Palatine bone
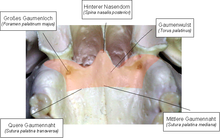
The palatine bone ( Latin: Os palatinum ) is a bone of the skull , more precisely the facial skull. In addition to the upper jaw, it helps to delimit the nasal and oral cavities and supports the back of the hard palate ( palatum durum ).
The palatal bone is divided into a horizontal plate ( lamina horizontalis ) and a vertical plate ( lamina perpendicularis ).
The lamina horizontalis forms part of the palate and is in connection with the ploughshare ( vomer ). Their rear edge limits the opening of the choan .
The lamina perpendicularis of the palatine bone, together with the sphenoid bone ( os sphenoidale ) and the wing bone ( os pterygoideum ) (which is also counted as part of the sphenoid bone in humans) in mammals, forms the alar palatal fossa ( pterygopalatine fossa ), in which nerves (branches of the maxillary nerve , pterygopalatine ganglion ) and vessels (branches of the maxillary artery ) run.
literature
Franz-Viktor Salomon: Bony skeleton . In: Franz-Viktor Salomon et al. (Hrsg.): Anatomie für die Tiermedizin . 3. Edition. Enke, Stuttgart 2015, ISBN 978-3-8304-1288-5 , pp. 102 .