Nymphaea caerulea
| Nymphaea caerulea | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Nymphaea caerulea |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Nymphaea caerulea | ||||||||||||
| Savigny |
Nymphaea caerulea , also known as blue lotus , is a species of the water lily genus ( Nymphaea ). The perennial aquatic plants are widespread in tropical Africa.
description
Nymphaea caerulea is a perennial aquatic plant. The leaves floating on the surface of the water arise from the bulbous, thickened rhizome . The leathery leaves are round to oval, 8 to 30 cm long and 6 to 28 cm wide, the edge of the leaf is entire or slightly wavy. The two leaf lobes end pointed or blunt; their edges can overlap, run parallel to each other or leave a gap. The upper side of the leaf is green and smooth, the underside is green or reddish. The leaf veins can protrude on the underside.
The flowers stand on fleshy flower stalks a little above the surface of the water. The flowers reach a diameter of 6 to 20 cm, their color is blue or pink. The outer four petals ( sepals ) are green, sometimes with reddish borders or reddish stripes or dots. The sepals are oblong-oval or oblong-lanceolate, their length is 3 to 8 cm with a width of 1.1 to 2.5 cm. There are 12 to 24 pieces of the inner petals ( petals ), they are elongated-lanceolate in shape, they end pointed or blunt. In some flowers, some petals show features of the outer petals (therefore there may be different information about the number of petals). There are 30 to 100 or more stamens present, the number of carpels is 12 to 24. The fruit is round with a diameter of 2 to 4 cm, the seeds are oval and 1.1 mm in size.
The flowers open in the morning and close in the late afternoon. They stay closed overnight, only to bloom again the next day. The outer sepals control the opening and closing rhythm of the flower. If the outer sepals are removed, the flower loses its ability to move.
The number of chromosomes is 2n = 28 or 56.
distribution
Nymphaea caerulea are found in slow-flowing rivers and stagnant waters throughout tropical and southern Africa, as well as in Egypt . Further deposits are in Yemen ; in Israel the species is extinct today. In Brazil and Argentina Nymphaea caerulea is naturalized as a neophyte .
Systematics and botanical history
Nymphaea caerulea was first scientifically described by Savigny in 1798 . Within the genus of water lilies ( Nymphaea ), it is classified in the subgenus Brachyceras, which includes other tropical water lilies whose flowers open during the day. In 1989 Verdcourt classified some African water lily species as subspecies of the Nymphaea nouchali widespread in India , including Nymphaea caerulea as Nymphaea nouchali var. Caerulea . An examination of the relationship based on the DNA revealed Nymphaea colorata ( Nymphaea nouchali var. Zanzibarica according to Verdcourt) as close relatives of Nymphaea caerulea .
Historical use
The flowers of Nymphaea caerulea contain psychoactive substances.
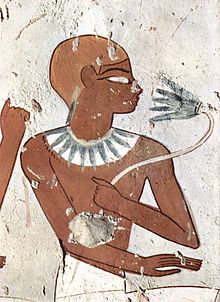
Nymphaea caerulea was already used in ancient Egypt . Dried flowers of tiger lotus and Nymphaea caerulea were found in the grave of Ramses II . The flowers of the tiger lotus ( Nymphaea lotus ) and Nymphaea caerulea can also be found in numerous depictions . While the white flowers of the tiger lotus adorn drinking vessels, the blue flowers of Nymphaea caerulea represent vessels and liquids used in rituals. From this and the fact that Nymphaea caerulea together with opium poppy and mandrake is shown, includes William A. Emboden that the psychoactive properties have been known and used.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b FA Mendoça: Nymphaeaceae . In: Flora Zambesiaca . tape 1 , no. 1 , 1960 ( Flora Zambesiaca ).
- ↑ a b Mark A. Hyde, Bart Wursten: Nymphaea nouchali Burm. f. var. caerulea (Savigny) Verdc. Flora of Zimbabwe, accessed June 23, 2012 .
- ↑ Kiel Botanical Garden of the Christian Albrechts University in Kiel: Blue lotus flower Nymphaea caerulea plant stories , accessed on May 25, 2012
- ↑ Nymphaea caerulea at Tropicos.org. In: IPCN Chromosome Reports . Missouri Botanical Garden, St. Louis
- ↑ a b c Nymphaea in the Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN), USDA , ARS , National Genetic Resources Program. National Germplasm Resources Laboratory, Beltsville, Maryland. Retrieved May 30, 2018.
- ↑ Thomas Borsch, Khidir W. Hilu, John H. Wiersema, Cornelia Lohne, Wilhelm Barthlott, Volker Wilde: Phylogeny of Nymphaea (Nymphaeaceae): Evidence from Substitutions and Microstructural Changes in the Chloroplast trnT-trnF Region . In: International Journal of Plant Science . tape 168 , no. 5 , 2007, p. 639-671 .
- ↑ Spice - a harmless blend of herbs? at www.uni-leipzig.de ( Memento from October 21, 2013 in the Internet Archive ) (accessed on July 17, 2014; PDF; 5.9 MB)
- ^ Philip Swindells, The Master Book of the Water Garden. London, Salamander 1997, 15
- ↑ William A. Emboden: Sacred Narcotic Water Lily of the Nile: Nymphaea caerulea Sav . In: Economic Botany . tape 33 , no. 1 , 1979, p. 395-407 .
Web links
- Nymphaea nouchali inthe IUCN 2013 Red List of Threatened Species . Posted by: Gupta, AK, 2010. Retrieved December 10, 2013.