N -methylideneaniline
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
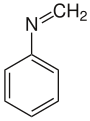
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | N -methylideneaniline | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 7 H 7 N | |||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 105.14 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
142-144 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
N -Methylideneaniline or N -Methylidenaminobenzene is an organic chemical compound and is one of the simplest azomethines . Like dibenzalacetone and benzalaniline , it is used in organometallic chemistry , for example as a ligand to palladium , titanium and platinum and as an intermediate in the synthesis of N -methylaniline .
Reactivity
Due to the double bond and the reactive methylidene group, the molecule has a high reactivity (like benzalaniline ) and can react with many other compounds . The polarized C = N double bond is therefore a good point of attack for nucleophilic and electrophilic particles. Nucleophiles attack the carbon atom of the C = N double bond, while electrophiles attack the nitrogen atom . The substance can easily be hydrogenated to N -methylaniline on the zeolite Y catalyst .
properties
N -methylideneaniline is an odorless, orange-red powder consisting of mixed crystals. The substance is insoluble in water, partially dissolves in chloroform and very well in concentrated sulfuric acid .
presentation
N -methylideneaniline is formed by condensation of aniline and formaldehyde in the presence of water-releasing agents or on a zeolite Y catalyst. Formally, one equivalent of formaldehyde reacts with one equivalent of aniline to form N -methylideneaniline.
In the first step engages nitrogen atom whose free electron pair , the carbonyl group ( aldehyde group ) of the formaldehyde. The double bonded oxygen atom of the carbonyl group becomes a negatively charged, single bonded oxygen atom. In the next step, the nitrogen releases its proton to the negatively charged oxygen atom - a hydroxyl group is formed . With subsequent elimination of water , the N- methylideneaniline is then formed .
Individual evidence
- ↑ JM Patterson, C.-Y. Shiue, WT Smith Jr .: Benzonitrile formation in the pyrolysis of aromatic nitrogen compounds , in J. Org. Chem. 1973 , 38 , 2447-2450; doi : 10.1021 / jo00954a007 .
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ^ A b c E. V. Steen (ed.), C. Claeys (ed.): Recent advances in the science and technology of zeolites and related materials: proceedings of the 14th International Zeolite Conference, Cape Town, South Africa, 25-30. April 2004, Part 3, Gulf Professional Publishing, 2004, ISBN 978-0-444-51825-5 , pp. 2221-2227.

