Zebra shark
| Zebra shark | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Adult zebra shark |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name of the family | ||||||||||||
| Stegostomatidae | ||||||||||||
| Gill , 1862 | ||||||||||||
| Scientific name of the genus | ||||||||||||
| Stegostoma | ||||||||||||
| Müller & Henle , 1837 | ||||||||||||
| Scientific name of the species | ||||||||||||
| Stegostoma fasciatum | ||||||||||||
| ( Hermann , 1783) |
The zebra shark ( Stegostoma fasciatum ; also: leopard shark ) belongs to the nurse shark-like (Orectolobiformes) and is the only species of the Stegostomatidae family.
distribution
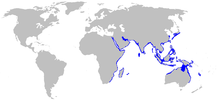
The zebra shark lives on the shelf of the continents, off islands in the Red Sea and in the Indo-Pacific from East Africa to Australia , New Caledonia and southern Japan , mostly at depths of 5 to 30 meters, up to a maximum of about 60 meters.
anatomy
The adults usually stay below 2.30 meters, but can possibly be up to 3.6 meters long. Zebra sharks are particularly noticeable for their disproportionately large tail fin , which can almost reach the length of the rest of the body. They have two stingless dorsal fins, the first much larger than the second. The adult animals have conspicuous edges on the sides of their bodies.
Your teeth are small. There are 20 to 23 rows of teeth in each jaw. The eyes are on the top of the head. The outer nostrils are near the mouth, have small barbels and are connected to the mouth by folds. The injection holes are medium-sized and sit behind the eyes. Of the five small gill slits, the last three are behind the base of the pectoral fin. The pectoral fins are large and rounded. Zebra sharks have 207 to 243 vertebrae.
Young animals that are smaller than 70 centimeters have a drawing of black and yellowish horizontal stripes; the adult sharks, on the other hand, are much lighter and darker. That is why they are also known as leopard sharks. But there is a risk of confusion with Triakis semifasciata , which has the same German name.
Way of life
Zebra sharks are particularly common on sandy and scree bottoms near coral reefs . In the Philippines it is also said to go into fresh waters. Zebra sharks are crepuscular, possibly also nocturnal and feed on mussels and snails, crabs , shrimps and small fish. They move slowly and can squeeze through narrow crevices and caves as they forage.
They are oviparous (laying eggs). The egg capsules are large, dark brown or blackish purple. The fry are 20 to 26 centimeters long at birth.
literature
- Joseph S. Nelson : Fishes of the World . John Wiley & Sons, 2006, ISBN 0-471-25031-7 .
- Kurt Fiedler: Textbook of Special Zoology, Volume II, Part 2: Fish . Gustav Fischer Verlag Jena, 1991, ISBN 3-334-00339-6 .
- Rikke Beckmann Dahl, Eva Egelyng Sigsgaard, Gorret Mwangi, Philip Francis Thomsen, René Dalsgaard Jørgensen, Felipe de Oliveira Torquato, Lars Olsen and Peter Rask Møller. 2019. The Sandy Zebra Shark: A New Color Morph of the Zebra Shark Stegostoma tigrinum , with A Redescription of the Species and A Revision of Its Nomenclature. Copeia . 107 (3); 524-541. DOI: 10.1643 / CG-18-115
Web links
- Zebra Shark on Fishbase.org (English)
- Family Stegostomatidae - Zebra sharks on Fishbase.org (English)
- Stegostoma fasciatum in endangered species red list of the IUCN 2006. Posted by: Pillans & Simpfendorfer, 2003. Retrieved on 11 May, 2006.