Somatostatin
| Somatostatin | ||
|---|---|---|
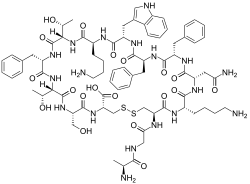
|
||
| Properties of human protein | ||
| Mass / length primary structure | 14 and 28 amino acids, respectively | |
| Precursor | 92 amino acids | |
| Identifier | ||
| Gene names | SST ; SMS; SMST; GHIH | |
| External IDs | ||
| Occurrence | ||
| Homology family | Somatostatin | |
| Parent taxon | Euteleostomi | |
| Orthologue | ||
| human | House mouse | |
| Entrez | 6750 | 20604 |
| Ensemble | ENSG00000157005 | ENSMUSG00000004366 |
| UniProt | P61278 | P60041 |
| Refseq (mRNA) | NM_001048 | NM_009215 |
| Refseq (protein) | NP_001039 | NP_033241 |
| Gene locus | Chr 3: 187.67 - 187.67 Mb | Chr 16: 23.89 - 23.89 Mb |
| PubMed search | 6750 |
20604
|
Somatostatin is a peptide hormone in vertebrates that is secreted by the pancreas during digestion and, as an inhibiting hormone of the hypothalamus, inhibits the formation of the growth hormone somatropin in the pituitary gland . This is where the synonym somatotropin (release) -inhibiting hormone (SIH or SRIH) or growth hormone (release) -inhibiting hormone (GHIH or GHRIH) comes from. It also takes part in signal transduction when initiating apoptosis . Synthetic analogues of somatostatin are lanreotide , pasireotide and octreotide , which are approved as medicinal substances . A peptide formerly known as bulbogastron is likely identical to somatostatin.
Somatostatin is not only produced by the δ cells of the pancreas, but also by individual cells of the hypothalamus and the gastrointestinal tract . It is an important regulator of the hormonal and nervous system and works by binding to G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) on the surface of various cell types.
Somatostatin inhibits the secretion of pancreatic enzymes , gastrin and pepsin and lowers the blood flow in the splanchnic nerve area (supply area of the visceral nerves major and minor splanchnic nerves ). It is therefore indicated for the treatment of severe acute gastroduodenal ulcer bleeding, bleeding in erosive or hemorrhagic gastritis, for adjuvant therapy to inhibit the secretion of heavily secreting postoperative fistulas of the pancreas and the upper small intestine, and for the prophylaxis of postoperative pancreatic complications after pancreatic surgery. It is also used for the therapy of secretory diarrhea. Somatostatin has a half-life of 1–3 minutes.
Biosynthesis and Isoforms
Two active forms (somatostatin-14 and somatostatin-28) are known, both of which form a cyclic structure through a disulfide bridge and are processed from a common precursor . The human SST gene encoding somatostatin is located in humans on chromosome 3 , gene locus 3q28.
regulation
In the pancreas, somatostatin has a paracrine role like a tissue hormone , whereby it inhibits the release of glucagon and insulin from the neighboring α and β cells. It is also known to have an inhibitory effect on STH (somatotropic hormone), gastrin and cholecystokinin .
The release of somatostatin is a slow response to the formation of the second messenger cAMP . Over the course of hours , cAMP induces gene expression of this hormone through the following steps:
- Activation of protein kinase A (PKA),
- thereby phosphorylation of the CREB ( CRE binding protein ) on a serine residue ,
- Binding of CREB modified in this way to a CRE recognition site ( cAMP response element ) on the promoter of the somatostatin gene,
- Expression of this gene.
See also
literature
- Di Bella G, Madarena M: Complete objective response of oesophageal squamocellular carcinoma to biological treatment Archived from the original on March 15, 2013. (PDF) In: Neuro Endocrinol. Lett. . 30, No. 3, 2009, pp. 312-21. PMID 19855352 .
- Di Bella G: Complete objective response to biological therapy of plurifocal breast carcinoma Archived from the original on October 21, 2013. (PDF) In: Neuro Endocrinol. Lett. . 29, No. 6, December 2008, pp. 857-66. PMID 19112416 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ David Binas et al. a .: Perioperative management in patients with carcinoid syndrome / neuroendocrine neoplasia. In: Anästh Intensivmed Volume 61, 2020, pp. 16–24, here: p. 22 (“Somatostatin inhibits all other gastrointestinal hormones”).
- ^ SST somatostatin
Web links
- Igor Gayk - The pancreatic hormones: Somatostatin and pancreatic polypeptide (www.igorgayk.de) ( Memento from September 5, 2011 in the Internet Archive ) (PDF file; 504 kB)
