Phthalide
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Phthalide | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 8 H 6 O 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless to yellowish powder |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 134.14 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.1613 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
71 - 73 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
290 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
slightly soluble in water (18.4 g l −1 at 25 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.536 (99 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
Phthalide is a chemical that is produced synthetically and also occurs as a secondary plant substance. The phthalide derivatives 3-butylphthalide and sedanolide are found in celery and lovage , for example .
Extraction and presentation
Phthalide can be obtained by reacting phthalimide with sodium hydroxide with an admixture of zinc and copper sulfate and then reacting the intermediate product with hydrogen chloride.
In general, phthalides can be obtained from 2-formyl aryl ketones in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) either by a Cannizarro-Tischtschenko reaction under nucleophilic catalysis (NaCN) or under photochemical conditions .
use
Phthalide is a raw material for many other syntheses, e.g. B. from kresoxim-methyl and picoxystrobin . In 2013, the usability of phthalide in the Suzuki coupling was demonstrated for the first time .
Derivatives
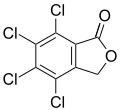
Tetrachlorophthalide ( Rabcide )
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f Entry for CAS no. 87-41-2 in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on April 17, 2013(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-308.
- ↑ a b Phthalide data sheet from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 17, 2013 ( PDF ).
- ^ Butyl Phthalide
- ↑ Textbook food chemistry and nutrition in the Google book search.
- ^ JH Gardner and CA Naylor jr .: Phthalide In: Organic Syntheses . 16, 1936, p. 71, doi : 10.15227 / orgsyn.016.0071 ; Coll. Vol. 2, 1943, p. 26 ( PDF ).
- ↑ DC Gerbino, D. Augner, N. Slavoy, H.-G. Schmalz: Phthalide synthesis . In: Org. Lett. , 2012, 14, 2338-2341.
- ↑ James McNulty, Kunal Keskar: Phthalide: a direct building block towards P, O and P, N hemilabile ligands. Application in the palladium-catalysed Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling of aryl chlorides. In: Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry. 11, 2013, p. 2404, doi : 10.1039 / C3OB40198G .