Picric acid
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
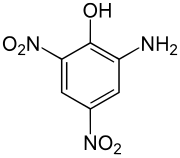
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Picric acid | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 6 H 5 N 3 O 5 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
red crystals |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 199.12 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.75 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
168 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
4.6 |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
The picramic acid ( 2-amino-4,6-dinitrophenol ) is an explosive organic nitro phenol which differs from the picric acid is derived.
Presentation and extraction
The compound can be obtained by a partial reduction from picric acid using sodium hydrogen sulfide , ammonium sulfide or copper and hydrazine .
properties
Picramic acid is a crystalline solid. The connection is explosive when dry due to impact, friction, heat and other ignition sources and is subject to the Explosives Act . The explosion is very violent, releasing large amounts of gas. A desensitization is possible with 20% water.
Table with important explosion-relevant properties: Educational energy −1168.0 kJ kg −1 Enthalpy of formation −1249.0 kJ kg −1 Oxygen balance −76.3% Nitrogen content 21.11% Normal gas volume 961 l kg −1 Explosion heat 2630 kJ kg −1 (H 2 O (l))
2509 kJ kg −1 (H 2 O (g))Specific energy 668 kJ kg −1 (68.1 mt / kg) Lead block bulge 16.6 cm 3 g −1 Deflagration point 240 ° C Steel sleeve test Limit diameter 2.5 mm Sensitivity to impact 34 Nm Rubbing sensitivity no reaction up to 353 N.
use
After diazotization , the initial explosive diazodinitrophenol can be obtained from the compound . The compound also serves as a starting material for azo dyes , as an indicator and as an oxidative hair dye.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on PICRAMIC ACID in the CosIng database of the EU Commission, accessed on March 21, 2020.
- ↑ a b c d Entry on picric acid. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on March 10, 2014.
- ↑ Entry at guidechem.com
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o Köhler, J .; Meyer, R .; Homburg, A .: Explosivstoffe , tenth, completely revised edition, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim 2008, p. 233, ISBN 978-3-527-32009-7 .
- ↑ Springer, A .; Jones, HC: A Study of the Conductivity and Dissociation of Certain Organic Acids in Aqueous Solution at Different Temperatures , in: Amer. Chem. J. 48 (1912) pp. 411-452 ( pdf ).
- ↑ Rose, AR; Sherwin, CP: Surface Tension as a Factor in Detoxication , in: J. Biol. Chem. 68 (1926) pp. 565-573.
- ^ Entry on 2-amino-4,6-dinitrophenol in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 1, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Entry on 2-amino-4,6-dinitrophenol in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on August 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ a b c Roth, L .; Weller, U .: Hazardous Chemical Reactions , 65th supplement, ecomed-Verlag 2011.
- ↑ Explosives Act (Germany), Appendix I, List of explosive substances to which the law applies in full.

