Sorbitan monostearate
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
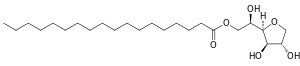
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Sorbitan monostearate | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 24 H 46 O 6 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 430.63 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.00 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
53-57 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
almost insoluble in water, hardly soluble in ethanol 96% |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Sorbitan monostearate (trade name: Span 60 ) is a sorbitan fatty acid ester , an ester of sorbitol or 1,4-sorbitan anhydride ( sorbitan for short ).
use
It is used as an emulsifier in the pharmaceutical and food industries. It is approved in the EU as a food additive with the number E 491 for certain foods (including various baked goods, ice cream, desserts, sugar products and creamer ).
Because sorbitan monostearate is a hydrophobic nonionic surfactant , it gels numerous organic solvents such as hexadecane , isopropyl myristate, and a number of vegetable oils . These gels can be used in the administration of drugs and antigens .
Health assessments
The permitted daily dose is 25 mg / kg body weight per day. The European Food Safety Authority concluded that exposure did not exceed this limit value in any population group.
properties
Pharmaceutical qualities represent a mixture mainly of partial esters of sorbitol and its mono- and dianhydrides with stearic acid . The pale yellow, waxy, solid substance has a melting temperature of 50 to 60 ° C. The hydroxyl number is 235 to 260, the saponification number 147 to 157. With regard to the fatty acid fraction, a distinction is made between two types:
- Type I with a stearic acid content of 40.0 to 60.0 percent
- Type II with a stearic acid content of 60.0 to 80.0 percent
In both types, the total palmitic and stearic acid content is at least 90.0 percent.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on E 491: Sorbitan monostearate in the European database for food additives, accessed on June 28, 2020.
- ↑ Entry on SORBITAN STEARATE in the CosIng database of the EU Commission, accessed on April 12, 2020.
- ↑ a b c d e f g Data sheet Sorbitan monostearate from AlfaAesar, accessed on June 24, 2013 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b European Pharmacopoeia, 8th edition, basic work 2014. P. 4856 f.
- ↑ Sudaxshina Murdan, Gregory Gregoriadis, Alexander T. Florence: Novel sorbitan monostearate organogels . In: Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences . tape 88 , no. 6 , 1999, ISSN 0022-3549 , p. 608-614 , doi : 10.1021 / js980342r ( jpharmsci.org ).
- ↑ Alicja Mortensen, Fernando Aguilar u. a .: Re ‐ evaluation of sorbitan monostearate (E491), sorbitan tristearate (E492), sorbitan monolaurate (E493), sorbitan monooleate (E494) and sorbitan monopalmitate (E495) when used as food additives. In: EFSA Journal. 15, 2017, doi : 10.2903 / j.efsa.2017.4788 .