Rorippa aquatica
| Rorippa aquatica | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
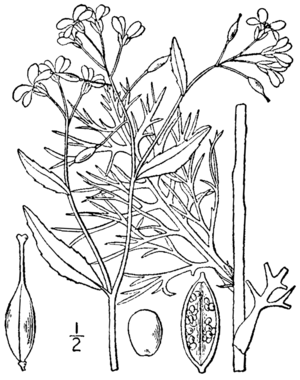
Illustration of Rorippa aquatica |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Rorippa aquatica | ||||||||||||
| ( Eaton ) EJPalmer & Steyerm. |
Rorippa aquatica is a species of the cruciferous family (Brassicaceae). This species, found only in North America, thrives as an aquatic plant .
description
Rorippa aquatica is an aquatic , hairless, perennial herbaceous plant . The upright stem , which is only branched in the upper area, has a length of 30 to 85 centimeters (up to 110 centimeters) and is partly located below the surface of the water. The flowers and pods, on the other hand, develop above water. It is anchored in the bottom of the water with a rhizome and fibrous roots. The leaves are distributed on the stem. The submerged leaves are short-stalked, one to fourfold pinnate, thread-like and finely designed. The leaves formed above the water surface are sessile with up to 2 millimeters long stalked, undivided lanceolate to oblong , rarely lobed, with a length of usually 2 to 5.5 centimeters or a maximum of 1.5 to 6.7 centimeters, a width of usually 7 to 15 millimeters (5 to 20 millimeters) and a smooth to sawn edge.
The racemose inflorescences are elongated. The short-stalked flowers are fourfold. The four elongated sepals with a length of 2 to 4 millimeters and a width of 1.4 to 1.8 millimeters fall off as they fade. The four white petals are 4 to 8 millimeters long, 2 to 3.5 millimeters wide, spatulate to obovate and rounded at the tip. The middle stamens are 3 to 4 millimeters long and the linear anthers are 1.7 to 2.2 millimeters long. The ovary contains 48-80 ovules . The 2 to 4 millimeter long stylus ends in a slightly bilobed scar.
The fruit stalk is straight to curved and (rarely 5 to) 7 to 15 millimeters long. In the straight, 4 to 7 mm × 2.5 to 3 mm large, elongated to ellipsoidal pod with a septum reduced to a rim, the seeds are arranged in two rows. The brown to reddish seeds are egg-shaped with a length of 0.7 to 0.8 millimeters and a diameter of 0.5 to 0.6 millimeters and show a net-like surface.
The number of chromosomes is 2n = 24.
Occurrence
Rorippa aquatica can be found in almost all states of the eastern half of the North American continent from the Canadian provinces of Québec and Ontario , then southward in the USA to the north of the state of Florida and westward to the state of Texas .
This species is found in calm, shallow water along the edges of lakes, in oxbow lakes of slow flowing streams, and edges of ponds. It has roots in organic or sandy subsoil just over 2 meters deep and usually also loves full sun exposure. The species, also known as water horseradish , can also be cultivated in the aquarium.
Systematics
Rorippa aquatica is a species of the genus Rorippa in the tribe Cardamineae from the cruciferous family (Brassicaceae). This species was first published as Nasturtium lacustre A.Gray in 1848 and forms the basionyma for Armoracia lacustris (A.Gray) Al-Shehbaz & VMBates . The shift to the genus Armoracia took place in 1987 or 1935 to the genus Rorippa , so IPNI does not provide any decision-making aid. In other sources this name is considered to be synonymous with a species called Neobeckia aquatica ( Eaton ) Greene . The following synonyms can be found: Armoracia aquatica (Eaton) Wiegand , Rorippa americana (A.Gray) Britton . In 2010, the Brassicaceae specialist Ihsan Ali Al-Shehbaz and, for example, TROPICOS signed up for Rorippa aquatica (Eaton) EJPalmer & Steyerm in the Flora of North America . decided as a valid name.
Hazardous situation and protective measures
Rorippa aquatica is considered an endangered species by eleven states in the USA and assigned different endangerment categories. Mechanical impairment of the habitat caused by humans, sudden changes in the water level, overgrowth by other vegetation due to the disadvantage of poor reproductive capacity threaten this species.
swell
- Ihsan A. Al-Shehbaz: Rorippa in the Flora of North America , Volume 7, 2010, p. 497: Rorippa aquatica - Online.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Plants Database: Plants Profile: Neobeckia aquatica (Eaton) Greene - lakecress. In: NRCS Natural Resources Concervation Service. USDA United States Department of Agriculture, accessed August 6, 2010 .
- ↑ Christel Kasselmann : aquarium plants. Ulmer Verlag, Stuttgart 1995; 2nd, revised and expanded edition 1999, ISBN 3-8001-7454-5 , p. 406.
- ↑ J. Arnold: Plant Name Details Brassicaceae Nasturtium lacustre A. Gray. In: International Plant Names Index (IPNI). The Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, The Harvard University Herbaria, and the Australian National Herbarium, accessed August 9, 2010 .
- ^ Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN): Taxon: Armoracia lacustris (A. Gray) Al-Shehbaz & VM Bates. In: GRIN Taxonomy for Plants. United States Department of Agriculture Agricultural Research Service, accessed August 9, 2010 .
- ^ J. Arnold: Plant Name Details Brassicaceae Armoracia lacustris (A. Gray) Al-Shehbaz & V.Bates. In: International Plant Names Index (IPNI). The Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, The Harvard University Herbaria, and the Australian National Herbarium, accessed August 6, 2010 .
- ^ J. Arnold: Plant Name Details Rorippa aquatica (Eaton) EJPalmer & Steyerm. In: International Plant Names Index (IPNI). The Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, The Harvard University Herbaria, and the Australian National Herbarium, accessed August 8, 2010 .
- ↑ ITIS Report Neobeckia aquatica (Eat.) Greene. Integrated Taxonomy Information System, accessed August 6, 2010 .
- ^ Rorippa aquatica (Eaton) EJ Palmer & Steyerm. In: Tropicos. Missouri Botanical Garden, accessed August 9, 2010 .
Web links
- Armoracia-lacustris-Lake-Cress in Wisconsin / USA. Robert W. Freckmann Herbarium University of Wisconsin - Stevens Point, accessed August 9, 2010 .
- Armoracia-lacustris Lake-Cress in Michigan / USA. Michigan Natural Features Inventory, accessed August 9, 2010 .