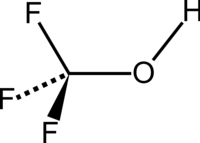
Trifluoromethanol
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||
| Surname | Trifluoromethanol | ||||||||||||
| other names |
Perfluoromethanol |
||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | CHF 3 O | ||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless, unstable gas |
||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 86.01 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||
| Physical state |
gaseous |
||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−82 ° C |
||||||||||||
| boiling point |
−20 ° C (extrapolated) |
||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||
Trifluoromethanol , also known as perfluoromethanol , is a colorless gas that is unstable at room temperature .
synthesis
Like all primary and secondary perfluoro alcohols, trifluoromethanol eliminates hydrogen fluoride in an endothermic reaction and forms carbonyl fluoride .
- (I)
At temperatures in the range of −120 ° C, trifluoromethanol can be prepared from trifluoromethoxychloride and hydrogen chloride according to the reaction
- (II)
can be synthesized. In this reaction, the recombination of a partially positively charged chlorine atom (in trifluoromethoxychloride) with a partially negatively charged chlorine atom (in hydrogen chloride) is used to form elemental chlorine. The unwanted products, starting materials and by-products chlorine, hydrogen chloride and chlorotrifluoromethane can be removed by pumping out at −110 ° C. The trifluoromethanol obtained has a melting point of −82 ° C and a calculated boiling point of approx. −20 ° C. The boiling point is about 85 Kelvin lower than that of methanol. This can be explained by the lack of intramolecular H ··· F bridge bonds, which are also not visible in the infrared gas phase spectrum .
A simpler synthesis uses reaction (I), the equilibrium of which can be shifted to the thermodynamically preferred trifluoromethanol at lower temperatures . If the trifluoromethanol formed is captured by protonation with the aid of super acids , for example HSbF 6 ( fluoroantimonic acid ), the equilibrium can be shifted further to the left, towards the desired product.
Similar to reaction (I), trifluoromethanolates (CF 3 O-) can be prepared from salt-like fluorides (e.g. NaF) and carbonyl fluoride. However, if the CF 3 O ion z. B. displaced by an acid in aqueous solution , the trifluoromethanol formed decomposes at room temperature.
Occurrence in the upper layers of the atmosphere
While trifluoromethanol is unstable under normal conditions, it is generated in the stratosphere from CF 3 · and CF 3 O · radicals by reaction with OF · and F · radicals. The decomposition of the trifluoromethanol formed in the process is negligible under the conditions prevailing in the atmosphere due to the high activation energy of the reaction. The calculated service life of trifluoromethanol is several million years at altitudes below 40 km.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e K. Seppelt: Trifluoromethanol, CF 3 OH. In: Angew. Chem. 1977 , 89 , 325.
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ a b c W. F. Schneider: Energetics and Mechanism of Decomposition of CF 3 OH. In: J. Phys. Chem. 100/1996, pp. 6097-6103.
- ^ KO Christe et al.: Convenient Access to Trifluoromethanol. In: Angew. Chem. 119/2007, pp. 6267-6270.
- ↑ K. Brudnik et al. a .: Kinetics of the formation reactions of trifluoromethanol and trifluoromethyl hypohalites in the gas phase. In: Journal of Molecular Structure 656/2003, pp. 333-339.
- ↑ WF Schneider et al .: Atmospheric Chemistry of CF 3 OH: Is Photolysis Important? In: Environmental Science & Technology 29/1995, pp. 247-250.
- ^ TJ Wellington, WF Schneider: The Stratospheric Fate of CF 3 OH. In: Environmental Science & Technology 28/1994, pp. 1198-1200.
literature
- G. Klöter, K. Seppelt: Trifluoromethanol and Trifluoromethylamine. In: JACS 101/1979, p. 347.
- JIG Cadogan, PH Rodes: Dictionary of organic compounds. Chapman and Hall, CRC Press, 1996, pp. 6204-6205. ISBN 0-412-54090-8
- RD Chambers: Fluorine in organic chemistry. CRC Press, 2004, p. 254. ISBN 1-4051-0787-1 .
- WE Doering et al: Cooperativity effects in cyclic trifluoromethanol trimer: an ab initio study. In: Journal of Molecular Structure: THEOCHEM 431/1998, pp. 119-126.

