Naptalam
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
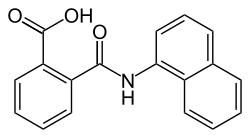
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Naptalam | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 18 H 13 NO 3 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
purple solid with an unpleasant odor |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 291.31 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.40 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
203 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
very sparingly soluble in water (<0.2 g l −1 at 20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Naptalam is a synthetically produced chemical compound from the group of benzamides that is used to control weeds .
Extraction and presentation
Naptalam can be obtained by reacting phthalic anhydride with 1-naphthylamine and sodium hydroxide .
properties
Naptalam is a flammable, not very volatile, purple-colored solid with an unpleasant odor, which is very sparingly soluble in water. It decomposes when heated. Its sodium salt is very soluble.
use
Naptalam is used as a herbicide . It disrupts the direction of growth of roots. The effect is based on the inhibition of the auxin transport.
Admission
The sodium salt of naptalam is approved in the USA as a pre-emergence herbicide for controlling leaf weeds in cucurbits and nursery stock. It was developed by the Uniroyal Chemical Company in 1949 and approved as a herbicide in 1956. In 2002, Naptalam was not included in the list of active ingredients in plant protection products approved in the EU . In Germany, Austria and Switzerland, no pesticides with this active ingredient are permitted.
safety instructions
The sodium salt of Naptalam has the harmonized classification H according to Annex VI of Regulation (EC) No. 1272/2008 (CLP)302.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k Entry for CAS no. 132-66-1 in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on June 14, 2013(JavaScript required) .
- ^ A b c Thomas J. Monaco, Steve C. Weller, Floyd M. Ashton: Weed Science: Principles and Practices . John Wiley & Sons, 2002, ISBN 0-471-27496-8 , pp. 370 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Thomas A. Unger: Pesticide synthesis handbook . 1996, ISBN 978-0-8155-1401-5 , pp. 43 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ a b EPA: Exposure and Risk Assessment on Lower Risk Pesticide Chemicals - Naptalam Sodium (PDF; 714 kB).
- ^ VSP Rao: Principles of Weed Science . Science Publishers, 2000, ISBN 1-57808-069-X , pp. 93 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Regulation (EC) No. 2076/2002 of the Commission of November 20, 2002 (PDF) extending the deadline according to Article 8 (2) of Council Directive 91/414 / EEC and on the non-inclusion of certain active substances in Annex I of this Directive and the revocation of the approval of plant protection products with these active substances.
- ^ Directorate-General for Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on Naptalam in the EU pesticide database; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; accessed on February 22, 2016.
- ↑ Harmonized classification and labeling of naptalam sodium (ISO); Sodium N-naphth-1-ylphthalamate in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on January 2, 2020.