North Atlantic Treaty
The North Atlantic Treaty - also the North Atlantic Pact - is the international treaty that NATO , the North Atlantic Treaty Organization , founded. It is a regional pact that regulates the collective right of self-defense for its members in accordance with Article 51 of the UN Charter . It was signed in Washington, DC on April 4, 1949 and came into effect on August 24, 1949.
background
The contract was drafted by a committee in talks in Washington, DC. The US diplomat Theodore Achilles chaired this committee . Previously, secret talks were held in the Pentagon from March 22 to April 1, 1948, about which Achilles said:
“The talks lasted about two weeks and by the time they finished, it had been secretly agreed that there would be a treaty, and I had a draft of one in the bottom drawer of my safe. It was never shown to anyone except Jack. I wish I had kept it, but when I left the Department in 1950, I dutifully left it in the safe and I have never been able to trace it in the archives. It drew heavily on the Rio Treaty, and a bit of the Brussels Treaty, which had not yet been signed, but of which we were being kept heavily supplied with drafts. The eventual North Atlantic Treaty had the general form, and a good bit of the language of my first draft, but with a number of important differences. "
“The talks lasted about two weeks, and by the time they ended they had secretly agreed that there would be an agreement, and I had the draft one in the bottom drawer of my safe. Nobody but Jack has ever seen him. I wish I had kept it, but when I left the department in 1950 I dutifully left it in the safe and never found it in the archives. It relied heavily on the Rio Pact and a little on the Brussels Pact , which had not yet been signed, but of which we were continuously supplied with drafts. The final North Atlantic Treaty had the principle form and a good part of the text of my first draft, but with some important differences. "
According to Achilles, another major author of the document was diplomat John D. Hickerson :
“More than any human being Jack was responsible for the nature, content, and form of the Treaty […]. It was a one-man Hickerson treaty. "
“More than any other person, Jack was responsible for the nature, content and form of the contract [...]. It was a one-man Hickerson contract. "
The treaty was developed with the assumption of an attack by the Soviet Union on Western Europe "in the back of the head", but the alliance did not have to be declared during the Cold War .
Member states
Founding States
The North Atlantic Treaty was signed in Washington, DC on April 4, 1949 . After all of the signatory states had deposited their instruments of ratification, the treaty entered into force on August 24, 1949. The following twelve nations signed the original document, thereby becoming founding members of NATO:
During the Cold War
In 1952 Greece and Turkey joined NATO, in 1955 the Federal Republic of Germany followed , which also received its sovereignty . Spain joined in 1982.
After the cold war
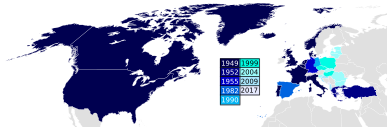
After the end of the East-West conflict in 1989/90, it was another ten years or so before NATO's eastward expansion , with which the first former states of the Warsaw Pact became members. It joined:
-
 Poland (1999)
Poland (1999) -
 Czech Republic (1999)
Czech Republic (1999) -
 Hungary (1999)
Hungary (1999) -
 Bulgaria (2004)
Bulgaria (2004) -
 Estonia (2004)
Estonia (2004) -
 Latvia (2004)
Latvia (2004) -
 Lithuania (2004)
Lithuania (2004) -
 Romania (2004)
Romania (2004) -
 Slovakia (2004)
Slovakia (2004) -
 Slovenia (2004)
Slovenia (2004) -
 Albania (2009)
Albania (2009) -
 Croatia (2009)
Croatia (2009) -
 Montenegro (2017)
Montenegro (2017) -
 North Macedonia (2020)
North Macedonia (2020)
Preamble: basic values
“The parties to this treaty reaffirm their belief in the purposes and principles of the United Nations Constitution and their desire to live in peace with all peoples and governments. They are determined to ensure the freedom, the common heritage and civilization of their peoples, based on the principles of democracy, freedom of person and the rule of law. "
By signing, the states commit themselves to the principle of democracy . (However, it took many years in the member states Greece and Portugal until a democracy could be realized, Turkey is still the subject of criticism today.) Other principles are freedom of the person and the rule of law , also with regard to that International Law and the United Nations . These basic values can be found in the preamble to the treaty. In Article 2, the treaty encourages political and military cooperation as well as economic cooperation and the settlement of economic disputes between the contracting states.
Article 5: Self Defense
"The parties agree that an armed attack against one or more of them in Europe or North America will be regarded as an attack against them all [...]."
The treaty's most important task is to protect all NATO partners against possible aggression. The key part of the treaty is Article 5, which defines the case for alliances . This allows NATO partners to view an armed attack on one or more of them in North America or Europe as an attack on all members. For the first time the existence of the Alliance case in 2001 was decided in response to the terrorist attacks on September 11, 2001 on the World Trade Center and the Pentagon .
The treaty does not contain any automatic military assistance. It is up to each member state, in cooperation with other partners, to take the measures it deems necessary, including the use of armed force.
Article 4 of the treaty contains provisions which, below the threshold of a military intervention, only trigger discussions on military questions. It has been used four times so far:
- three times through Turkey :
- At the end of February 2014, Poland and Lithuania convened the consultations after Russia had occupied and annexed Crimea and shortly thereafter carried out unannounced maneuvers with armed weapons in the western military district on the Baltic Sea.
Article 13: withdrawal from the contract
"After twenty years of the contract, either party may withdraw from the contract one year after notifying the government of the United States of America of the termination [...]."
According to Article 13, the termination must be notified to the US government, and the termination is final one year later.
See also
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b trumanlibrary.org
- ↑ Nato Article 4 - A clear warning to Syria. In: Hamburger Abendblatt , June 25, 2012, accessed on October 3, 2012.
- ↑ What Article 4 means in the NATO Treaty. In: Spiegel Online , October 3, 2012, accessed October 3, 2012.
- ↑ Andrew Rettman: Nato reassures Poland, Baltic states on Russia threat . EU Observer March 4, 2014