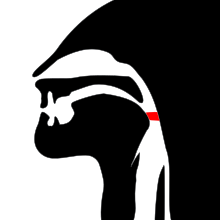
Pharyngeal

Sagittal plane of the human oral cavity , oro pharynx and Laryno pharynx . Articulation locations (active and passive): 1 exolabial (outer part of the lip)
2 endolabial (inner part of the lip)
3 dental (teeth)
4 alveolar (front part of the dental dam)
5 postalveolar (rear part of the dental dam and a little behind it)
6 prepalatally (front part of the hard palate)
7 palatal (hard palate)
8 velar (soft palate)
9 uvular (also postvelar; uvula)
10 pharyngeal (pharynx)
11 glottal (also laryngeal ; vocal cords)
12 epiglottal (epiglottis)
13 radical (tongue root)
14 posterodorsal (rear part of the tongue)
15 anterodorsal (front part of the tongue)
16 laminal (tongue leaf )
17 apical (tip of the tongue)
18 sublaminal (also subapical; underside of the tongue)
2 endolabial (inner part of the lip)
3 dental (teeth)
4 alveolar (front part of the dental dam)
5 postalveolar (rear part of the dental dam and a little behind it)
6 prepalatally (front part of the hard palate)
7 palatal (hard palate)
8 velar (soft palate)
9 uvular (also postvelar; uvula)
10 pharyngeal (pharynx)
11 glottal (also laryngeal ; vocal cords)
12 epiglottal (epiglottis)
13 radical (tongue root)
14 posterodorsal (rear part of the tongue)
15 anterodorsal (front part of the tongue)
16 laminal (tongue leaf )
17 apical (tip of the tongue)
18 sublaminal (also subapical; underside of the tongue)
In phonetics , pharyngeal describes the place of articulation of a sound. In the case of a pharyngeal , a narrowing is formed in the throat , the pharynx . A pharyngeal sound is German as revenge According designated.
The International Phonetic Alphabet has two pharyngeal consonants . They do not occur in German and are typical of the Arabic language and other Semitic languages .
- Voiced pharyngeal fricative [ ʕ ]
- Voiceless pharyngeal fricative [ ħ ]
The tongue is pulled back and the neck muscles ( hyoid bone ) tensed. The voiceless pharyngeal [ ħ ] sounds like a gehecheltes "H"; the pressed-sounding [ ʕ ] is its voiced counterpart.
See also
literature
- John Clark; Collin Yallop; Janet Fletcher: An Introduction to Phonetics and Phonology. 3rd edition. Blackwell Textbooks in Linguistics, Wiley-Blackwell, 2006
- T. Alan Hall: Phonology: An Introduction. De Gruyter Study Book, de Gruyter, Berlin / New York 2000, ISBN 3-1101-5641-5
- Peter Ladefoged ; Ian Maddieson: The Sounds of the World's Languages. Blackwell, Oxford 1996, ISBN 0-631-19814-8 .
Web links
Individual evidence
- ^ Christian Ebert: Phonetics & Phonology. Articulatory Phonetics. (Hall, Chapters 1.1 - 1.5; Clark & Yallop, Chapters 2 & 3) Bielefeld University. Faculty of Linguistics and Literary Studies. WS 2005/2006
- ^ Christian Ebert: Phonetics & Phonology. Articulatory Phonetics. Bielefeld University. Faculty of Linguistics and Literary Studies. WS 2005/2006 (Clark & Yallop, Chapter 2 & 6)
- ^ Christian Ebert: Phonetics & Phonology. Articulatory Phonetics. (Hall, Chapters 1.1 - 1.5; Clark & Yallop, Chapters 2 & 3) Exercises & Solutions, Bielefeld University. Faculty of Linguistics and Literary Studies. WS 2005/2006