Rohilkhand
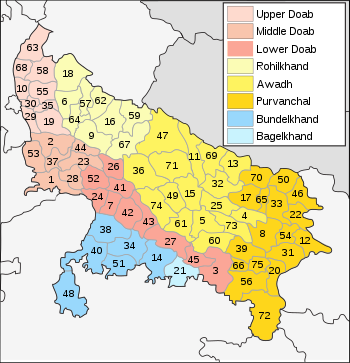
Rohilkhand ( Hindi : रोहिलखंड , Urdu : روہیل کھنڈ; Rohilkhanḍ ) was a historical region of India with the center in today's state of Uttar Pradesh , which was named after the Pashtun tribe of the Rohilla , who immigrated from Afghanistan during the Mughal period . The region's capitals were Bareilly and Rampur ; other important cities are Bijnor , Badaun , Moradabad , Shahjahanpur and Pilibhit .
geography
The Rohilkhand region, with an area of around 25,000 km², is located at altitudes of around 150 to 300 m in the fertile upper Ganges plain. In the northwest, the region borders on the Indian state of Uttarakhand , which was created in 2000 and whose south historically also belonged to Rohilkhand, and to a lesser extent on Nepal ; in the southeast is the economically and historically important region of Avadh (also Oudh) with the capital Lucknow . The country is traversed by numerous rivers (e.g. Ramganga ), which have their origin in the Himalayan mountains. The climate is hot and - especially in the monsoon season - rainy.
population
Approx. 59% of the region's 20 million inhabitants are Hindus , approx. 39% are Muslims ; the remaining 2% are distributed among other religions ( Jains , Sikhs , Buddhists , Christians). The male part of the population exceeds (as is customary in northern India) the female part by more than 10%.
economy
The region was and is largely agriculturally oriented, with cattle breeding playing only a very minor role in India. Mainly rice, wheat, lentils etc. are grown. The cities function to this day as regional trade, handicraft and service centers.
history
The region was already settled in ancient times and is mentioned under the name Madhyadesh in the Mahabharata epic. In the Middle Ages it belonged to the Sultanate of Delhi . After the disintegration of the Mughal Empire after the death of Aurangzeb (1707), the immigrant Rohillas were subjugated in the middle of the 18th century by the Nawabs of Avadh (Oudh) , who, however, in the second half of the century with the ever-increasing advance of the Central Indian Marathas and the British had to deal with. The latter annexed the area into their empire as a result of the uprising of 1857-1859 .
Web links
- Rohilkhand - Encyclopaedia Britannica (English)
