genus Dependovirus (family Parvoviridae ), which, as a helper virus, enable them to multiply.
Systematics
The assignment of the discovered virus isolates of the mastadenoviruses to individual species is very complex. Originally, a classification based on the different properties of these viruses including serological tests, GC base content , haemagglutination properties was carried out. a. was replaced by comparisons of the genome sequences. Both systems differ considerably from each other. Thus it is, for example, for classification of the original serotype bovine adenovirus 9 in the species Human Mastadenovirus C .
Chimpanzee adenoviruses : Adenoviruses isolated from chimpanzees are classified into “human” adenovirus species due to their great similarity to certain human adenoviruses (HAdVs). Thus, the simian adenoviruses are SADV-22 to-25 SADV to the species human Mastadenovirus E and SADV-21 to the species human Mastadenovirus B .
- Genus mastadenovirus
- Species Bovine Mastadenovirus A (BAdV-1)
- Species Bovine Mastadenovirus B (BAdV-3)
- Species Bovine Mastadenovirus C (BAdV-10)
- Species Canine Mastadenovirus A (CAdV-1 and -2)
- Species deer mastadenovirus B ( Deer mastadenovirus B ; OdAdV-2)
- Species dolphin mastadenovirus A and B (BDAdV-2 and BDAdV-1, sic!)
- Species equines mastadenovirus A (EAdV-1)
- Species equines mastadenovirus B (EAdV-2)
- Species bat mastadenovirus A - G ( Bat mastadenovirus A - G ; BaAdV-3, -2, -4, -7, -8, -9 and -11)
- Species human mastadenovirus A (HAdV-12 with serotypes 12, 18, 31)
- Species human mastadenovirus B (HAdV-3 with serotypes 3, 7, 11, 14, 16, 21, 34, 35, 50, 55; SAdV-21)
- Species human mastadenovirus C (HAdV-2 with serotypes 1, 2, 5, 6, 57)
- Species human mastadenovirus D (HAdV-9 with serotypes 8, 9, 10, 13, 15, 17, 19, 20, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 32, 33, 36 , 37, 38, 39, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 51, 53, 54, 56)
- Species human mastadenovirus E (HAdV-4 with serotype 4, SAdV-22 - SAdV-25)
- Species human mastadenovirus F (HAdV-40 with serotypes 40, 41)
- Species human mastadenovirus G (SAdV-1; HAdV-52 with serotype 52)
- Species Murine Mastadenovirus A - C (MAdV-1 - MAdV-3)
- Species New World Monkey Mastadenovirus A ( Platyrrhini Mastadenovirus A ; TMAdV)
- Species Ovines Mastadenovirus A (BAdV-2, sic!)
- Species Ovines Mastadenovirus B (OAdV-1)
- Species Porcine Mastadenovirus A (PAdV-3)
- Species Porcine Mastadenovirus B (PAdV-4)
- Species Porcine Mastadenovirus C (PAdV-5)
- Species sea lion mastadenovirus A ( Sea lion mastadenovirus A ; CSLAdV-1)
- Species Simianes mastadenovirus A - I (SAdV-3, SAdV-49, BabAdV-3, SAdV-13, SAdV-16, SAdV-18, SAdV-20, SAdV-54, SAdV-55)
- Species Skunk Mastadenovirus A (SkAdV)
- Species shrews-Mastadenovirus A ( tree squirrel-Mastadenovirus , Tree shrew mastadenovirus ; TSAdV-1)
- Species of squirrel mastadenovirus ( Squirrel mastadenovirus A; SqAdV-1)
Preliminary and unclassified species of the genus Mastadenovirus :
- Species caprine adenovirus (Goat adenovirus 2, GAdV-2) in goats
- Species adenovirus of the guinea pig ( Guinea pig adenovirus 1 , GPAdV-1)
- Species Ovine adenovirus C (Ovine adenovirus 6, OAdV-6) in sheep in sheep
swell
- M. Benko, B. Harrach et al. : Genus mastadenovirus . In: C. M. Fauquet, M. A. Mayo et al. : Eighth Report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses , London, San Diego 2004, pp. 217-220
Web links
- Genus Mastadenovirus (NCBI)
- Highly Contagious Viral Infection What is Eye Flu? , on: n-tv of February 8, 2020, see Keratoconjunctivitis epidemica
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e ICTV: ICTV Taxonomy history: Human mastadenovirus C , EC 51, Berlin, Germany, July 2019; Email ratification March 2020 (MSL # 35)
- ↑ Page no longer available , search in web archives: 9th report / dsdna-viruses-2011 / w / dsdna viruses / 93 / adenoviridae ICTV 9th Report (2011): Adenoviridae
- ↑ ICTV: Virus Metadata Repository: version November 27, 2019; MSL34
- ↑ Malcolm A. Martin, David M. Knipe, Bernard N. Fields, Peter M. Howley, Diane Griffin, Robert Lamb, Robert: Fields' virology . Wolters Kluwer Health / Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia 2007, ISBN 978-0-7817-6060-7 , p. 2395.
- ↑ Walsh MP, Seto J, Liu EB, Dehghan S, Hudson NR, Lukashev AN, Ivanova O, Chodosh J, Dyer DW, Jones MS, Seto D: Computational analysis of two species C human adenoviruses provides evidence of a novel virus . In: Journal of Clinical Microbiology . 49, No. 10, October 2011, pp. 3482-3490. doi : 10.1128 / JCM.00156-11 . PMID 21849694 . PMC 3187342 (free full text).
- ↑ Robinson CM, Singh G, Henquell C, Walsh MP, Peigue-Lafeuille H, Seto D, Jones MS, Dyer DW, Chodosh J: Computational analysis and identification of an emergent human adenovirus pathogen implicated in a respiratory fatality . In: Virology . 409, No. 2, January 2011, pp. 141-147. doi : 10.1016 / j.virol.2010.10.020 . PMID 21056888 . PMC 3006489 (free full text).
- ↑ Jones MS, Harrach B, Ganac RD, Gozum MM, Dela Cruz WP, Riedel B, Pan C, Delwart EL, Schnurr DP: New adenovirus species found in a patient presenting with gastroenteritis . In: Journal of Virology . 81, No. 11, June 2007, pp. 5978-5984. doi : 10.1128 / JVI.02650-06 . PMID 17360747 . PMC 1900323 (free full text).
- ^ A b D. Raoult: Virus Taxonomy: Eighth Report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses , 2005: The Double Stranded DNA Viruses, ( Mastadenovirus :) TENTATIVE SPECIES IN THE GENUS