Urea resin
According to DIN 7728, urea resins are aminoplasts ( plastics ) which can be produced as condensation products from urea (or urea derivatives) and aldehydes (especially formaldehyde ) and cured chemically or thermally.
The urea-formaldehyde resins are briefly referred to as UF resins (from English urea = urea).
Manufacturing
Technically, the production of UF resins takes place in large reactors (approx. 20 to 40 m³ ), which are equipped with a stirrer , heating and cooling coils and metering options for the "large" raw materials as well as acids , alkalis and any additives .
The "classic" manufacturing process for UF resins takes the following technical steps:
- Methylolation: addition of urea to formaldehyde solution
- Condensation: addition of acid or acidic salts (such as ammonium sulfate )
- Ending the condensation: by increasing the pH value with lye (pH> 7)
- Setting the correct molar ratio of formaldehyde and urea
- Setting the correct solids content (if necessary, by removing water by distillation )
For special applications, such as glues for joinery applications, the largely dried powder glues are used. These are produced by spray drying the UF liquor instead of the distillation step.
Methylolation
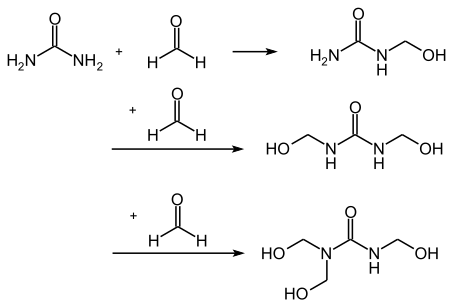
In an addition reaction of formaldehyde to urea, methylolureas are essentially formed (see also hydroxymethyl group ):
condensation
The monomers combine to form larger molecules ( oligomers and polymers ) through a condensation reaction of the methylolureas with urea, or with each other, controlled by time , temperature and pH . Methylene bridges and ether bridges are formed in the process. The degree of condensation is checked by measuring the degree of condensation-dependent parameters such as viscosity or water compatibility.

- Chain extension by condensation reaction with the formation of methylene groups
Last addition of urea
The last addition of urea sets the molar ratio of formaldehyde to urea (F / U) that is required for the application. In some cases, ether bridges are broken down again . Terminal methylols (-CH 2 -OH) also react with the added urea.
properties
Liquid resin
This is the product that is used as glue . The following parameters are checked as application criteria or as part of quality assurance (as well as typical values):
- Viscosity : approx. 300 - 2000 mPa s
- Gel time : depending on hardener and temperature, less than 1 minute to hours
- pH value : around 8 to 9
- Dry matter (also known as solid resin ): about 66%
Hardened resin
When hardened, urea resins form very lightfast, hardly flammable, mostly white masses that are not , however, hydrolysis-resistant . They are particularly attacked by strong acids and alkalis as well as boiling water . Urea-formaldehyde resins provide light-resistant, hard, scratch-resistant films that are easy to sand.
use
Due to the relatively low costs (both of the production and the raw materials ) as well as the fast curing (= high reactivity) and the good dry bonding strength, the majority of UF resins are used as adhesives for the production of (not outdoor climate-resistant) wood-based materials and HPL panels (e.g. B. Formica ) is used. In the 1930s, household items were produced under the brand name Pollopas , which, in contrast to the common phenoplasts, had a wide range of colors.
Further areas of application are:
- Impregnation resins ( impregnating resins )
- Insulating resins
- Textile finishing agents
- Binder for wet strength papers
The release of formaldehyde from the resin can be hazardous to health. However, UF resins that have been used in buildings for many years do not necessarily have to be replaced, as the volatile components are often outgassed over time.
Manufacturer
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ Otto-Albrecht Neumüller (Ed.): Römpps Chemie-Lexikon. Volume 3: H-L. 8th revised and expanded edition. Franckh'sche Verlagshandlung, Stuttgart 1983, ISBN 3-440-04513-7 , p. 1631.
- ^ A b Siegfried Hauptmann : Organic Chemistry , 2nd edition, VEB Deutscher Verlag für Grundstoffindindustrie, Leipzig, 1985, p. 737, ISBN 3-342-00280-8 .
- ↑ Health Center Formaldehyde FAQ . Archived from the original on February 7, 2006. Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Press Release N ° 153 . Archived from the original on September 10, 2018. Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. Retrieved May 11, 2017.
- ^ Occupational-toxicological risk related to the exposure to MDF wood dust . In: Archives des Maladies Professionnelles et de l'Environnement . 69, August, pp. 655-666. doi : 10.1016 / j.admp.2008.09.007 .