Virgaviridae
| Virgaviridae | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
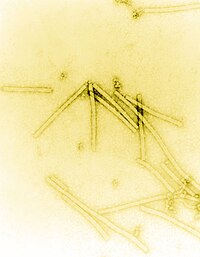
TEM uptake of virions of the tobacco mosaic virus (TMV), |
||||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
| Taxonomic characteristics | ||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||||
| Virgaviridae | ||||||||||||||
| Left | ||||||||||||||
|
The Virgaviridae are a family of single-stranded RNA viruses with positive polarity . Their natural hosts are plants. There are currently at least 59 species in this family, divided into 7 genera. The name of the family is derived from the Latin virga 'stick, stick' , also 'rod' (since all viruses in this family are rod-shaped or rod-shaped).
construction
The virus particles ( virions ) of the Virgaviridae are not enveloped, their geometry is rigidly rod-shaped and they have a helical symmetry. The diameter is 20-25 nm . The virions have a central “channel”.
The genome consists of a linear, single-stranded positive sense RNA with a 3'- tRNA -like structure and no poly-A tail . The genome can be present in one, two or three segments (mono-, bi- or tripartite) depending on the genus. The envelope proteins range in size from 19 to 24 kilodaltons .
Propagation cycle
Replication of the virus particles is cytoplasmic (i.e. it takes place in the cytoplasm ) and follows the replication model of positive strand RNA viruses. The transcription method is also the usual one for positive-strand RNA viruses. The translation used by leaky scanning and suppression of termination.
The natural hosts are plants.
Systematics
Internal system
According to the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) as of March 2019, the internal systematics of the Virgaviridae are as follows:
Family Virgaviridae
- Genus: Furovirus
- Species: Chinese wheat mosaic virus (CWMV)
- Species: Japanese soil-borne wheat mosaic virus (JSBWMV)
- Species: Oat golden stripe virus (OGSV)
- Species: Soil-borne cereal mosaic virus (SBCMV)
- Species: Soil-borne wheat mosaic virus (SBWMV, type species)
- Species: Sorghum chlorotic spot virus
- Genus: Goravirus
- Species: Drakaea virus A (DVA)
- Species: Gentian ovary ringspot virus (GORV, type species)
- Genus: Hordeivirus
- Species: Anthoxanthum latent blanching virus
- Species: Barley stripe mosaic virus (BSMV, type species)
- Species: Lychnis ringspot virus
- Species: Poa semilatent virus
- Genus: Pecluvirus
- Species: Indian peanut clump virus (IPCV)
- Species: Peanut clump virus (PCV, type species)
- Genus: Pomovirus
- Species: Beet soil-borne virus
- Species: Beet virus Q (BVQ)
- Species: Broad bean necrosis virus
- Species: Potato mop-top virus (PMTV, type species)
- Genus: Tobamovirus
- Species: Bell pepper mottle virus (BPeMV)
- Species: Brugmansia mild mottle virus
- Species: Cactus mild mottle virus (CMMoV)
- Species: Clitoria yellow mottle virus (CliYMV)
- Species: Cucumber fruit mottle mosaic virus (CFMMV0)
- Species: Cucumber green mottle mosaic virus (CGMMV)
- Species: Cucumber mottle virus (CMV)
- Species: Frangipani mosaic virus (FrMV)
- Species: Hibiscus latent Fort Pierce virus (HLFPV)
- Species: Hibiscus latent Singapore virus (HLSV)
- Species: Kyuri green mottle mosaic virus
- Species: Maracuja mosaic virus (MarMV)
- Species: Obuda pepper virus (ObPV)
- Species: Odontoglossum ringspot virus (ORSV)
- Species: Bell pepper mild mottle virus
- Species: Passion fruit mosaic virus
- Species: Pepper mild mottle virus (PMMoV)
- Species: Rattail cactus necrosis-associated virus (RCNaV)
- Species: Rehmannia mosaic virus
- Species: Ribgrass mosaic virus (HRV)
- Species: Sammons's Opuntia virus (SOV)
- Species: Streptocarpus flower break virus
- Species: Sunn-hemp mosaic virus (SHMV)
- Species: Tobacco latent virus (TLV)
- Species: Tobacco mild green mosaic virus (TMGMV)
- Species: Tobacco mosaic virus ( tobacco mosaic virus , TMV, T2MV)
- Species: Tomato mosaic virus ( tomato mosaic virus , ToMV)
- Species: Tomato mottle mosaic virus (ToMMV)
- Species: Tropical soda apple mosaic virus
- Species: Turnip vein-clearing virus (TVCV)
- Species: Ullucus mild mottle virus
- Species: Wasabi mottle virus (WMoV)
- Species: Yellow tailflower mild mottle virus
- Species: Youcai mosaic virus ( Oilseed rape mosaic virus , YoMV, ORMV)
- Species: Zucchini green mottle mosaic virus
- Genus: Tobravirus
- Species: Pea early-browning virus (PEBV)
- Species: Pepper ringspot virus (PEPRSV)
- Species: Tobacco rattle virus ( tobacco rattle virus , TRV)
External system
In 2015, Koonin et al taxonomically assigned the Virgaviridae (due to their relationship) to the supergroup 'Alphavirus-like superfamily' they postulated. The sister group is thereafter the family Closteroviridae . According to the authors, the family tree of this supergroup is as follows:
| " Alphavirus- like superfamily " |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
The members of this proposed supergroup belong to different groups of the Baltimore classification , usually they are single-stranded RNA viruses of positive polarity ((+) ssRNA, Baltimore group 4), but there are also double-stranded representatives (marked with dsRNA, Find Baltimore Group 3).
Although its members are rod-shaped and infect plants, the genus Benyvirus does not belong to this family, but to the Benyviridae ; the proteins of the two groups are apparently only largely related. According to the proposal, another related genus is Charavirus with the species Charavirus canadensis (CV-Can) and Charavirus australis (CV-Aus), these viruses attack charophytes .
Individual evidence
- ↑ ICTV Master Species List 2018b.v2 . MSL # 34, March 2019
- ↑ a b c d ICTV: ICTV Master Species List 2019.v1 , New MSL including all taxa updates since the 2018b release, March 2020 (MSL # 35)
- ↑ Michael J. Adams, Scott Adkins, Claude Bragard, David Gilmer, Dawei Li, Stuart A. MacFarlane, Sek-Man Wong, Ulrich Melcher, Claudio Ratti, Ki Hyun Ryu: ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Virgaviridae . In: Journal of General Virology . 98, No. 8, August 1, 2017, pp. 1999–2000. doi : 10.1099 / jgv.0.000884 . PMID 28786782 . PMC 5656781 (free full text).
- ↑ a b c d e f g ICTV Report Virgaviridae .
- ↑ a b c d e f g Viral Zone . ExPASy. Retrieved September 2, 2019.
- ↑ Adams MJ, Antoniw JF, crosses J: Virgaviridae : a new family of rod-shaped plant viruses. Arch Virol 154 (12), 2009, pp. 1967-1972
- ↑ ICTV: Virus Taxonomy: 2015 Release . Retrieved June 4, 2016.
- ↑ virga | Latin → German , on: Pons.de
- ↑ ICTV : ICTV MSL # 34v 2018b.v2 , March 2019
- ↑ MJ Adams, P. Jones, AG Swaby: Purification and some properties of oat golden stripe virus , in: Annals of Applied Biology, April 1988, doi: 10.1111 / j.1744-7348.1988.tb02064.x
- ↑ Min BE, Chung BN, Kim MJ, Ha JH, Lee BY, Ryu KH: Cactus mild mottle virus is a new cactus-infecting tobamovirus . In: Archives of Virology . 151, No. 1, January 2006, pp. 13-21. doi : 10.1007 / s00705-005-0617-7 . PMID 16132178 .
- ↑ Since this group (referred to by the authors as English superfamily ) contains an order with the Tymovirales , their rank must be higher than this and should not be understood as a superfamily . Ranks higher than order were not given by the ICTV at the time of the work.
- ^ Eugene V. Koonin, Valerian V. Dolja, Mart Krupovic: Origins and evolution of viruses of eukaryotes: The ultimate modularity , in: Virology from May 2015; 479-480. 2-25, Epub March 12, 2015, PMC 5898234 (free full text), PMID 25771806
- ↑ SIB: Alphatetraviridae , on: ViralZone
- ↑ SIB: Carmotetraviridae , on: ViralZone
- ↑ SIB: Permutotetraviridae , on: ViralZone
- ↑ SIB: Nodaviridae , on: ViralZone
- ↑ ICTV Report Benyviridae .
- ^ Marli Vlok, Adrian J. Gibbs. Curtis A. Suttle: Metagenomes of a Freshwater Charavirus from British Columbia Provide a Window into Ancient Lineages of Viruses , in: Viruses, Volume 11, No. 3, 299, March 25, 2019, doi: 10.3390 / v11030299 , PMC 6466400 (freer Full text), PMID 30934644