Rhenium (IV) sulfide
| Crystal structure | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
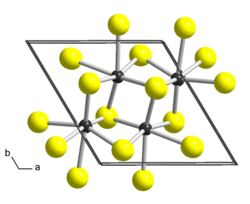
|
||||||||||||||||
| __ Re 4+ __ S 2− | ||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Rhenium (IV) sulfide | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
Rhenium disulfide |
|||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | ReS 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
black odorless solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 250.33 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
7.506 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
almost insoluble in water |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Rhenium (IV) sulfide , also known as rhenium disulfide , is an inorganic chemical compound of rhenium from the group of sulfides with the chemical composition ReS 2 .
Occurrence
Rhenium (IV) sulfide occurs naturally in the form of the mineral rheniite .
Extraction and presentation
Rhenium (IV) sulfide can be produced by reacting rhenium with sulfur at around 1000 ° C.
It can also be obtained by thermal decomposition of rhenium (VII) sulfide at 1100 ° C.
properties
Rhenium (IV) sulfide is a black, odorless solid that is insoluble in water and is the most stable rhenium sulfide. It is resistant to hydrochloric acid , alkalis and alkali sulfide, is oxidized to ReO 4 - by hypochlorous acid , nitric acid , etc. It reacts with quartz at 1000 ° C and does not react with sulfur even when heated. At temperatures above 700 ° C it breaks down into rhenium and sulfur in a vacuum and is reduced to rhenium by hydrogen at elevated temperatures. The compound is a diamagnetic semiconductor and has a triclinic crystal structure with the space group P 1 (space group no. 2) and the lattice parameters a = 645.5 pm, b = 636.2 pm, c = 640.1 pm, α = 105 , 04 °, β = 91.60 ° and γ = 118.97 °, which corresponds to a distorted cadmium (II) chloride layer structure and is isotypic to that of rhenium diselenide .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f data sheet Rhenium (IV) sulfide, 99% from AlfaAesar, accessed on August 1, 2013 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c Georg Brauer (Ed.) U. a .: Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry. 3rd, revised edition. Volume III, Ferdinand Enke, Stuttgart 1981, ISBN 3-432-87823-0 , p. 1619.
- ↑ Erwin Riedel: Inorganic Chemistry . Walter de Gruyter, 2004, ISBN 3-11-018168-1 , p. 811 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ Christoph Janiak, Hans-Jürgen Meyer, Dietrich Gudat, Ralf Alsfasser: Riedel Modern Inorganic Chemistry . Walter de Gruyter, 2012, ISBN 3-11-024901-4 , p. 338 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ H.-J. Lamfers, A. Meetsma, GA Wiegers, JL de Boer: The crystal structure of some rhenium and technetium dichalcogenides. In: Journal of Alloys and Compounds , 241, 1996, pp. 34-39, doi: 10.1016 / 0925-8388 (96) 02313-4 .

