Norflurazon
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
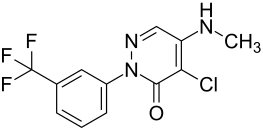
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Norflurazon | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 12 H 9 ClF 3 N 3 O | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless, light gray or light brown odorless crystals |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 303.67 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
184 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility | ||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Norflurazon is a chemical compound from the pyridazinone group .
Extraction and presentation
Norflurazon can be made by reacting N -trifluoromethylaniline with sodium nitrite , sodium sulfite , mucochloric acid and methylamine .
properties
Norflurazon occurs as colorless, light gray or light brown, odorless, light-sensitive crystals that are insoluble in water. It is stable in acidic and basic conditions, but decomposes when exposed to sunlight.
use
Norflurazon is in the 1970s by Sandoz developed herbicide ( pesticides ) from the group of pyridazine - derivatives (see also lactams ).
It is used, for example, in cotton and lingonberries. It works by inhibiting photosynthesis by reducing carotenoid biosynthesis by inhibiting phytoene desaturase.
No pesticides containing this active ingredient are permitted in EU countries such as Germany and Austria or in Switzerland .
Derived connections
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Entry on norflurazon in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 9, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Pesticide Management Education Program: Norflurazon (Zorial, Solicam) Herbicide Profile 12/84 , accessed March 23, 2013 (English).
- ↑ Thomas A. Unger: Pesticide Synthesis Handbook . William Andrew, 1996, ISBN 0-8155-1853-6 , pp. 522 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ A b Terence Robert Roberts, DH Hutson: Metabolic Pathways of Agrochemicals: Insecticides and fungicides . Royal Society of Chemistry, 1998, ISBN 0-85404-494-9 , pp. 411 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ Dataset at the Fluoride Action Network (English) .
- ↑ Entry in maximum residue level regulation .
- ↑ Study on photosynthesis (PDF; 874 kB).
- ↑ General Directorate Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on norflurazon in the EU pesticide database; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; Retrieved March 3, 2016.
