Molybdenum (II) chloride
| Crystal structure | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| __ Mo 2+ __ Cl - | |||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Molybdenum (II) chloride | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
Molybdenum dichloride |
||||||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | MoCl 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
yellow solid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 166.845 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
3.71 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
530 ° C (decomposition) |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Molybdenum (II) chloride is an inorganic chemical compound of molybdenum from the group of chlorides .
Extraction and presentation
Molybdenum (II) chloride can be obtained by
- the reaction of molybdenum with phosgene
- or the reaction of molybdenum (IV) chloride with elemental molybdenum
properties
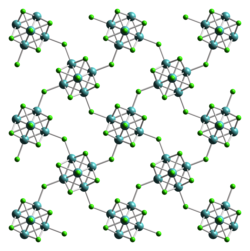
Molybdenum (II) chloride is a yellow, diamagnetic, air-resistant, hygroscopic powder that is insoluble in water , glacial acetic acid , toluene and gasoline . It is soluble in ethanol , ether , acetone , pyridine , dilute strong bases and concentrated hydrochloric acid . It has an orthorhombic crystal structure with the space group Bbem (space group no. 64, position 5) , a = 1124.9 pm, b = 1128.0 pm, c = 1406.7 pm.
Molybdenum (II) chloride MoCl 2 (Mo 6 Cl 12 ) contains an octahedral Mo 6 cluster and thus belongs to the metal clusters . The reactions and the physical properties of molybdenum halide complexes with a {Mo 6 X 8 } 4+ cluster core (X = Cl, Br) were determined by a long-lived luminescence of some analogous compounds and their structural similarity to superconducting Chevrel-Sergent- Phases intensively researched. Molybdenum (II) chloride has a polymeric structure and can be described by the formula [{Mo 6 Cl 8 } Cl 4/2 Cl 2 ] ∞ . In the structure, the {Mo 6 Cl 8 } 4+ cluster cores are connected by chloride ligands to form infinite layers.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f Georg Brauer: Handbook of preparative inorganic chemistry . 3., reworked. Edition. tape III . Enke, Stuttgart 1981, ISBN 3-432-87823-0 , pp. 1531 .
- ^ Dale L. Perry: Handbook of Inorganic Compounds, Second Edition . Taylor & Francis US, 2011, ISBN 1-4398-1462-7 , pp. 491 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ a b c Piero Nannelli and BP Block: Molybdenum (II) halides - A. Molybdenum (II) chloride . In: Robert W. Parry (Ed.): Inorganic Syntheses . tape 12 . McGraw-Hill Book Company, Inc., 1970, ISBN 07-048517-8 ( defective ) , p. 170-178 (English).
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ The former name of this group of rooms was Bbam .
- ↑ Ralf Alsfasser, HJ Meyer: Moderne Anorganische Chemie . Walter de Gruyter, 2007, ISBN 3-11-019060-5 , p. 353 ff . ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Zh. S. Kozhomuratova, NG Naumov, D. Yu. Naumov, EM Uskov, VE Fedorov: Octahedral cluster Mo complexes (Bz3NH) 3 [Mo6OCl13] and (Bz3NH) 2 [Mo6Cl14] ‚· 2CH3CN: Synthesis, crystal structure and properties. In: Russian Journal of Coordination Chemistry. 33, 2007, pp. 213-221, doi : 10.1134 / S1070328407030104 .
![{\ displaystyle \ mathrm {12 \ MoCl_ {3} \ longrightarrow [Mo_ {6} Cl_ {8}] Cl_ {4} +6 \ MoCl_ {4}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/6d2c55657457fdfac8e2efd35d50b1b6fc534032)
![{\ displaystyle \ mathrm {6Mo + 6 \ COCl_ {2} \ longrightarrow [Mo_ {6} Cl_ {8}] Cl_ {4} +6 \ CO}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/1f6f43b2e549bc57641d4a4da4880a9baea3c939)
