Tungsten (VI) oxide tetrachloride
| Crystal structure | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| __ W 6+ __ Cl - __ O 2− | |||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Tungsten (VI) oxide tetrachloride | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | WOCl 4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
red solid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 341.65 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
3.98 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
211 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
227.5 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Tungsten (VI) oxide tetrachloride is an inorganic chemical compound of tungsten from the group of oxide chlorides .
Extraction and presentation
Tungsten (VI) oxide tetrachloride can be obtained by reacting tungsten (VI) oxide , tungsten (VI) chloride or sodium tungstate with thionyl chloride .
The representation by heating tungsten (VI) oxide with a solution of chlorine in carbon tetrachloride at 200 ° C or by reacting tungsten powder with sulfuryl chloride at 300 ° C is also possible.
It is also formed during the thermal decomposition of tungsten (VI) dioxide dichloride
as well as when boiling tungsten (VI) oxide in octachlorocyclopentene
and when reacting stoichiometric amounts of tungsten (VI) oxide with tungsten (VI) chloride in an evacuated ampoule at 200 ° C:
properties
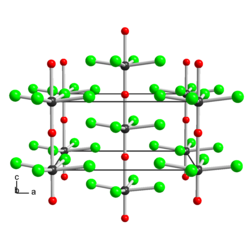
Tungsten (VI) oxide tetrachloride is in the form of long, shiny, red needles that appear yellow in transmitted light. It is immediately decomposed by water and more slowly by the humidity, with the formation of tungstic acid. It has a tetragonal crystal structure with the space group I 4 (space group no. 79) and the lattice parameters a = 848 pm and c = 399 pm. In addition to the red tungsten (VI) oxide tetrachloride WOCl 4 , the yellow tungsten (VI) dioxide dichloride WO 2 Cl 2 , the olive green tungsten (V) oxide trichloride WOCl 3 and the golden brown tungsten (IV) oxide dichloride WOCl 2 are further oxide chlorides of the Tungsten.
use
Tungsten (VI) oxide tetrachloride is used in incandescent lamps and as a catalyst in the production of olefins .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e Georg Brauer: Handbook of preparative inorganic chemistry . 3., reworked. Edition. tape III . Enke, Stuttgart 1981, ISBN 3-432-87823-0 , pp. 1569 .
- ↑ a b c d data sheet Tungsten (VI) oxychloride, 98% from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on July 13, 2013 ( PDF ).
- ^ Matthias F. Groh, Ulrike Müller, Ejaz Ahmed, Alexander Rothenberger, Michael Ruck: Substitution of Conventional High-temperature Syntheses of Inorganic Compounds by Near-room-temperature Syntheses in Ionic Liquids. In: Zeitschrift für Naturforschung B. 68, 2013, doi: 10.5560 / ZNB.2013-3141 .
- ↑ a b c d Dale L. Perry: Handbook of Inorganic Compounds, Second Edition . Taylor & Francis US, 2011, ISBN 978-1-4398-1462-8 , pp. 441 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ a b Susan E. Feil et al .: Tungsten oxide tetrachloride . In: S. Young Tyree, Jr. (Ed.): Inorganic Syntheses . tape 9 . McGraw-Hill Book Company, Inc., 1967, p. 123-126 (English).
- ↑ a b J. Tillack: Tungsten oxyhalides - B. Tungsten (VI) tetrachloride oxide . In: Aaron Wold and John K. Ruff (Eds.): Inorganic Syntheses . tape 14 . McGraw-Hill Book Company, Inc., 1973, ISBN 07-071320-0 ( defective ) , p. 109-122 (English).
- ↑ Balaram Sahoo, Nimain C. Nayak, Asutosh Samantaray, Prafulla K. Pujapanda, Sahoo Balaram, nayak Nimai Charan, samantaray Asutosh, pujapanda Prafulla Kumar: Inorganic Chemistry . 2012, ISBN 978-81-203-4308-5 , pp. 840 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ H. Hess, H. Hartung: The crystal structure of tungsten oxychloride WOCl 4 and tungsten oxybromide WOBr 4 . In: Journal of Inorganic and General Chemistry. 344, 1966, pp. 157-166, doi: 10.1002 / zaac.19663440306 .
- ↑ Royal Society of Chemistry: General and Synthetic Methods . Royal Society of Chemistry, 1982, ISBN 0-85186-864-9 , pp. 9 ( limited preview in Google Book search).




