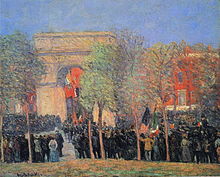William Glackens
William James Glackens (born March 13, 1870 in Philadelphia , Pennsylvania , † May 22, 1938 in Westport , Connecticut ) was an American painter and illustrator. In 1908 he co-founded the Ashcan School in New York .
life and work
After graduating, William Glackens worked first for the daily newspaper The Philadelphia Record and then as an illustrator for the Philadelphia Press. After work he studied for a while at the Pennsylvania Academy of the Fine Arts with Thomas Anshutz ; He met Robert Henri through his fellow student John French Sloan . The Ashcan School grew out of this circle .
In 1895 Glackens traveled to Europe with other painters. After Holland he moved to Paris for a year. On his return to Philadelphia he began painting in the style of James McNeill Whistler , with landscape painting. Together with George Benjamin Luks he visited Cuba in 1898 and began painting big city scenes again in Pennsylvania. In 1906, again in France , he also visited Spain. In 1908 he had a first exhibition together with The Eight .
In 1912 he traveled to Paris for his school friend Albert C. Barnes to acquire modern European painting, which later formed the basis for the Barnes Foundation in Philadelphia. These included, for example, works by Paul Cézanne , Pierre-Auguste Renoir and Pablo Picasso . Glackens was also sponsored by Barnes and his work was included in his art collection. He took part in the exhibition of the Armory Show in New York in 1913 and participated in the first exhibition of the Society of Independent Artists in 1917 , of which he was first chairman. In this function he rejected Marcel Duchamp's Ready-made Fountain , which he had submitted under the pseudonym R. Mutt, in a press release. His reasoning was that the submitted object was not a work of art. Duchamp and Walter Conrad Arensberg then resigned from the board in protest.
In New York, Glackens continued his subject, the hustle and bustle of big city life as a motif. Stylistically, he was based on the Impressionists, especially Édouard Manet . In the course of his work his style of painting became lighter.
In 1936 he was elected to the American Academy of Arts and Letters .
Works in public collections
A collection of more than 500 works by Glackens is on display in a dedicated wing at the Museum of Art Fort Lauderdale in Florida , USA .
literature
- Ira Glackens: William Glackens and the Ashcan Group: The Emergence of Realism in American Art . Crown Publishers, New York City, USA 1957.
- William H. Gerdts / Jorge E. Santis: William Glackens . Abbeville Press, New York City and Fort Lauderdale Museum 1996, ISBN 1-55859-868-5 .
Web links
- Biography at Encyclopædia Britannica Online (engl.)
- William Glackens at artfacts.net
- Selection of works at The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York (English)
- Glacken's illustrations from: Scribner's Monthly Magazine
Individual evidence
- ^ William Glackens ( August 10, 2014 memento in the Internet Archive ), barnesfoundation.org, accessed June 24, 2014
- ↑ Calvin Tomkins: Marcel Duchamp. A biography . Hanser, Munich et al. 1999, ISBN 3-446-19669-2 , p. 211 ff
- ^ Members: William J. Glackens. American Academy of Arts and Letters, accessed March 31, 2019 .
| personal data | |
|---|---|
| SURNAME | Glackens, William |
| ALTERNATIVE NAMES | Glackens, William James (full name); Glackens, William J. |
| BRIEF DESCRIPTION | American painter |
| DATE OF BIRTH | March 13, 1870 |
| PLACE OF BIRTH | Philadelphia , Pennsylvania |
| DATE OF DEATH | May 22, 1938 |
| Place of death | Westport , Connecticut |