Palladium (II) chloride
| Crystal structure | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
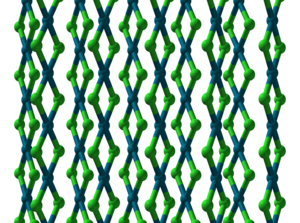
|
||||||||||||||||
| __ Pd 2+ __ Cl - | ||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Palladium (II) chloride | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | PdCl 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
red to dark brown powder or crystals |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 177.31 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
4.0 g cm −3 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Sublimation point |
590 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Palladium (II) chloride is the palladium salt of hydrochloric acid .
Extraction and presentation
Palladium (II) chloride is obtained by dissolving metallic palladium in aqua regia or in hydrochloric acid in the presence of chlorine . Alternatively, it can be obtained by heating sponge palladium in chlorine gas at 500 ° C.
properties
Physical Properties
α-Palladium (II) chloride forms red rhombohedral crystals which slowly dissolve in water with a red color to form PdCl 2 (H 2 O) 2 . It is also soluble in ethanol and acetone . It dissolves quickly in hydrochloric acid. It is almost odorless and slightly hazardous to water.
Chemical properties
Palladium (II) chloride decomposes from 600 ° C into palladium and chlorine. It dissolves in hydrochloric acid and forms a tetrachloropalladate [PdCl 4 ] 2− :
This catalyzes various organic reactions, such as the oxidation of ethylene to acetaldehyde ( Wacker-Hoechst process ).
When introducing hydrogen sulfide , brown-black palladium monosulfide PdS precipitates.
When heated with sulfur to 450 to 500 ° C, formation of palladium disulfide PdS 2 .
When ammonia is introduced into the aqueous solution, tetraammine palladium (II) chloride [Pd (NH 3 ) 4 ] Cl 2 is formed , even with dry PdCl 2 .
use
Palladium (II) chloride is the starting material for various palladium compounds. It is also used for the detection of carbon monoxide . To do this, paper is soaked in a very dilute PdCl 2 solution. This is colored black by CO or other reducing substances with the deposition of metallic palladium. It is also used in electroplating solutions and for porcelain pictures.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Entry on palladium (II) chloride in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on July 23, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Data sheet Palladium (II) chloride (PDF) from Merck , accessed on August 15, 2016.
- ↑ a b c d Cotton, Simon; The Chemistry of Precious Metals ; Springer 1997.
- ^ AF Holleman , E. Wiberg , N. Wiberg : Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry . 101st edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 1995, ISBN 3-11-012641-9 .



![{\ displaystyle \ mathrm {PdCl_ {2} + 2Cl ^ {-} \ longrightarrow [PdCl_ {4}] ^ {2-}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/c9c00f8edd9a80ea0776f20638c90f57cc74cf12)
