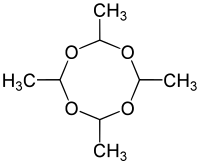
Metaldehyde
| Structural formula | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||
| Structural formula of the tetramer of acetaldehyde without stereochemistry | ||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||
| Surname | Metaldehyde | |||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 8 H 16 O 4 | |||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless, tasteless, highly flammable solid with a weak characteristic odor |
|||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||
| Molar mass | 176.21 g mol −1 | |||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||
| density |
1.27 g cm −3 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||
| Melting point |
45.5 ° C |
|||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
0.3 h Pa (20 ° C) |
|||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||
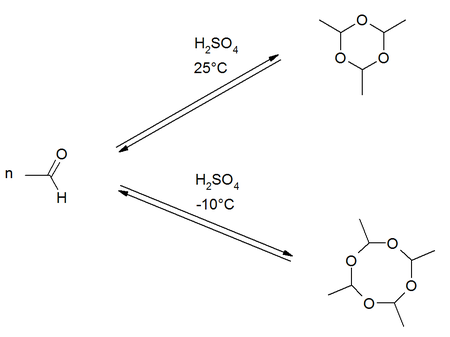
Metaldehyde is a cyclic ether . It is the cyclic tetramer of acetaldehyde . The trimer is called paraldehyde . Polymeric acetaldehyde (CH 3 CHO) n is also marketed under the name metaldehyde . It is used as a dry fuel and molluscicide , but may, according to German Cosmetics Regulation not be used in the manufacture or treatment of cosmetic products. Metaldehyde is found in slug pellets, for example .
Extraction and presentation
Metaldehyde is formed by the cyclization of four molecules of acetaldehyde in the presence of sulfuric acid at low temperatures. The product formation of the cyclization reaction is temperature dependent. The formation of the trimer paraldehyde is preferred at room temperature . At lower temperatures around −10 ° C, the tetrameric metaldehyde is more likely to form.
properties
Metaldehyde is a colorless, tasteless, highly flammable solid with a faint characteristic odor and a melting point of 45.5 ° C. The melting and sublimation temperatures between 100 ° C and 250 ° C given in the literature relate to polymeric acetaldehyde and rather result from depolymerization processes.
As with paraldehyde , several stereoisomers can be formulated for the molecular structure of metaldehyde . The methyl groups can each be axial or equatorial on the ring.
The calorific value is 3370 kJ / mol, corresponding to 19.1 MJ / kg.
See also
Web links
- Poisons Information Monograph (PIM) for Metaldehydes
- Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology: metaldehyde
Individual evidence
- ↑ Data metaldehyde in AlfaAesar, accessed on 14 April 2010 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d enius: metaldehyde , accessed on 4 February 2018th
- ↑ a b c d e f Entry on 2,4,6,8-tetramethyl-1,3,5,7-tetraoxacycloctane in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 8, 2020(JavaScript required) .
- ^ A b E.C. Craven, H. Jowitt, WR Ward: Polymeric forms of acetaldehyde. In: Journal of Applied Chemistry. 12, 1962, pp. 526-535, doi : 10.1002 / jctb.5010121202 .
- ↑ David R. Lide: CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 85th edition, 2005, CRC Press, chap. 3, p. 356.
- ↑ Entry on 2,4,6,8-tetramethyl-1,3,5,7-tetraoxacyclooctane in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can use the harmonized classification and labeling expand .
- ↑ WHO / FAO Data Sheet on Pesticides (PDS) for Metaldehydes , accessed December 9, 2014.
- ↑ a b Aldrich Catalog Manual Fine Chemicals and Laboratory Equipment 2009/2010.
- ↑ HP Lacha; U. Kazmaier; HA Klein: Chemistry for Biologists , Springer Verlag 2005, p. 515, ISBN 3-540-21161-6 .
- ^ Entry on Metaldehyde in the Hazardous Substances Data Bank , accessed on February 10, 2019.