Sodium selenide
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| __ Se 2− __ Na + | ||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Sodium selenide | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | Well 2 se | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
red powder with an unpleasant odor |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 124.94 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
2.625 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
875 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Sodium selenide is an inorganic chemical compound of sodium from the group of selenides .
Extraction and presentation
Sodium selenide can be obtained by reacting sodium with selenium in ammonia .
If there is an excess of selenium, sodium diselenide Na 2 Se 2 , sodium triselenide Na 2 Se 3 , sodium tetraselenide Na 2 Se 4 and sodium hexaselenide Na 2 Se 6 are also formed , which are gray solids that are unstable in moist air.
The reaction of selenium with hydrazine and sodium hydroxide produces sodium diselenide, which can be reduced to sodium selenide with sodium dithionite .
properties
Sodium selenide is a hygroscopic red powder with an unpleasant odor that decomposes in water.
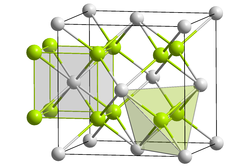
In its pure form, it is white and soluble in water, but dissolves in air with a red color due to selenium deposition and the formation of polyselenides. It has a cubic crystal structure (of the anti- calcium fluoride type) with the space group Fm 3 m (space group no. 225) . Four hydrates are also known of the compound.
It reacts with hydrogen chloride to form hydrogen selenium .
use
Sodium selenide can be used for organic synthesis.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Entry on sodium selenide in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 8, 2020(JavaScript required) .
- ^ A b Jean D'Ans, Ellen Lax: Paperback for chemists and physicists . Springer DE, 1997, ISBN 3-540-60035-3 , pp. 626 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Georg Brauer (Hrsg.): Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry 3rd Edition, Volume 1, Ferdinand Enke Verlag Stuttgart 1975, p. 415.
- ^ A b J. Newton Friend: A Text-Book of Inorganic Chemistry . Forgotten Books, 2012, ISBN 978-1-4510-0469-4 , pp. 147 (English, limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Christos D. Malliakas: Charge Density Waves and Structural Modulations in Polytelluride Compounds . ProQuest, 2008, ISBN 978-0-549-61737-2 , pp. 5 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Thomas Wirth: Organoselenium Chemistry: Modern Developments in Organic Synthesis . Springer, 2000, ISBN 3-540-66516-1 , pp. 60 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Will Kleber , Joachim Bohm : Introduction to Crystallography . Oldenbourg Verlag, 1998, ISBN 3-486-27319-1 , p. 142 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ G. Singh: Chemistry Of Lanthanides And Actinides . Discovery Publishing House, 2007, ISBN 978-81-8356-241-6 , pp. 250 ( limited preview in Google Book Search).
- ↑ Thomas G. Back: organoselenium Chemistry: A Practical Approach . Oxford University Press, 1999, ISBN 0-19-850141-2 , pp. 116 ( limited preview in Google Book search).







