Oxygen difluoride
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Oxygen difluoride | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
Difluoroxide |
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | OF 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless gas with a foul odor |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 54,00 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
gaseous |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
2.42 g l −1 (0 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−223.8 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
−144.8 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
poor in water (68 cm 3 / l at 0 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
Switzerland: 0.05 ml m −3 or 0.1 mg m −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Oxygen difluoride is a fluoride of oxygen with the empirical formula OF 2 . It belongs to the group of oxygen fluorides and is one of the very few substances in which oxygen occurs with a positive oxidation number . The name difluoroxide sometimes used for this compound is incorrect because oxygen in oxides has a negative oxidation number.
Extraction and presentation
Oxygen difluoride was first reported in 1929, when it was shown in the electrolysis of molten potassium fluoride and hydrogen fluoride in water. Nowadays, oxygen difluoride is obtained by introducing fluorine into caustic soda or potassium hydroxide :
properties
Oxygen difluoride is one of the strongest known oxidizing agents that can even react with the noble gas xenon to form xenon tetrafluoride (XeF 4 ):
The reason for this reaction is the strong electronegativity of fluorine, and also the strong electronegativity of oxygen, which has a partial positive charge in oxygen difluoride.
It is not very soluble in water, dissolved oxygen difluoride reacts with water to form hydrogen fluoride and oxygen ( comproportionation ):
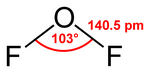
It condenses at −144.8 ° C to form an orange-colored liquid that is reminiscent of water in terms of structure. The bond angle enclosed by the two OF bonds is 103 °, the bond length of the OF bonds in each case 140.5 pm.
use
Oxygen difluoride has been investigated as an oxidizing agent for rocket fuels because it delivers a high specific impulse (e.g. together with lithium hydride 4112 m / s.)
safety instructions
Due to its extremely strong oxidizing effect, oxygen difluoride is dangerous for humans and animals. After inhalation, it causes severe breathing difficulties, which often only set in after several hours and last for hours.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e Entry on oxygen difluoride in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 22, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c Entry on Oxygen Fluoride. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on June 12, 2017.
- ^ A b Holleman / Wiberg: Basics and main group elements Volume 1: Basics and main group elements . Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co KG, 2016, ISBN 3-11-049585-6 , p. 532 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Swiss Accident Insurance Fund (Suva): Limits - Current MAK and BAT values (search for 7783-41-7 or oxygen difluoride ), accessed on November 2, 2015.
- ↑ Entry on Oxygen Fluoride. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on July 14, 2014.
- ↑ List of materials used as war material by the Swiss Confederation .
- ↑ Rocket fuels on Bernd Leitenberger's space travel homepage .
- ↑ Georg Brauer (Ed.), With the collaboration of Marianne Baudler a . a .: Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry. 3rd, revised edition. Volume I, Ferdinand Enke, Stuttgart 1975, ISBN 3-432-02328-6 , p. 179.