Prodiamine
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
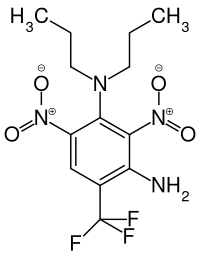
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Prodiamine | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 13 H 17 F 3 N 4 O 4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
yellow, crystalline powder |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 350.30 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
124 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
practically insoluble in water (0.03 mg · l -1 at 25 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Prodiamine is a chemical compound from the dinitroaniline group . It is one of US Borax and Velsicol found and Sandoz (now Syngenta ) in 1987 introduced into the market herbicide .
Extraction and presentation
Prodiamine can be obtained from 2,4-dichlorobenzotrifluoride by reacting with nitric acid in the presence of sulfuric acid as well as with dipropylamine and ammonia .
use
Prodiamine is used as a selective pre-emergence herbicide in soy, vine, alfalfa, cotton and ornamental plant cultivation. Prodiamine inhibits the formation of microtubules .
Admission
Plant protection products with this active ingredient are neither approved in an EU country nor in Switzerland.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f Entry on prodiamine. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on February 26, 2014.
- ↑ a b Data sheet Prodiamine solution, 10 μg / mL in cyclohexane, PESTANAL at Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on October 18, 2016 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Thomas A. Unger: Pesticide synthesis handbook . 1996, ISBN 978-0-8155-1401-5 , pp. 877 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ Herbicide Mode-Of-Action Summary. Section Soil Applied Herbicides . In: purdue.edu. Purdue University , accessed July 29, 2016 .
- ^ Directorate-General for Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: EU pesticide database ; Entry in the national directory of plant protection products in Switzerland ; accessed on February 17, 2016.



