Wikipedia:Department of Fun/Word Association/Reverse Radial Ultra Cross and Xenu: Difference between pages
Kwamikagami (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{otheruses}} |
|||
==Reverse Radial Ultra game: Turkey fryer== |
|||
{{User:Xhin/six}} |
|||
As the name sugguests this is the Radial Ultra game in reverse - you start from the four corners and work towards the centre. New words must associate with all existing adjacent ones, and be next to either two existing words or one existing word and the edge of the table. The gold square in the centre of the table must be left to last and associate with all four surrounding words. |
|||
'''Xenu''', also '''Xemu''' ({{pron-en|ˈziːnuː}} or {{IPAlink-en|ˈziːmuː}}), was, according to [[Scientology]] founder (and [[science fiction]] writer) [[L. Ron Hubbard]], the [[dictator]] of the "[[Galactic Confederacy]]" who, 75 million years ago, brought billions<ref name=thmill>Thousands of millions in [[Long and short scales|Long Scale]]</ref> of his people to Earth in [[Douglas DC-8|DC-8]]-like spacecraft, stacked them around [[volcano]]es and killed them using [[Nuclear weapon#Fusion bombs|hydrogen bombs]]. Scientology holds that the essences of these many people remained, and that they form around people in modern times, causing them spiritual harm.<ref name=scott1>Scott, Michael Dennis (2004) "Internet And Technology Law Desk Reference", Aspen Publishers, ISBN 0735547432</ref><ref name=lewis1>Lewis James R (2003) "The Oxford Handbook of New Religious Movements", Oxford University Press, ISBN 0195149866</ref> Members of the [[Church of Scientology]] widely [[#The Church of Scientology's position on Xenu|deny or try to hide]] the Xenu story. |
|||
This particular game had the words chosen by clicking on the "Random Article" link. |
|||
These events are known within Scientology as "Incident II", and the traumatic memories associated with them as '''The Wall of Fire'''. The story of Xenu is part of Scientologist teachings about extraterrestrial civilizations and alien interventions in Earthly events, collectively described as ''[[Space opera in Scientology doctrine|space opera]]'' by Hubbard. Hubbard detailed the story in [[Operating Thetan]] level III ('''OT III''') in 1967, warning that this material was <!-- DON'T FIX -->"calculated to kill (by [[pneumonia]] etc) anyone who attempts to solve it."<sup><nowiki>[</nowiki>''[[sic]]''<nowiki>]</nowiki></sup><!-- DON'T FIX That's an exact quote --><ref>OT III materials as described by Margery Wakefield</ref> |
|||
The results of the previous game can be found [http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Wikipedia:Sandbox/Word_Association/Reverse_Radial_Ultra_Cross&oldid=241501787 here]. It began with '''[[Difference of Gaussians]]''', '''[[John Stokell Dodds]]''', '''''[[Geek!]]''''', and '''[[Union for Europe]]'''; it ended with '''[[Inugami]]'''. |
|||
[[Scientology controversy|Criticism]] of the Church of Scientology often includes details of the Xenu story. The Church has tried to keep Xenu confidential<ref>{{cite web | work = Ruling Scientology vs. providers and Karin Spaink | title = Summary proceedings |date=12 March 1996 | url=http://www.xs4all.nl/~kspaink/cos/verd1eng.html|accessdate = 2006-08-09}}</ref> but critics say the story should be made public, given the high prices charged for OT III, part of Scientology's secret "Advanced Technology" doctrines taught only to members who have already contributed large amounts of money to the organization.<ref>{{cite journal | last = Sappell | first = Joel | coauthors = Robert W. Welkos | title = The Scientology Story | journal = [[Los Angeles Times]] | pages = page A36:1 | date = 24 June 1990 | url = http://www.latimes.com/news/local/inland/la-scientology-sg,1,7389843.storygallery?coll=la-editions-inland-news | accessdate = 2006-08-09}} [http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~dst/Library/Shelf/la90/la90.html Additional convenience link].</ref> The Church avoids making mention of Xenu in public statements and has gone to considerable effort to maintain the story's confidentiality, including [[Scientology controversy|legal action]] on the grounds of both [[copyright]] and [[trade secret|trade secrecy]]. Despite this, much material on Xenu has leaked to the public, largely via the [[Scientology and the Internet|Internet]]. |
|||
{| width=100% border="1" cellpadding="4" cellspacing="3" style="margin: 1em 1em 1em 0; background: #FFE4B5" |
|||
|-<!-- Leave everything above this line alone! --> |
|||
<!-- ----------------------------------------- --> |
|||
<!-- "|" begins a row. --> |
|||
<!-- "||" moves across the row. --> |
|||
<!-- "|-" moves down a row. --> |
|||
<!-- ----------------------------------------- --> |
|||
<!-- ######################################### --> |
|||
|- |
|||
| '''[[Turkey fryer]]''' || [[Fire]] || [[Fire department]] || [[Police department]] || [[Crime fiction]] || [[Story of O]] || '''[[O (Cyrillic)]]''' |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[Giblets]] || [[barbecue|Barbecued chicken]] || [[Hot sauce]] || ''[[Hot Fuzz]]'' || ''[[Super Fuzz]]'' || [[Cinema of Russia]] || [[Cyrillic alphabet]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[Gizzard]] || [[Indigestion]] || [[Peptic ulcer]] || [[Cold sore]] || [[Cold War]] || [[Literature of Russia]] || [[Russian language]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[Lizard]] || [[Iguana]] <!--The iguana is supposed to be edible--> || [[Jalapeno]] || [[Chilly]] || || || [[Russification]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[Komodo dragon]] || [[Reptile]] || [[Vegetable]] || [[Chili pepper]] || || || [[Americanisation]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[Gila monster]] || [[Pit viper]] || [[Potato]] || || || || [[Cocacolonization]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[Arizona]] || ''[[Arizona elegans]]'' || || || || || [[Inca Kola]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[New Mexico]] || [[Geococcyx californianus]] || ||bgcolor="gold"| || || || [[Indigenous peoples of the Americas]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| ''[[Bless Me, Ultima]]'' || || || || || || [[Croatoan]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| ''[[To Kill a Mockingbird]]'' || || || || || || [[Croatia]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[Bird watching]] || || || || || || [[Serbia]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[Bill Oddie]] || [[Animal conservation]] || ''[[Emergency!]]'' || [[Sprain]] || [[Turf toe]] || [[Karađorđe Stadium]] || [[Novi Sad]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[Odie]] || [[St. Bernard (dog)]] || [[Mountain rescue]] || [[Stretcher]] || [[Sports injury]] || [[Sport in Serbia]] || [[Belgrade]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| [[Garfield and Friends]] || [[Snow bunny]] || [[Bunny slope]] || [[Slider]] || [[Sport in Italy]] || [[Sport in Belize]] || [[Belmopan]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| '''[[Ildar Garifullin]]''' || [[Skiing]] || [[Colorado]] || [[Dave LaRoche]] || [[Ferrero Rocher]] || [[Juan Carlos Ferrero]] || '''[[San Carlos, Belize]]''' |
|||
|- |
|||
<!-- No more rows - board size 7 x 15 --> |
|||
==Summary== |
|||
<!-- ######################################### --> |
|||
[[Image:McDonnell Douglas DC-8-60.jpg|200px|thumb|right|A [[Douglas DC-8]] aircraft. Hubbard described Xenu's spacecraft as looking exactly like DC-8s without "fans".]] |
|||
<!-- ----------------------------------------- --> |
|||
The story of Xenu is covered in OT III, part of Scientology's secret "Advanced Technology" doctrines taught only to advanced members who have undergone many expensive hours of [[Auditing (Scientology)|auditing]] and reached the state of [[Clear (Scientology)|Clear]]. It is described in more detail in the accompanying confidential "Assists" lecture of 3 October 1968 and is dramatized in ''[[Revolt in the Stars]]'' (a [[screenplay]] written by L. Ron Hubbard in [[1977 in film|1977]]). Direct quotations in this section are from these sources. (See also [[Scientology beliefs and practices#Scientology language and terms (Scientologese)|Scientology beliefs and practices]]) |
|||
<!-- Leave everything beneath this line alone! --> |
|||
|} |
|||
Scientologists believe that seventy-five million years ago, Xenu was the ruler of a Galactic Confederacy which consisted of 26 stars and 76 planets including Earth, which was then known as Teegeeack. The planets were overpopulated, each having an average population of 178 billion.<ref name=thmill/><ref name=scott1/><ref name=lewis1/> The Galactic Confederacy's civilization was comparable to our own, with aliens "walking around in clothes which looked very remarkably like the clothes they wear this very minute" and using cars, trains and boats looking exactly the same as those "circa 1950, 1960" on Earth.{{Fact|date=September 2008}} |
|||
{{Word Association}} |
|||
Xenu was about to be deposed from power, so he devised a plot to eliminate the excess population from his dominions. With the assistance of [[psychiatry|psychiatrists]], he summoned billions<ref name=thmill/> of his citizens together under the pretense of [[income tax]] inspections, then paralyzed them and froze them in a mixture of [[ethanol|alcohol]] and [[ethylene glycol|glycol]] to capture their souls. The kidnapped populace was loaded into spacecraft for transport to the site of extermination, the planet of Teegeeack (Earth). The appearance of these spacecraft would later be subconsciously expressed in the design of the [[Douglas DC-8]], the only difference being: "the DC8 had fans, propellers on it and the space plane didn't."<ref>{{cite web | work = Scientology Leader Gave ABC First-Ever Interview | title = ABC Interview Transcript |date=18 November 2006 | url=http://abcnews.go.com/Nightline/Story?id=2664713|accessdate = 2008-08-02}}</ref>. When they had reached Teegeeack/Earth, the paralyzed citizens were unloaded around the bases of volcanoes across the planet. [[Nuclear weapon#Fusion bombs|Hydrogen bomb]]s were then lowered into the volcanoes and detonated simultaneously. Only a few aliens' physical bodies survived. Hubbard described the scene in his film script, ''Revolt in the Stars'': |
|||
{{quotation|Simultaneously, the planted charges erupted. Atomic blasts ballooned from the craters of Loa, Vesuvius, Shasta, Washington, Fujiyama, Etna, and many, many others. Arching higher and higher, up and outwards, towering clouds mushroomed, shot through with flashes of flame, waste and fission. Great winds raced tumultuously across the face of Earth, spreading tales of destruction. Debris-studded, and sickly yellow, the atomic clouds followed close on the heels of the winds. Their bow-shaped fronts encroached inexorably upon forest, city and mankind, they delivered their gifts of death and radiation. A skyscraper, tall and arrow-straight, bent over to form a question mark to the very idea of humanity before crumbling into the screaming city below...|L. Ron Hubbard, ''Revolt in the Stars'' treatment}} |
|||
The now-disembodied victims' souls, which Hubbard called ''thetans'', were blown into the air by the blast. They were captured by Xenu's forces using an "electronic ribbon" ("which also was a type of [[standing wave]]") and sucked into "vacuum zones" around the world. The hundreds of billions<ref>A billion in [[Long and short scales|Short Scale]] is a thousand million in Long Scale.</ref> of captured thetans were taken to a type of [[movie theater|cinema]], where they were forced to watch a "[[3-D film|three-D]], super colossal motion picture" for thirty-six days. This implanted what Hubbard termed "various misleading data"' (collectively termed the R6 [[implant (Scientology)|implant]]) into the memories of the hapless thetans, "which has to do with [[God]], the [[Devil]], [[Space opera in Scientology doctrine|space opera]], et cetera". This included all [[Major religious groups|world religions]], with Hubbard specifically attributing [[Roman Catholic Church|Roman Catholicism]] and the image of the [[Crucifixion]] to the influence of Xenu. The [[interior decoration]] of "all modern theaters" is also said by Hubbard to be due to an unconscious recollection of Xenu's implants. The two "implant stations" cited by Hubbard were said to have been located on [[Hawaii]] and [[Las Palmas (province)|Las Palmas]] in the [[Canary Islands]]. |
|||
In addition to implanting new beliefs in the thetans, the images deprived them of their sense of [[Identity (social science)|personal identity]]. When the thetans left the projection areas, they started to cluster together in groups of a few thousand, having lost the ability to differentiate between each other. Each cluster of thetans gathered into one of the few remaining bodies that survived the explosion. These became what are known as ''[[body thetan]]s'', which are said to be still clinging to and adversely affecting everyone except those Scientologists who have performed the necessary steps to remove them. |
|||
A government faction known as the Loyal Officers finally overthrew Xenu and his renegades, and locked him away in a mountain, where he was imprisoned forever by a [[Force field (science fiction)|force field]] powered by an eternal battery. Although the location of Xenu is sometimes said to be the [[Pyrenees]] on Earth, this is actually the location Hubbard gave elsewhere for an ancient "Martian report station."<ref>Hubbard, ''Scientology: A History of Man''</ref> Teegeeack/Earth was subsequently abandoned by the Galactic Confederacy and remains a pariah "prison planet" to this day, although it has suffered repeatedly from incursions by alien "Invader Forces" since that time. |
|||
===Xenu's volcanoes=== |
|||
[[Image:Krakajawiazerohour.png|thumb|200px|right|Illustration of Incident II: Xenu dumped his surplus population in the vicinities of volcanoes, which he then ordered "H-bombs" dropped in to creating huge explosions which sent [[thetan]]s into an "energy ribbon" above.]] |
|||
In OT III, Hubbard names the locations around the world where Xenu's mass murder took place, in addition to the two implant stations located at Hawaii and Las Palmas.<ref>{{cite web | title = Operation Clambake presents: A Scientific scrutiny of OT 3|date=7 June 1996 | url=http://www.xenu.net/archive/ot/peter_forde.html|accessdate = 2007-04-26 }}</ref> In ''Revolt in the Stars'', the volcanoes named differ somewhat from those in OT III; for instance, [[Etna|Mount Etna]] and [[Vesuvius|Mount Vesuvius]] are named in ''Revolt'' but not in OT III.<ref>{{cite web | title = The Forbidden Story of Xenu |
|||
| url=http://www.mystae.com/streams/gnosis/otiii.html|accessdate = 2007-04-26 }}</ref> The volcanoes which Xenu blew up were said to have been situated at: |
|||
*'''The Americas''' |
|||
**"Mount Washington" (unclear which of the fifteen Mount Washingtons in North America is meant, but [[Mount Washington (Oregon)|Mount Washington, Oregon]] is a major [[shield volcano]]) |
|||
**[[Mount Rainier]], [[Washington]] |
|||
**[[Mount Hood]], [[Oregon]] |
|||
**[[Mount Shasta]], [[Northern California]] |
|||
**[[Mount San Gorgonio]], [[Southern California]] |
|||
**Canada |
|||
**[[Andes]], South America |
|||
*'''Atlantic Ocean and Africa''' |
|||
**[[Tangier]], [[Morocco]] |
|||
**[[Saint Helena]] |
|||
**"Kolomonjero" (non-existent location, possibly a misspelling of [[Kilimanjaro]], [[Tanzania]]) |
|||
**[[Las Palmas (province)|Las Palmas]], [[Canary Islands]] |
|||
*'''Asia and Pacific Ocean''' |
|||
**North Japan |
|||
**South Japan |
|||
**"Krakajawia" (non-existent location, possibly a misspelling of [[Krakatau]] or Krakatoa) |
|||
**[[Philippines]] |
|||
**[[Himalayas]] |
|||
**[[Hawaii]] |
|||
==Xenu in Scientology doctrine== |
|||
Within Scientology, the Xenu story is referred to as "The Wall of Fire" or "Incident II". Hubbard attached tremendous importance to it, saying that it constituted "the secrets of a disaster which resulted in the decay of life as we know it in this sector of the galaxy".<ref>Hubbard, ''Mission into Time''</ref> The broad outlines of the story — that 75 million years ago a great catastrophe happened in this sector of the galaxy which caused profoundly negative effects for everyone since then — are publicly admitted to lower-level Scientologists. However, the details are kept strictly confidential, at least within the Church. |
|||
Hubbard said that he was the first to map a precise route through the Wall of Fire, "probably the only one ever to do so in 75,000,000 years". He first publicly announced his "breakthrough" in ''[[Ron's Journal 67]]'' (''RJ67''), a tape Hubbard recorded on 20 September 1967 to be sent to all members of the Church. According to Hubbard, his research was achieved at the cost of a broken back, knee and arm. OT III contains a warning that the R6 implant is "calculated to kill (by pneumonia etc) anyone who attempts to solve it." In ''RJ67'', Hubbard then alludes to the devastating effect of Xenu's genocide: |
|||
{{cquote|And it is very true that a great catastrophe occurred on this planet and in the other 75 planets which formed this [Galactic] Confederacy 75 million years ago. It has since that time been a desert, and it has been the lot of just a handful to try to push its technology up to a level where someone might adventure forward, penetrate the catastrophe, and undo it. We're well on our way to making this occur.}} |
|||
OT III also deals with ''Incident I'', set four [[quadrillion]]<ref>Four thousand billion in [[Long and short scales|Long Scale]].</ref> years ago (or roughly 300,000 times longer than the current [[scientific consensus|scientifically accepted]] value for the [[age of the universe]]). In Incident I, the unsuspecting thetan was subjected to a loud snapping noise followed by a flood of luminescence, then saw a [[chariot]] followed by a trumpeting [[cherub]]. After a loud set of snaps, the thetan was overwhelmed by darkness. This is described as the implant offering the gateway to this universe, meaning that these traumatic memories are what separate thetans from their static (natural, godlike) state. |
|||
Hubbard uses the existence of body thetans to explain many of the physical and mental ailments of humanity which, he says, prevent people from achieving their highest spiritual levels. OT III tells the Scientologist to locate body thetans and release them from the effects of Incidents I and II by auditing them. This is accomplished in solo auditing, where the Scientologist holds both cans of an [[E-meter]] in one hand and asks questions as an auditor. The Scientologist is directed to find a cluster of body thetans, address it [[telepathy|telepathically]] as a cluster and take first the cluster then each individual member of the cluster through Incident II, then Incident I if needed. Hubbard warns that this is a painstaking procedure, and that OT levels IV to VII are necessary to continue the long process of dealing with one's body thetans. |
|||
The Church has objected to the Xenu story being used to paint Scientology as a mere [[science fiction]] fantasy.<ref name="Observer 2004">{{cite news| url=http://observer.guardian.co.uk/uk_news/story/0,6903,1217884,00.html| publisher=The Observer| title=Lure of the celebrity sect|date=16 May 2004|accessdate=2006-10-05| first=Jamie| last= Doward}}</ref> See: [[Space opera in Scientology doctrine]]. Hubbard's statements concerning the R6 implant have been a source of contention. Critics and some Christians state that Hubbard's statements regarding R6 prove that Scientology doctrine is incompatible with [[Christianity]],<ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.gerryarmstrong.org/50grand/cult/hcob-1963-05-11-routine-3-heaven-ex.html| title= Gerry Armstrong--HCOB 05-11-1963 Routine 3 Heaven| accessdate=2006-10-05}}</ref><ref>{{cite news| url=http://www.christianitytoday.com/ct/2000/010/8.93.html| publisher=Christianity Today| title=Why Christians Object to Scientology| first= Jody| last= Veenker | date= 9/8/00| accessdate=2006-10-05}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal| url=http://www.watchman.org/sci/hubrel03.htm| journal=The Watchman Expositor| volume= 13| issue= 2| year= 1996| title=Hubbard's Religion| first=Craig| last= Branch| accessdate=2006-10-05}}</ref><ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.sweenytod.com/cos/| title=Scientology and Christianity Examined| accessdate=2006-10-05}}</ref> despite the Church<!-- only once per sentence: of Scientology-->'s statements to the contrary.<ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.scientology-detroit.org/ans3.htm| publisher=Church of Scientology of Michigan| title=Scientology and Other Practices| accessdate=2006-10-05}}</ref> In "Assists", Hubbard says: |
|||
{{cquote|Everyman is then shown to have been crucified so don't think that it's an accident that this crucifixion, they found out that this applied. Somebody somewhere on this planet, back about 600 BC, found some pieces of R6, and I don't know how they found it, either by watching madmen or something, but since that time they have used it and it became what is known as Christianity. The man on the Cross. There was no [[Christ]]. But the man on the cross is shown as Everyman.}} |
|||
==Origins of the Xenu story== |
|||
Hubbard wrote OT III in late 1966 and early 1967 in [[North Africa]] while on his way to [[Las Palmas de Gran Canaria|Las Palmas]] to join the ''Enchanter'', the first vessel of his private Scientology fleet (the "[[Sea Org]]").<ref>Miller, ch. 16, p. 266, "[http://www.clambake.org/archive/books/bfm/bfm16.htm Launching the Sea Org]"</ref> (OT III says "In December 1967 I knew someone had to take the plunge", but the material was publicised well before this.) He emphasized later that OT III was his own personal discovery. |
|||
Critics of Scientology have suggested that other factors may have been at work. In a letter of the time to his wife [[Mary Sue Hubbard|Mary Sue]],<ref>Corydon, pp58–59, 332–333; letter filed as evidence in ''Church of Scientology v. Gerald Armstrong'', 1984, Los Angeles Superior Court, Case No. C420153</ref> Hubbard said that, in order to assist his research, he was drinking alcohol and taking [[stimulant]]s and [[depressant]]s ("I'm drinking lots of rum and popping pinks and greys"). His assistant at the time, Virginia Downsborough, said that he "was existing almost totally on a diet of drugs." <ref>Atack, part 4, ch. 1, "[http://www.clambake.org/archive/books/apobs/bs4-1.htm Scientology at Sea]"</ref> Miller (p. 290) speculates that it was important for Hubbard to be found in a debilitated condition, so as to present OT III as "a research accomplishment of immense magnitude". |
|||
Elements of the Xenu story appeared in Scientology before OT III. Hubbard's descriptions of extraterrestrial conflicts were put forward as early as 1952 and were enthusiastically endorsed by Scientologists, who documented their [[Reincarnation|past lives]] on other planets (published in 1960 as ''[[Have You Lived Before This Life]]''). OT III may not even have been Hubbard's first mention of Xenu, albeit in a different form. In an obscure lecture of 25 July 1958, "The Rock: Putting The PC At Cause", he refers to "Mount Zenu". Xenu, Hubbard says, was imprisoned under a mountain. |
|||
The idea that Earth is a prison planet, maintained by "entheta" [evil] beings or [[Targ]]s who dumped their enemies on Earth, was first publicly put forward in an obscure taped demonstration of [[Auditing (Scientology)|Scientology auditing]] recorded in April 1952 and released as "Electropsychometric Scouting: Battle of the Universes". <ref>{{cite web| url=http://freezoneamerica.org/pilot/lrhtapes/1952.html| title=Complete List of LRH Lectures: Tapes of 1952| accessdate=2006-10-05}}</ref> In many respects, OT III is virtually a retelling of this early tape, delivered in the first month of Scientology's existence. Hubbard describes how entheta (insane) beings defeat mutinous "theta" (sane) beings and decided that "the battleground is too rough and these things have mutinied so let's put 'em all in one place and lock 'em on to Earth." The entheta beings were "controlled over by religion"; Mary Sue Hubbard asks "Is that when Christianity came into being?" to which Hubbard replies, "That's an entheta operation." [[Communism]] is also apparently "their great success" — "anybody who thinks in this society is immediately attacked, you're surrounded by Targs." A steady flow of [[Unidentified flying object|flying saucers]] is still dropping off more entheta beings. The "Battle of the Universes" tape is no longer available from the Church of Scientology. |
|||
==The influence of OT III on Scientology== |
|||
[[Image:LRonHubbard-Dianetics-ISBN1403105464-cover.jpg|thumb|The volcano and fireball on the cover of ''Dianetics'' refers to the Xenu story.<ref name="savino">{{cite book| last =Savino| first =John| coauthors =Marie D. Jones| title =Supervolcano: The Catastrophic Event That Changed the Course of Human History| publisher =Career Press| date =2007| pages =Page 54| isbn = 1564149536}}</ref>]] |
|||
In the wake of Hubbard's revelation of the Wall of Fire, aspects of OT III and reflections of the Xenu story were adopted as symbols by the Church of Scientology. Hubbard is reported to have ordered that Scientology books be reissued with covers based on images from OT III.<ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.religio.de/atack/occ4.html#108| work=Hubbard and the Occult| title=References| accessdate=2006-10-05| first=Jon |last=Atack}}</ref> The 1968 and subsequent reprints of ''[[Dianetics]]'' have had covers depicting an exploding volcano, apparently alluding to the volcanoes in the Xenu story — "Man responds to an exploding volcano" (Hubbard, "Assists"). Other cover images may reference Xenu as well: the cover of the 1972 edition of ''[[Dianetics: The Evolution of a Science]]'' shows pictures of uniformed men in white helmets carrying boxes in and out of a spaceship, which may refer to the transportation of Xenu's victims. Some of the cover images are more obscure but are conjectured to refer to other elements of OT III: |
|||
{{cquote|A special 'Book Mission' was sent out to promote these books, now empowered and made irresistible by the addition of these overwhelming symbols or images. Organization staff were assured that if they simply held up one of the books, revealing its cover, that any bookstore owner would immediately order crateloads of them. A customs officer, seeing any of the book covers in one's luggage, would immediately pass one on through.|20px|20px|Bent Corydon|[http://www.clambake.org/archive/books/mom/Messiah_or_Madman.txt Messiah or Madman?]}} |
|||
[[Image:Sea org.png|thumb|left|90px|The Sea Org logo.]] |
|||
Since the 1980s, the volcano has also been depicted in [[Television advertisement|television commercials]] advertising ''Dianetics''. Scientology's "[[Sea Org]]", an elite group within the church that originated with Hubbard's personal staff aboard his fleet of ships, takes many of its symbols from the story of Xenu and OT III. It is explicitly intended to be a revival of the "Loyal Officers" who overthrew Xenu. Its logo, a wreath with 26 leaves, represents the 26 stars of Xenu's Galactic Confederacy.<ref>Hubbard, "Ron's Talk to Pubs Org World Wide", tape of April 1968</ref> According to the ''Dianetics and Scientology Technical Dictionary'', "the Sea Org symbol, adopted and used as the symbol of a Galactic Confederacy far back in the history of this sector, derives much of its power and authority from that association." |
|||
In the Advanced Orgs in [[Edinburgh]] and [[Los Angeles, California|Los Angeles]], Scientology staff were at one time ordered to wear all-white uniforms with silver boots, to mimic Xenu's Galactic Patrol as depicted on the cover of ''[[Dianetics: The Evolution of a Science]]''. This was reportedly done on the basis of Hubbard's declaration in his Flag Order 652 that mankind would accept regulation from that group which had last betrayed it — hence the imitation of Xenu's henchmen. (This was almost certainly a misinterpretation of what Hubbard meant — he was most likely referring to [[psychiatry|psychiatrist]]s, whom he believed had played a key role in Xenu's crimes.) In Los Angeles, a nightwatch was ordered to watch for returning spaceships.<ref>Atack, p. 190</ref> These measures were discarded after a time. |
|||
A more lasting legacy of OT III was Scientology's [[organizational structure]]. The current "org board" is "a refined board of an old galactic civilization ''[the Galactic Confederacy]''. We applied Scientology to it and found why it eventually failed. It lacked a couple of departments and that was enough to mess it all up. They lasted 80 trillion<ref>Billion in [[Long and short scales|Long Scale]]</ref> [years]."<ref>Hubbard, SHSBC 57, "Org Board and Livingness", 6 April 1965</ref> |
|||
==Xenu or Xemu?== |
|||
[[Image:Xenu-LRH-handwriting.png|frame|right|The manuscript of OT III contains the only known example of Xenu's name in Hubbard's handwriting.]] |
|||
The name has been spelled both as ''Xenu'' and ''Xemu''. The Class VIII course material includes a three-page text, handwritten by Hubbard, headed "Data", in which the Xenu story is given in detail. Hubbard's indistinct handwriting makes either spelling possible, particularly as the use of the name on the first page of OT III is the ''only'' known example of the name in his handwriting. In the "Assists" lecture, Hubbard speaks of ''"Xenu, ahhh, could be spelled X-E-M-U"'' and clearly says "Xemu" several times on the recording. The treatment of ''Revolt In The Stars'', which is typewritten (presumably by Hubbard), uses ''Xenu'' exclusively. Ex-Scientologists have reported that ''Xenu'' is the more commonly used form (Touretzky). Hubbard may have had two separate names for the "Xenu" figure. |
|||
==The Church of Scientology's position on Xenu== |
|||
In its public statements, the Church of Scientology has been notably reluctant to admit the existence of writings on Xenu and even to mention Xenu's name; court filings and legal correspondence issued by the Church of Scientology in the 1990s frequently struck out the name "Xenu" and replaced it with "Xxxx",<ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.solitarytrees.net/pickets/sp910.htm| title=Unsorted harassment reports| accessdate=2006-10-05}}</ref> a treatment given to no other term. In the relatively few instances in which it has acknowledged Xenu, the Church has stated the story is a religious writing that can be seen as the equivalent of the [[Old Testament]]—in which miraculous events are described that are unlikely to have occurred in real life, assuming true meaning only after years of study. They complain of critics using it to paint the religion as a science fiction fantasy.<ref name="Observer 2004"/> |
|||
Senior members of the [[Church of Scientology]] have several times publicly denied or minimized the importance of the Xenu story, but others have admitted its existence. In a [[Scientology and Me|BBC ''Panorama'' program]] that aired on 14 May 2007, senior Scientologist Tommy Davis interrupted when celebrity members are asked about Xenu, saying: "None of us know what you're talking about. It's loony. It's weird." When John Carmichael, the president of the Church of Scientology of New York, was asked about the Xenu story in the 9 September 2007 edition of the ''[[Daily Telegraph]]'', he said "That's not what we believe."<ref>{{cite web | title = Friends, thetans, countrymen| url = http://www.telegraph.co.uk/arts/main.jhtml?xml=/arts/2007/09/09/sm_scientology.xml&page=2| work = Seven| publisher = ''[[The Daily Telegraph]]''| page = 2| date = [[2007-09-09]]| accessdate = 2007-09-22}}</ref> In "A Conversation with David Miscavige", a story that ran on [[American Broadcasting Company|ABC]]'s ''[[Nightline (US news program)|Nightline]]'' on 14 February 1992, [[Ted Koppel]] directly asked Miscavige about the Xenu story, and Miscavige said that this was not a part of current or modern Scientology.<ref>{{cite web| url=http://abcnews.go.com/Nightline/story?id=2664713&page=1|date=14 February 1992|title=ABC News, Nightline: A Conversation with David Miscavige"|accessdate=2007-07-30}}</ref> However, in a 2006 interview with ''[[Rolling Stone]]'', [[Mike Rinder]], the director of the church's [[Office of Special Affairs]], said that "It is not a ''story'', it is an auditing level," when asked about the validity of the Xenu story.<ref name="Inside">{{cite web | first = Janet| last = Reitman | title = Inside Scientology| url = http://www.rollingstone.com/politics/story/9363363/inside_scientology/print| publisher = [[Rolling Stone]] | date = [[2006-02-23]]| accessdate = 2007-09-22}}</ref> |
|||
Scientology has many graduated levels through which one can progress. Many who remain at lower levels in the church are unaware of much of the space-opera doctrines, which mostly begin at [[Operating Thetan]] level three, or "OT III".<ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.xenu.net/archive/ot/| title=Operation Clambake Presents: OT Levels| accessdate=2006-10-05}}</ref> Because the information imparted to members is to be kept secret from others who have not attained that level, the member must publicly deny its existence when asked. OT III recipients must sign an agreement promising never to reveal its contents before they are given the manila envelope containing the Xenu knowledge.<ref name="Inside" /> It is knowledge so dangerous, members are told, that anyone learning this material before he is ready could die. After the Xenu story received considerable [[Mass media|mainstream media]] attention from mid-2005, upper-level Scientologists involved in recent debates with critics have acknowledged the legitimacy of the story.<ref>{{cite web| url=http://xenutv.bogie.nl/panels/humanist.htm| title=The Humanist Society of San Diego Meeting| date= 2005-02-20| accessdate=2006-10-05}}</ref> Recent public statements by the Church tend to position the tale as a very small part of the religion. |
|||
==Xenu and Scientology critics== |
|||
Despite the Church's efforts to keep the story secret, details have been leaked over the years. OT III was first revealed in Robert Kaufman's 1972 book ''[[Inside Scientology|Inside Scientology: Or How I Found Scientology and Became Super Human]]'', in which Kaufman detailed his own experiences of OT III. It was later described in a 1981 Clearwater ''Sun'' article by Richard Leiby, and came to greater public fame in a 1985 court case brought against the Church by [[Lawrence Wollersheim]]. The Church attempted to keep the case file checked out by a reader at all times, but the story was summarized in the ''[[Los Angeles Times]]'', 5 November 1985 and detailed in [[William Poundstone]]'s ''Bigger Secrets'' (1986) from information presented in the Wollersheim case. |
|||
Church lawyer Warren McShane said in a 1995 court case that the story had ''never'' been secret,<ref>{{cite web| url=http://www-2.cs.cmu.edu/~dst/OTIII/mcshane-rj67.txt| title=Re: Ron's Journal 67| work=alt.religion.scientology| accessdate=2006-10-05| date=28 August 1998| first=Mike | last=O'Connor| id=lepton-2808981630510001@lepton.dialup.access.net| format=TXT}} (testimony under oath by Warren McShane of the Church of Scientology in RTC v. FactNet, Civil Action No. 95B2143, United States Courthouse, Denver, Colorado, September 11, 1995)</ref> although maintaining there were nevertheless [[trade secret]]s contained in OT III. Notably, McShane discussed the details of the story at some length and specifically attributed the authorship of the story to Hubbard.<Ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.mystae.com/streams/gnosis/secrets.html| title=Trade Secrets?| accessdate=2006-10-05}}</ref> |
|||
On 24 December 1994, the text of OT III was published on the Internet for the first time in a posting to the [[Usenet]] [[newsgroup]] [[alt.religion.scientology]], through an [[anonymous remailer]].<ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.whyaretheydead.net/krasel/aff_de.html |
|||
| title=Affidavit of Dennis Erlich| accessdate=2007-04-26| date=16 November 1995| format=TXT}}</ref> This subsequently brought on the actions of Scientology lawyers, leading to the online battle described as [[Scientology versus the Internet]]. Older versions of OT levels I to VII were brought as exhibits attached to a declaration by [[Steven Fishman]] on 9 April 1993 as part of ''Church of Scientology International v. Fishman and Geertz''. The text of this declaration and its exhibits, collectively known as the [[Fishman Affidavit]], were posted to the Internet newsgroup [[alt.religion.scientology]] in [[1995|August 1995]] by [[Arnaldo Lerma|Arnie Lerma]] and on the [[World Wide Web]] by [[David S. Touretzky]]. This was a subject of great controversy and legal battles for several years, notably a [[copyright]] raid on Lerma's house (leading to massive [[Mirror (computing)|mirroring]] of the documents) and a suit against [[Netherlands|Dutch]] writer [[Karin Spaink]] — the Church bringing suit on [[Copyright infringement|copyright violation]] grounds for reproducing the source material, and also claiming rewordings would reveal a trade secret. |
|||
The Church's attempts to keep Xenu under wraps have been cited in court findings against it. In September 2003, a Dutch court, in a ruling in the case against Karin Spaink, stated that one objective in keeping OT II and OT III secret was to wield power over members of the Church and prevent discussion about the Church's teachings and practices:<ref>''"Uit de hiervoor onder 8.3 vermelde teksten blijkt dat Scientology c.s. met hun leer en organisatie de verwerping van democratische waarden niet schuwen. Uit die teksten volgt tevens dat met de geheimhouding van OT II en OT III mede wordt beoogd macht uit te oefenen over leden van de Scientology-organisatie en discussie over de leer en praktijken van de Scientology-organisatie te verhinderen."''[http://www.rechtspraak.nl/ljn.asp?ljn=AI5638 Translation by Spaink]{{Fact|date=May 2007}}<!-- by who..? --></ref> "The texts previously quoted show that in its teachings and its structure, Scientology c.s. do not shun the rejection of democratic values. From these texts it is also apparent that one of the objectives of keeping OT II and OT III secret is to wield power over members of the Scientology organization and to prevent discussion about the teachings and practices of the Scientology organization." |
|||
Xenu is also widely cited by Scientology critics, who accuse the Church of being a scam. The price of the OT III auditing level alone ([[United States dollar|US$]]19,500 in 1997) is given as evidence that Scientology peddles bad [[science fiction]] for a high price.<ref>{{cite web| url=http://www-2.cs.cmu.edu/~dst/OTIII/ot3-ad.txt| format=TXT| accessdate=2006-10-05| title=FWD: Re: Another part of the "Bait and Switch"| work=alt.religion.scientology| date=30 November 1997| id=3481749c.387609633@news.sol.no| first=Andreas | last=Heldal-Lund}}</ref> [[Operation Clambake]], the most popular critical Web site concerning Scientology, uses the Internet [[domain name]] xenu.net. Geoffrey Filbert, a [[Free Zone (Scientology)|Free Zone]] (non-CoS) Scientologist, wrote a book, ''Excalibur Revisited'', in 1982, containing his own version of OT III. This was the first of several versions available in the Free Zone. Roland Rashleigh-Berry, an ex-[[List of Scientologists|Scientologist]], wrote a "Xenu leaflet", popular with critics, that summarizes the story of OT III. The leaflet includes part of the first page of OT III in Hubbard's handwriting, mentioning Xenu. |
|||
==Xenu in popular culture== |
|||
[[Image:Xenu BBC Panorama.jpg|right|thumb|Xenu as depicted by ''[[Panorama (TV series)|Panorama]]'']] |
|||
L. Ron Hubbard had apparently intended to publicize the Xenu story to the wider world under the title of ''[[Revolt in the Stars]]'', an extended version of the story of OT III, which he wrote in the late 1970s. It has not been officially published, although the [[film treatment|treatment]] was circulated around [[Hollywood, California|Hollywood]] in the early 1980s (Young). Copies of the treatment leaked, and Scientology critic [[Grady Ward]] published a summary.<ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.suburbia.net/~fun/scn/pers/fun/xenu/revolt.html| title=Revolt In The Stars by L. Ron Hubbard, Summarized by Grady Ward| accessdate=2006-10-05}}</ref> |
|||
Although the Xenu story first leaked in 1972 and was widely publicized on the Internet and in news stories from 1995 onwards, it only achieved currency in popular culture in the middle of 2005, when actor [[Tom Cruise]] changed publicists, dismissing Patricia Kingsley in favor of members of his own family, and actively promoted Scientology while he was doing publicity for ''[[War of the Worlds (2005 film)|War of the Worlds]]''; the press responded by citing the Xenu story in numerous articles. |
|||
A number of television shows have featured visual depictions of Xenu, either as a cartoon or a [[Computer-generated imagery|computer-generated]] character. Hubbard did not describe the physical form of Xenu in the OT III documents and provided no illustrations of him; portrayals of Xenu have therefore varied considerably. In 1987, the [[BBC]]'s investigative news series ''[[Panorama (TV series)|Panorama]]'' aired a report entitled "The Road to Total Freedom?" in which it featured an outline of the OT III story illustrated with an animation showing Xenu, spaceships carrying captured aliens to Earth and the bombing of the volcanoes. Xenu is depicted as a bald, bearded warlord in a militaristic uniform.<ref>''Panorama'', "The Road to Total Freedom", 1987</ref> |
|||
===South Park=== |
|||
{{Main|Trapped in the Closet (South Park)}} |
|||
[[Image:South Park Xenu.jpg|thumb|right|Xenu as depicted in ''[[South Park]]''.]] |
|||
In November 2005, "[[Trapped in the Closet (South Park)|Trapped in the Closet]]", an episode of the [[animated]] [[television series]] ''[[South Park]]'', [[satire|satirized]] Scientology, including an animated retelling of the Xenu story, with the words "THIS IS WHAT SCIENTOLOGISTS ACTUALLY BELIEVE" superimposed on-screen for most of it. Xenu is depicted as a vaguely humanoid alien with tentacles for arms. In the ''South Park'' episode, the aliens are directly dropped into the volcanoes, and the thetans rise in an effort to return but are then captured. |
|||
The episode became the subject of a controversy when its rebroadcast by [[Comedy Central]] was dropped, with another episode being substituted. The channel stated that the substitution was intended to pay tribute to [[Isaac Hayes]]. The creators of ''[[South Park]],'' [[Matt Stone]] and [[Trey Parker]], disagreed and asserted that Comedy Central's owners [[Viacom]] had replaced the episode because the Church of Scientology intervened (or interfered) and, more specifically, because Tom Cruise (who was himself lampooned in the episode) threatened distributor Paramount (also a Viacom property) with refusal to cooperate with the promotional campaign on the upcoming film ''[[Mission Impossible 3]]''. Cruise's representative denied this, but Parker and Stone issued a satirical press release that was published in the entertainment newspaper, ''[[Daily Variety]]'':<ref>{{cite news| url=http://www.mtv.com/news/articles/1526757/20060321/index.jhtml?headlines=true&rsspartner=rssYahooNewscrawler| title=South Park' Cooks Up Plan For Chef In Season Premiere| date=2006-03-21| publisher=MTV News| accessdate=2006-10-05}}</ref> |
|||
:"So, Scientology, you may have won THIS battle, but the million-year war for Earth has just begun! Temporarily anozinizing our episode will NOT stop us from keeping Thetans forever trapped in your pitiful man-bodies. Curses and drat! You have obstructed us for now, but your feeble bid to save humanity will fail! HAIL XENU!!!" |
|||
Comedy Central did eventually rebroadcast the episode on 19 July 2006. |
|||
===Nip/Tuck=== |
|||
[[Image:Xenu nip-tuck.jpg|right|thumb|Xenu appearing with [[Kimber Henry]] ([[Kelly Carlson]]) in a dream sequence in ''[[Nip/Tuck]]''.]] |
|||
Xenu appeared in "[[Willy Ward]]", the penultimate episode of season 4 of the [[FX (TV network)|FX]] show ''[[Nip/Tuck]]'' (first broadcast 5 December 2006). In a dream sequence, Scientologist character [[Kimber Henry]] ([[Kelly Carlson]]) has a vision of Xenu while experiencing hallucinations and doubts about Scientology. Xenu is depicted as a cross between [[Ming the Merciless]] and a stereotypical [[greys|grey alien]].<ref>"Looking for a change, 'Nip/Tuck' heads west", ''Arizona Republic'', 16 December 2006<br>..Christian and Dawn Budge's (O'Donnell) sexual tryst, sexy Kimber's faceoff with the Scientology figure Xenu..</ref><ref>"TELEVISION; `Nip/Tuck' warms up to Scientology; The FX drama", ''Los Angeles Times'', 1 October 2006<br>...that most human problems can be traced to lingering spirits of an extraterrestrial people massacred By their ruler, Xenu, over 75 million years ago..</ref> |
|||
{{clear}} |
|||
== See also == |
|||
{{Portal|Scientology|Scientology e meter blue.jpg}} |
|||
* [[Space opera in Scientology scripture]] |
|||
* [[Incident (Scientology)]] |
|||
* [[Implant (Scientology)]] |
|||
{{clear}} |
|||
==Notes== |
|||
<small>Note: '''HCOB''' refers to "Hubbard Communications Office Bulletins", '''HCOPL''' refers to "Hubbard Communications Office Policy Letters", and '''SHSBC''' refers to "Saint Hill Special Briefing Courses". All have been made publicly available by the Church of Scientology in the past, both as individual documents or in bound volumes.</small> |
|||
{{Reflist|2}} |
|||
== References == |
|||
;Sources |
|||
{{refbegin}} |
|||
* [[Jon Atack]], ''[http://www.clambake.org/archive/books/apobs/index.html A Piece Of Blue Sky]'' (Kensington Publishing Corporation, New York, 1990; ISBN 0-8184-0499-X) |
|||
* Bent Corydon and L. Ron Hubbard Jr., ''L. Ron Hubbard: Messiah Or Madman?'' (Lyle Stuart, New Jersey, 1987; ISBN 0-8184-0444-2) |
|||
* L. Ron Hubbard, ''Scientology: A History of Man'' (American Saint Hill Organization, 1968; current edition Bridge Publications ISBN 0-88404-306-1) |
|||
* L. Ron Hubbard, ''Mission into Time'' (American Saint Hill Organization, 1973; current edition Bridge Publications ISBN 0-88404-023-2) |
|||
* L. Ron Hubbard, ''Have You Lived Before This Life?'' (1958; current edition Bridge Publications ISBN 0-88404-447-5) |
|||
* [[Russell Miller]], ''[http://www.clambake.org/archive/books/bfm/bfmconte.htm Bare-Faced Messiah: The True Story Of L. Ron Hubbard]'' (Henry Holt, New York, 1988; ISBN 1-55013-027-7) |
|||
* [http://www.religio.de/atack/occ1.html FACTnet report: Hubbard and the Occult] (Jon Atack) |
|||
* Robert Kaufman, ''Inside Scientology: Or How I Found Scientology and Became Super Human'', (Olympia Press ISBN 0-7004-0110-5, 1972; ([http://www.clambake.org/archive/books/isd/isd.htm 1995 edition published on Web]) |
|||
* [http://www.lermanet.com/scientologynews/clearwatersun/sun-leiby-083081.htm Sect courses resemble science fiction] (Richard Leiby, Clearwater ''Sun'', vol. 68 no. 118, 30 August 1981) |
|||
* [http://home.snafu.de/tilman/851105.txt Scientologists Block Access To Secret Documents: 1,500 crowd into courthouse to protect materials on fundamental beliefs] (Joel Sappell and Robert Welkos, ''Los Angeles Times'', 5 November 1985) |
|||
* [http://www.xs4all.nl/~kspaink/cos/coskit/faegre/injunc/young.html Testimony under oath] (pp274–275) from [[Robert Vaughn Young]] in ''RTC v. FactNet'', Civil Action No. 95B2143, United States Courthouse, Denver, Colorado, September 11, 1995 |
|||
*[http://www.xenu.net/archive/multimedia.html Audio extracts from Class VIII "Assists" lecture] (3 October 1968) |
|||
* ''[http://freezoneamerica.org/excal/excal00.html Excalibur Revisited: The Akashic Book of Truth]'' (Geoffrey Filbert) |
|||
{{refend}} |
|||
;Other references |
|||
{{refbegin}} |
|||
* {{cite book |last= Dawson |first= Lorne L. |coauthors= Douglas E. Cowan |editor= |others= |title= Religion Online |origdate= |origyear= |accessdate= |accessyear= |date= 2004-04-01 |publisher= Routledge (UK) |id= ISBN 0-415-97022-9 |pages= 261 et. seq. |quote = }} |
|||
* {{Harvard reference|Surname= Grünschloß |Given= Andreas |Year= 2003-12-01 |Chapter= Waiting for the "Big Beam," UFO Religions and "UFOlogical" Themes in New Religious Movements, Page 427 et. seq |Editor=James R. Lewis |Title= The Oxford Handbook of New Religious Movements |Place=|Publisher= Oxford University Press US |ID= ISBN 0-19-514786-6 |URL=}} |
|||
{{refend}} |
|||
==External links== |
|||
{{commons}} |
|||
* [http://www.whatisscientology.org/Html/Part11/Chp33/pg0592.html What is Scientology: OT III Released] |
|||
*[http://www.xenutv.com/ Xenu TV] |
|||
* [http://www.scientology.org/wis/wiseng/17/17-ot.htm Scientology.org: OT Level Successes] |
|||
* [http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~dst/OTIII/index.html OT III Scholarship Page] ([[David S. Touretzky]]; includes page scans, commentary, audio files) |
|||
* [http://www.suburbia.net/~fun/scn/pers/fun/xenu/revolt.html Revolt In The Stars summary] ([[Grady Ward]]) |
|||
* [http://www.xenu.net/archive/leaflet/ Xenu Leaflet] (Roland Rashleigh-Berry) |
|||
* [http://www.spaink.net/fishman/ot3.html The Fishman Affidavit: OT III] (extracts and synopsis by [[Karin Spaink]]) |
|||
* [http://www.spaink.net/cos/essays/forde_volcanos.html A Scientific scrutiny of OT III] (Peter Forde, June 1996) |
|||
*''[http://xenutv.bogie.nl/int/ot3.htm The Story of OTIII]'': A [[RealPlayer]] animation that takes a humorous yet accurate look at the Xenu doctrine. From the ''[[Panorama (TV series)|BBC Panorama]]'' documentary "The Road to Total Freedom?" |
|||
* [http://www.xenu.net/ Operation Clambake - The Inner Secrets Of Scientology] |
|||
* [http://www.xenu.net/archive/OTIII-scholar/bts-or-dts.txt Research essay describing OT 3 as a drug induced hallucination] posted to alt.religion.scientology on 3/29/96 by Prignillius |
|||
* [http://gawker.com/5037013/the-history-of-xenu-as-explained-by-l-ron-hubbard-himself-in-8-minutes The History Of Xenu, As Explained By L. Ron Hubbard In 8 Minutes] |
|||
{{Scientology}} |
|||
{{featured article}} |
|||
[[Category:Scientology controversies]] |
|||
[[Category:Xenu| ]] |
|||
[[de:Xenu]] |
|||
[[es:Xenu]] |
|||
[[eo:Ksenu]] |
|||
[[fr:Xenu]] |
|||
[[it:Xenu]] |
|||
[[lt:Xenu incidentas]] |
|||
[[pl:Xenu]] |
|||
[[ru:Ксену (Саентология)]] |
|||
[[fi:Xenu]] |
|||
[[sv:Xenu]] |
|||
[[tr:Xenu]] |
|||
Revision as of 06:33, 10 October 2008
Xenu, also Xemu (Template:Pron-en or Template:IPAlink-en), was, according to Scientology founder (and science fiction writer) L. Ron Hubbard, the dictator of the "Galactic Confederacy" who, 75 million years ago, brought billions[1] of his people to Earth in DC-8-like spacecraft, stacked them around volcanoes and killed them using hydrogen bombs. Scientology holds that the essences of these many people remained, and that they form around people in modern times, causing them spiritual harm.[2][3] Members of the Church of Scientology widely deny or try to hide the Xenu story.
These events are known within Scientology as "Incident II", and the traumatic memories associated with them as The Wall of Fire. The story of Xenu is part of Scientologist teachings about extraterrestrial civilizations and alien interventions in Earthly events, collectively described as space opera by Hubbard. Hubbard detailed the story in Operating Thetan level III (OT III) in 1967, warning that this material was "calculated to kill (by pneumonia etc) anyone who attempts to solve it."[sic][4]
Criticism of the Church of Scientology often includes details of the Xenu story. The Church has tried to keep Xenu confidential[5] but critics say the story should be made public, given the high prices charged for OT III, part of Scientology's secret "Advanced Technology" doctrines taught only to members who have already contributed large amounts of money to the organization.[6] The Church avoids making mention of Xenu in public statements and has gone to considerable effort to maintain the story's confidentiality, including legal action on the grounds of both copyright and trade secrecy. Despite this, much material on Xenu has leaked to the public, largely via the Internet.
Summary
The story of Xenu is covered in OT III, part of Scientology's secret "Advanced Technology" doctrines taught only to advanced members who have undergone many expensive hours of auditing and reached the state of Clear. It is described in more detail in the accompanying confidential "Assists" lecture of 3 October 1968 and is dramatized in Revolt in the Stars (a screenplay written by L. Ron Hubbard in 1977). Direct quotations in this section are from these sources. (See also Scientology beliefs and practices)
Scientologists believe that seventy-five million years ago, Xenu was the ruler of a Galactic Confederacy which consisted of 26 stars and 76 planets including Earth, which was then known as Teegeeack. The planets were overpopulated, each having an average population of 178 billion.[1][2][3] The Galactic Confederacy's civilization was comparable to our own, with aliens "walking around in clothes which looked very remarkably like the clothes they wear this very minute" and using cars, trains and boats looking exactly the same as those "circa 1950, 1960" on Earth.[citation needed]
Xenu was about to be deposed from power, so he devised a plot to eliminate the excess population from his dominions. With the assistance of psychiatrists, he summoned billions[1] of his citizens together under the pretense of income tax inspections, then paralyzed them and froze them in a mixture of alcohol and glycol to capture their souls. The kidnapped populace was loaded into spacecraft for transport to the site of extermination, the planet of Teegeeack (Earth). The appearance of these spacecraft would later be subconsciously expressed in the design of the Douglas DC-8, the only difference being: "the DC8 had fans, propellers on it and the space plane didn't."[7]. When they had reached Teegeeack/Earth, the paralyzed citizens were unloaded around the bases of volcanoes across the planet. Hydrogen bombs were then lowered into the volcanoes and detonated simultaneously. Only a few aliens' physical bodies survived. Hubbard described the scene in his film script, Revolt in the Stars:
Simultaneously, the planted charges erupted. Atomic blasts ballooned from the craters of Loa, Vesuvius, Shasta, Washington, Fujiyama, Etna, and many, many others. Arching higher and higher, up and outwards, towering clouds mushroomed, shot through with flashes of flame, waste and fission. Great winds raced tumultuously across the face of Earth, spreading tales of destruction. Debris-studded, and sickly yellow, the atomic clouds followed close on the heels of the winds. Their bow-shaped fronts encroached inexorably upon forest, city and mankind, they delivered their gifts of death and radiation. A skyscraper, tall and arrow-straight, bent over to form a question mark to the very idea of humanity before crumbling into the screaming city below...
— L. Ron Hubbard, Revolt in the Stars treatment
The now-disembodied victims' souls, which Hubbard called thetans, were blown into the air by the blast. They were captured by Xenu's forces using an "electronic ribbon" ("which also was a type of standing wave") and sucked into "vacuum zones" around the world. The hundreds of billions[8] of captured thetans were taken to a type of cinema, where they were forced to watch a "three-D, super colossal motion picture" for thirty-six days. This implanted what Hubbard termed "various misleading data"' (collectively termed the R6 implant) into the memories of the hapless thetans, "which has to do with God, the Devil, space opera, et cetera". This included all world religions, with Hubbard specifically attributing Roman Catholicism and the image of the Crucifixion to the influence of Xenu. The interior decoration of "all modern theaters" is also said by Hubbard to be due to an unconscious recollection of Xenu's implants. The two "implant stations" cited by Hubbard were said to have been located on Hawaii and Las Palmas in the Canary Islands.
In addition to implanting new beliefs in the thetans, the images deprived them of their sense of personal identity. When the thetans left the projection areas, they started to cluster together in groups of a few thousand, having lost the ability to differentiate between each other. Each cluster of thetans gathered into one of the few remaining bodies that survived the explosion. These became what are known as body thetans, which are said to be still clinging to and adversely affecting everyone except those Scientologists who have performed the necessary steps to remove them.
A government faction known as the Loyal Officers finally overthrew Xenu and his renegades, and locked him away in a mountain, where he was imprisoned forever by a force field powered by an eternal battery. Although the location of Xenu is sometimes said to be the Pyrenees on Earth, this is actually the location Hubbard gave elsewhere for an ancient "Martian report station."[9] Teegeeack/Earth was subsequently abandoned by the Galactic Confederacy and remains a pariah "prison planet" to this day, although it has suffered repeatedly from incursions by alien "Invader Forces" since that time.
Xenu's volcanoes

In OT III, Hubbard names the locations around the world where Xenu's mass murder took place, in addition to the two implant stations located at Hawaii and Las Palmas.[10] In Revolt in the Stars, the volcanoes named differ somewhat from those in OT III; for instance, Mount Etna and Mount Vesuvius are named in Revolt but not in OT III.[11] The volcanoes which Xenu blew up were said to have been situated at:
- The Americas
- "Mount Washington" (unclear which of the fifteen Mount Washingtons in North America is meant, but Mount Washington, Oregon is a major shield volcano)
- Mount Rainier, Washington
- Mount Hood, Oregon
- Mount Shasta, Northern California
- Mount San Gorgonio, Southern California
- Canada
- Andes, South America
- Atlantic Ocean and Africa
- Tangier, Morocco
- Saint Helena
- "Kolomonjero" (non-existent location, possibly a misspelling of Kilimanjaro, Tanzania)
- Las Palmas, Canary Islands
- Asia and Pacific Ocean
- North Japan
- South Japan
- "Krakajawia" (non-existent location, possibly a misspelling of Krakatau or Krakatoa)
- Philippines
- Himalayas
- Hawaii
Xenu in Scientology doctrine
Within Scientology, the Xenu story is referred to as "The Wall of Fire" or "Incident II". Hubbard attached tremendous importance to it, saying that it constituted "the secrets of a disaster which resulted in the decay of life as we know it in this sector of the galaxy".[12] The broad outlines of the story — that 75 million years ago a great catastrophe happened in this sector of the galaxy which caused profoundly negative effects for everyone since then — are publicly admitted to lower-level Scientologists. However, the details are kept strictly confidential, at least within the Church.
Hubbard said that he was the first to map a precise route through the Wall of Fire, "probably the only one ever to do so in 75,000,000 years". He first publicly announced his "breakthrough" in Ron's Journal 67 (RJ67), a tape Hubbard recorded on 20 September 1967 to be sent to all members of the Church. According to Hubbard, his research was achieved at the cost of a broken back, knee and arm. OT III contains a warning that the R6 implant is "calculated to kill (by pneumonia etc) anyone who attempts to solve it." In RJ67, Hubbard then alludes to the devastating effect of Xenu's genocide:
And it is very true that a great catastrophe occurred on this planet and in the other 75 planets which formed this [Galactic] Confederacy 75 million years ago. It has since that time been a desert, and it has been the lot of just a handful to try to push its technology up to a level where someone might adventure forward, penetrate the catastrophe, and undo it. We're well on our way to making this occur.
OT III also deals with Incident I, set four quadrillion[13] years ago (or roughly 300,000 times longer than the current scientifically accepted value for the age of the universe). In Incident I, the unsuspecting thetan was subjected to a loud snapping noise followed by a flood of luminescence, then saw a chariot followed by a trumpeting cherub. After a loud set of snaps, the thetan was overwhelmed by darkness. This is described as the implant offering the gateway to this universe, meaning that these traumatic memories are what separate thetans from their static (natural, godlike) state.
Hubbard uses the existence of body thetans to explain many of the physical and mental ailments of humanity which, he says, prevent people from achieving their highest spiritual levels. OT III tells the Scientologist to locate body thetans and release them from the effects of Incidents I and II by auditing them. This is accomplished in solo auditing, where the Scientologist holds both cans of an E-meter in one hand and asks questions as an auditor. The Scientologist is directed to find a cluster of body thetans, address it telepathically as a cluster and take first the cluster then each individual member of the cluster through Incident II, then Incident I if needed. Hubbard warns that this is a painstaking procedure, and that OT levels IV to VII are necessary to continue the long process of dealing with one's body thetans.
The Church has objected to the Xenu story being used to paint Scientology as a mere science fiction fantasy.[14] See: Space opera in Scientology doctrine. Hubbard's statements concerning the R6 implant have been a source of contention. Critics and some Christians state that Hubbard's statements regarding R6 prove that Scientology doctrine is incompatible with Christianity,[15][16][17][18] despite the Church's statements to the contrary.[19] In "Assists", Hubbard says:
Everyman is then shown to have been crucified so don't think that it's an accident that this crucifixion, they found out that this applied. Somebody somewhere on this planet, back about 600 BC, found some pieces of R6, and I don't know how they found it, either by watching madmen or something, but since that time they have used it and it became what is known as Christianity. The man on the Cross. There was no Christ. But the man on the cross is shown as Everyman.
Origins of the Xenu story
Hubbard wrote OT III in late 1966 and early 1967 in North Africa while on his way to Las Palmas to join the Enchanter, the first vessel of his private Scientology fleet (the "Sea Org").[20] (OT III says "In December 1967 I knew someone had to take the plunge", but the material was publicised well before this.) He emphasized later that OT III was his own personal discovery.
Critics of Scientology have suggested that other factors may have been at work. In a letter of the time to his wife Mary Sue,[21] Hubbard said that, in order to assist his research, he was drinking alcohol and taking stimulants and depressants ("I'm drinking lots of rum and popping pinks and greys"). His assistant at the time, Virginia Downsborough, said that he "was existing almost totally on a diet of drugs." [22] Miller (p. 290) speculates that it was important for Hubbard to be found in a debilitated condition, so as to present OT III as "a research accomplishment of immense magnitude".
Elements of the Xenu story appeared in Scientology before OT III. Hubbard's descriptions of extraterrestrial conflicts were put forward as early as 1952 and were enthusiastically endorsed by Scientologists, who documented their past lives on other planets (published in 1960 as Have You Lived Before This Life). OT III may not even have been Hubbard's first mention of Xenu, albeit in a different form. In an obscure lecture of 25 July 1958, "The Rock: Putting The PC At Cause", he refers to "Mount Zenu". Xenu, Hubbard says, was imprisoned under a mountain.
The idea that Earth is a prison planet, maintained by "entheta" [evil] beings or Targs who dumped their enemies on Earth, was first publicly put forward in an obscure taped demonstration of Scientology auditing recorded in April 1952 and released as "Electropsychometric Scouting: Battle of the Universes". [23] In many respects, OT III is virtually a retelling of this early tape, delivered in the first month of Scientology's existence. Hubbard describes how entheta (insane) beings defeat mutinous "theta" (sane) beings and decided that "the battleground is too rough and these things have mutinied so let's put 'em all in one place and lock 'em on to Earth." The entheta beings were "controlled over by religion"; Mary Sue Hubbard asks "Is that when Christianity came into being?" to which Hubbard replies, "That's an entheta operation." Communism is also apparently "their great success" — "anybody who thinks in this society is immediately attacked, you're surrounded by Targs." A steady flow of flying saucers is still dropping off more entheta beings. The "Battle of the Universes" tape is no longer available from the Church of Scientology.
The influence of OT III on Scientology

In the wake of Hubbard's revelation of the Wall of Fire, aspects of OT III and reflections of the Xenu story were adopted as symbols by the Church of Scientology. Hubbard is reported to have ordered that Scientology books be reissued with covers based on images from OT III.[25] The 1968 and subsequent reprints of Dianetics have had covers depicting an exploding volcano, apparently alluding to the volcanoes in the Xenu story — "Man responds to an exploding volcano" (Hubbard, "Assists"). Other cover images may reference Xenu as well: the cover of the 1972 edition of Dianetics: The Evolution of a Science shows pictures of uniformed men in white helmets carrying boxes in and out of a spaceship, which may refer to the transportation of Xenu's victims. Some of the cover images are more obscure but are conjectured to refer to other elements of OT III:
A special 'Book Mission' was sent out to promote these books, now empowered and made irresistible by the addition of these overwhelming symbols or images. Organization staff were assured that if they simply held up one of the books, revealing its cover, that any bookstore owner would immediately order crateloads of them. A customs officer, seeing any of the book covers in one's luggage, would immediately pass one on through.
— Bent Corydon, Messiah or Madman?
Since the 1980s, the volcano has also been depicted in television commercials advertising Dianetics. Scientology's "Sea Org", an elite group within the church that originated with Hubbard's personal staff aboard his fleet of ships, takes many of its symbols from the story of Xenu and OT III. It is explicitly intended to be a revival of the "Loyal Officers" who overthrew Xenu. Its logo, a wreath with 26 leaves, represents the 26 stars of Xenu's Galactic Confederacy.[26] According to the Dianetics and Scientology Technical Dictionary, "the Sea Org symbol, adopted and used as the symbol of a Galactic Confederacy far back in the history of this sector, derives much of its power and authority from that association."
In the Advanced Orgs in Edinburgh and Los Angeles, Scientology staff were at one time ordered to wear all-white uniforms with silver boots, to mimic Xenu's Galactic Patrol as depicted on the cover of Dianetics: The Evolution of a Science. This was reportedly done on the basis of Hubbard's declaration in his Flag Order 652 that mankind would accept regulation from that group which had last betrayed it — hence the imitation of Xenu's henchmen. (This was almost certainly a misinterpretation of what Hubbard meant — he was most likely referring to psychiatrists, whom he believed had played a key role in Xenu's crimes.) In Los Angeles, a nightwatch was ordered to watch for returning spaceships.[27] These measures were discarded after a time.
A more lasting legacy of OT III was Scientology's organizational structure. The current "org board" is "a refined board of an old galactic civilization [the Galactic Confederacy]. We applied Scientology to it and found why it eventually failed. It lacked a couple of departments and that was enough to mess it all up. They lasted 80 trillion[28] [years]."[29]
Xenu or Xemu?
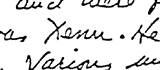
The name has been spelled both as Xenu and Xemu. The Class VIII course material includes a three-page text, handwritten by Hubbard, headed "Data", in which the Xenu story is given in detail. Hubbard's indistinct handwriting makes either spelling possible, particularly as the use of the name on the first page of OT III is the only known example of the name in his handwriting. In the "Assists" lecture, Hubbard speaks of "Xenu, ahhh, could be spelled X-E-M-U" and clearly says "Xemu" several times on the recording. The treatment of Revolt In The Stars, which is typewritten (presumably by Hubbard), uses Xenu exclusively. Ex-Scientologists have reported that Xenu is the more commonly used form (Touretzky). Hubbard may have had two separate names for the "Xenu" figure.
The Church of Scientology's position on Xenu
In its public statements, the Church of Scientology has been notably reluctant to admit the existence of writings on Xenu and even to mention Xenu's name; court filings and legal correspondence issued by the Church of Scientology in the 1990s frequently struck out the name "Xenu" and replaced it with "Xxxx",[30] a treatment given to no other term. In the relatively few instances in which it has acknowledged Xenu, the Church has stated the story is a religious writing that can be seen as the equivalent of the Old Testament—in which miraculous events are described that are unlikely to have occurred in real life, assuming true meaning only after years of study. They complain of critics using it to paint the religion as a science fiction fantasy.[14]
Senior members of the Church of Scientology have several times publicly denied or minimized the importance of the Xenu story, but others have admitted its existence. In a BBC Panorama program that aired on 14 May 2007, senior Scientologist Tommy Davis interrupted when celebrity members are asked about Xenu, saying: "None of us know what you're talking about. It's loony. It's weird." When John Carmichael, the president of the Church of Scientology of New York, was asked about the Xenu story in the 9 September 2007 edition of the Daily Telegraph, he said "That's not what we believe."[31] In "A Conversation with David Miscavige", a story that ran on ABC's Nightline on 14 February 1992, Ted Koppel directly asked Miscavige about the Xenu story, and Miscavige said that this was not a part of current or modern Scientology.[32] However, in a 2006 interview with Rolling Stone, Mike Rinder, the director of the church's Office of Special Affairs, said that "It is not a story, it is an auditing level," when asked about the validity of the Xenu story.[33]
Scientology has many graduated levels through which one can progress. Many who remain at lower levels in the church are unaware of much of the space-opera doctrines, which mostly begin at Operating Thetan level three, or "OT III".[34] Because the information imparted to members is to be kept secret from others who have not attained that level, the member must publicly deny its existence when asked. OT III recipients must sign an agreement promising never to reveal its contents before they are given the manila envelope containing the Xenu knowledge.[33] It is knowledge so dangerous, members are told, that anyone learning this material before he is ready could die. After the Xenu story received considerable mainstream media attention from mid-2005, upper-level Scientologists involved in recent debates with critics have acknowledged the legitimacy of the story.[35] Recent public statements by the Church tend to position the tale as a very small part of the religion.
Xenu and Scientology critics
Despite the Church's efforts to keep the story secret, details have been leaked over the years. OT III was first revealed in Robert Kaufman's 1972 book Inside Scientology: Or How I Found Scientology and Became Super Human, in which Kaufman detailed his own experiences of OT III. It was later described in a 1981 Clearwater Sun article by Richard Leiby, and came to greater public fame in a 1985 court case brought against the Church by Lawrence Wollersheim. The Church attempted to keep the case file checked out by a reader at all times, but the story was summarized in the Los Angeles Times, 5 November 1985 and detailed in William Poundstone's Bigger Secrets (1986) from information presented in the Wollersheim case.
Church lawyer Warren McShane said in a 1995 court case that the story had never been secret,[36] although maintaining there were nevertheless trade secrets contained in OT III. Notably, McShane discussed the details of the story at some length and specifically attributed the authorship of the story to Hubbard.[37]
On 24 December 1994, the text of OT III was published on the Internet for the first time in a posting to the Usenet newsgroup alt.religion.scientology, through an anonymous remailer.[38] This subsequently brought on the actions of Scientology lawyers, leading to the online battle described as Scientology versus the Internet. Older versions of OT levels I to VII were brought as exhibits attached to a declaration by Steven Fishman on 9 April 1993 as part of Church of Scientology International v. Fishman and Geertz. The text of this declaration and its exhibits, collectively known as the Fishman Affidavit, were posted to the Internet newsgroup alt.religion.scientology in August 1995 by Arnie Lerma and on the World Wide Web by David S. Touretzky. This was a subject of great controversy and legal battles for several years, notably a copyright raid on Lerma's house (leading to massive mirroring of the documents) and a suit against Dutch writer Karin Spaink — the Church bringing suit on copyright violation grounds for reproducing the source material, and also claiming rewordings would reveal a trade secret.
The Church's attempts to keep Xenu under wraps have been cited in court findings against it. In September 2003, a Dutch court, in a ruling in the case against Karin Spaink, stated that one objective in keeping OT II and OT III secret was to wield power over members of the Church and prevent discussion about the Church's teachings and practices:[39] "The texts previously quoted show that in its teachings and its structure, Scientology c.s. do not shun the rejection of democratic values. From these texts it is also apparent that one of the objectives of keeping OT II and OT III secret is to wield power over members of the Scientology organization and to prevent discussion about the teachings and practices of the Scientology organization."
Xenu is also widely cited by Scientology critics, who accuse the Church of being a scam. The price of the OT III auditing level alone (US$19,500 in 1997) is given as evidence that Scientology peddles bad science fiction for a high price.[40] Operation Clambake, the most popular critical Web site concerning Scientology, uses the Internet domain name xenu.net. Geoffrey Filbert, a Free Zone (non-CoS) Scientologist, wrote a book, Excalibur Revisited, in 1982, containing his own version of OT III. This was the first of several versions available in the Free Zone. Roland Rashleigh-Berry, an ex-Scientologist, wrote a "Xenu leaflet", popular with critics, that summarizes the story of OT III. The leaflet includes part of the first page of OT III in Hubbard's handwriting, mentioning Xenu.
Xenu in popular culture

L. Ron Hubbard had apparently intended to publicize the Xenu story to the wider world under the title of Revolt in the Stars, an extended version of the story of OT III, which he wrote in the late 1970s. It has not been officially published, although the treatment was circulated around Hollywood in the early 1980s (Young). Copies of the treatment leaked, and Scientology critic Grady Ward published a summary.[41]
Although the Xenu story first leaked in 1972 and was widely publicized on the Internet and in news stories from 1995 onwards, it only achieved currency in popular culture in the middle of 2005, when actor Tom Cruise changed publicists, dismissing Patricia Kingsley in favor of members of his own family, and actively promoted Scientology while he was doing publicity for War of the Worlds; the press responded by citing the Xenu story in numerous articles.
A number of television shows have featured visual depictions of Xenu, either as a cartoon or a computer-generated character. Hubbard did not describe the physical form of Xenu in the OT III documents and provided no illustrations of him; portrayals of Xenu have therefore varied considerably. In 1987, the BBC's investigative news series Panorama aired a report entitled "The Road to Total Freedom?" in which it featured an outline of the OT III story illustrated with an animation showing Xenu, spaceships carrying captured aliens to Earth and the bombing of the volcanoes. Xenu is depicted as a bald, bearded warlord in a militaristic uniform.[42]
South Park

In November 2005, "Trapped in the Closet", an episode of the animated television series South Park, satirized Scientology, including an animated retelling of the Xenu story, with the words "THIS IS WHAT SCIENTOLOGISTS ACTUALLY BELIEVE" superimposed on-screen for most of it. Xenu is depicted as a vaguely humanoid alien with tentacles for arms. In the South Park episode, the aliens are directly dropped into the volcanoes, and the thetans rise in an effort to return but are then captured.
The episode became the subject of a controversy when its rebroadcast by Comedy Central was dropped, with another episode being substituted. The channel stated that the substitution was intended to pay tribute to Isaac Hayes. The creators of South Park, Matt Stone and Trey Parker, disagreed and asserted that Comedy Central's owners Viacom had replaced the episode because the Church of Scientology intervened (or interfered) and, more specifically, because Tom Cruise (who was himself lampooned in the episode) threatened distributor Paramount (also a Viacom property) with refusal to cooperate with the promotional campaign on the upcoming film Mission Impossible 3. Cruise's representative denied this, but Parker and Stone issued a satirical press release that was published in the entertainment newspaper, Daily Variety:[43]
- "So, Scientology, you may have won THIS battle, but the million-year war for Earth has just begun! Temporarily anozinizing our episode will NOT stop us from keeping Thetans forever trapped in your pitiful man-bodies. Curses and drat! You have obstructed us for now, but your feeble bid to save humanity will fail! HAIL XENU!!!"
Comedy Central did eventually rebroadcast the episode on 19 July 2006.
Nip/Tuck
Xenu appeared in "Willy Ward", the penultimate episode of season 4 of the FX show Nip/Tuck (first broadcast 5 December 2006). In a dream sequence, Scientologist character Kimber Henry (Kelly Carlson) has a vision of Xenu while experiencing hallucinations and doubts about Scientology. Xenu is depicted as a cross between Ming the Merciless and a stereotypical grey alien.[44][45]
See also
Notes
Note: HCOB refers to "Hubbard Communications Office Bulletins", HCOPL refers to "Hubbard Communications Office Policy Letters", and SHSBC refers to "Saint Hill Special Briefing Courses". All have been made publicly available by the Church of Scientology in the past, both as individual documents or in bound volumes.
- ^ a b c Thousands of millions in Long Scale
- ^ a b Scott, Michael Dennis (2004) "Internet And Technology Law Desk Reference", Aspen Publishers, ISBN 0735547432
- ^ a b Lewis James R (2003) "The Oxford Handbook of New Religious Movements", Oxford University Press, ISBN 0195149866
- ^ OT III materials as described by Margery Wakefield
- ^ "Summary proceedings". Ruling Scientology vs. providers and Karin Spaink. 12 March 1996. Retrieved 2006-08-09.
- ^ Sappell, Joel (24 June 1990). "The Scientology Story". Los Angeles Times: page A36:1. Retrieved 2006-08-09.
{{cite journal}}:|pages=has extra text (help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) Additional convenience link. - ^ "ABC Interview Transcript". Scientology Leader Gave ABC First-Ever Interview. 18 November 2006. Retrieved 2008-08-02.
- ^ A billion in Short Scale is a thousand million in Long Scale.
- ^ Hubbard, Scientology: A History of Man
- ^ "Operation Clambake presents: A Scientific scrutiny of OT 3". 7 June 1996. Retrieved 2007-04-26.
- ^ "The Forbidden Story of Xenu". Retrieved 2007-04-26.
- ^ Hubbard, Mission into Time
- ^ Four thousand billion in Long Scale.
- ^ a b Doward, Jamie (16 May 2004). "Lure of the celebrity sect". The Observer. Retrieved 2006-10-05.
- ^ "Gerry Armstrong--HCOB 05-11-1963 Routine 3 Heaven". Retrieved 2006-10-05.
- ^ Veenker, Jody (9/8/00). "Why Christians Object to Scientology". Christianity Today. Retrieved 2006-10-05.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Branch, Craig (1996). "Hubbard's Religion". The Watchman Expositor. 13 (2). Retrieved 2006-10-05.
- ^ "Scientology and Christianity Examined". Retrieved 2006-10-05.
- ^ "Scientology and Other Practices". Church of Scientology of Michigan. Retrieved 2006-10-05.
- ^ Miller, ch. 16, p. 266, "Launching the Sea Org"
- ^ Corydon, pp58–59, 332–333; letter filed as evidence in Church of Scientology v. Gerald Armstrong, 1984, Los Angeles Superior Court, Case No. C420153
- ^ Atack, part 4, ch. 1, "Scientology at Sea"
- ^ "Complete List of LRH Lectures: Tapes of 1952". Retrieved 2006-10-05.
- ^ Savino, John (2007). Supervolcano: The Catastrophic Event That Changed the Course of Human History. Career Press. pp. Page 54. ISBN 1564149536.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Atack, Jon. "References". Hubbard and the Occult. Retrieved 2006-10-05.
- ^ Hubbard, "Ron's Talk to Pubs Org World Wide", tape of April 1968
- ^ Atack, p. 190
- ^ Billion in Long Scale
- ^ Hubbard, SHSBC 57, "Org Board and Livingness", 6 April 1965
- ^ "Unsorted harassment reports". Retrieved 2006-10-05.
- ^ "Friends, thetans, countrymen". Seven. The Daily Telegraph. 2007-09-09. p. 2. Retrieved 2007-09-22.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ "ABC News, Nightline: A Conversation with David Miscavige"". 14 February 1992. Retrieved 2007-07-30.
- ^ a b Reitman, Janet (2006-02-23). "Inside Scientology". Rolling Stone. Retrieved 2007-09-22.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Operation Clambake Presents: OT Levels". Retrieved 2006-10-05.
- ^ "The Humanist Society of San Diego Meeting". 2005-02-20. Retrieved 2006-10-05.
- ^ O'Connor, Mike (28 August 1998). "Re: Ron's Journal 67" (TXT). alt.religion.scientology. lepton-2808981630510001@lepton.dialup.access.net. Retrieved 2006-10-05. (testimony under oath by Warren McShane of the Church of Scientology in RTC v. FactNet, Civil Action No. 95B2143, United States Courthouse, Denver, Colorado, September 11, 1995)
- ^ "Trade Secrets?". Retrieved 2006-10-05.
- ^ "Affidavit of Dennis Erlich" (TXT). 16 November 1995. Retrieved 2007-04-26.
- ^ "Uit de hiervoor onder 8.3 vermelde teksten blijkt dat Scientology c.s. met hun leer en organisatie de verwerping van democratische waarden niet schuwen. Uit die teksten volgt tevens dat met de geheimhouding van OT II en OT III mede wordt beoogd macht uit te oefenen over leden van de Scientology-organisatie en discussie over de leer en praktijken van de Scientology-organisatie te verhinderen."Translation by Spaink[citation needed]
- ^ Heldal-Lund, Andreas (30 November 1997). "FWD: Re: Another part of the "Bait and Switch"" (TXT). alt.religion.scientology. 3481749c.387609633@news.sol.no. Retrieved 2006-10-05.
- ^ "Revolt In The Stars by L. Ron Hubbard, Summarized by Grady Ward". Retrieved 2006-10-05.
- ^ Panorama, "The Road to Total Freedom", 1987
- ^ "South Park' Cooks Up Plan For Chef In Season Premiere". MTV News. 2006-03-21. Retrieved 2006-10-05.
- ^ "Looking for a change, 'Nip/Tuck' heads west", Arizona Republic, 16 December 2006
..Christian and Dawn Budge's (O'Donnell) sexual tryst, sexy Kimber's faceoff with the Scientology figure Xenu.. - ^ "TELEVISION; `Nip/Tuck' warms up to Scientology; The FX drama", Los Angeles Times, 1 October 2006
...that most human problems can be traced to lingering spirits of an extraterrestrial people massacred By their ruler, Xenu, over 75 million years ago..
References
- Sources
- Jon Atack, A Piece Of Blue Sky (Kensington Publishing Corporation, New York, 1990; ISBN 0-8184-0499-X)
- Bent Corydon and L. Ron Hubbard Jr., L. Ron Hubbard: Messiah Or Madman? (Lyle Stuart, New Jersey, 1987; ISBN 0-8184-0444-2)
- L. Ron Hubbard, Scientology: A History of Man (American Saint Hill Organization, 1968; current edition Bridge Publications ISBN 0-88404-306-1)
- L. Ron Hubbard, Mission into Time (American Saint Hill Organization, 1973; current edition Bridge Publications ISBN 0-88404-023-2)
- L. Ron Hubbard, Have You Lived Before This Life? (1958; current edition Bridge Publications ISBN 0-88404-447-5)
- Russell Miller, Bare-Faced Messiah: The True Story Of L. Ron Hubbard (Henry Holt, New York, 1988; ISBN 1-55013-027-7)
- FACTnet report: Hubbard and the Occult (Jon Atack)
- Robert Kaufman, Inside Scientology: Or How I Found Scientology and Became Super Human, (Olympia Press ISBN 0-7004-0110-5, 1972; (1995 edition published on Web)
- Sect courses resemble science fiction (Richard Leiby, Clearwater Sun, vol. 68 no. 118, 30 August 1981)
- Scientologists Block Access To Secret Documents: 1,500 crowd into courthouse to protect materials on fundamental beliefs (Joel Sappell and Robert Welkos, Los Angeles Times, 5 November 1985)
- Testimony under oath (pp274–275) from Robert Vaughn Young in RTC v. FactNet, Civil Action No. 95B2143, United States Courthouse, Denver, Colorado, September 11, 1995
- Audio extracts from Class VIII "Assists" lecture (3 October 1968)
- Excalibur Revisited: The Akashic Book of Truth (Geoffrey Filbert)
- Other references
- Dawson, Lorne L. (2004-04-01). Religion Online. Routledge (UK). pp. 261 et. seq. ISBN 0-415-97022-9.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameters:|accessyear=and|origdate=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Template:Harvard reference
External links
- What is Scientology: OT III Released
- Xenu TV
- Scientology.org: OT Level Successes
- OT III Scholarship Page (David S. Touretzky; includes page scans, commentary, audio files)
- Revolt In The Stars summary (Grady Ward)
- Xenu Leaflet (Roland Rashleigh-Berry)
- The Fishman Affidavit: OT III (extracts and synopsis by Karin Spaink)
- A Scientific scrutiny of OT III (Peter Forde, June 1996)
- The Story of OTIII: A RealPlayer animation that takes a humorous yet accurate look at the Xenu doctrine. From the BBC Panorama documentary "The Road to Total Freedom?"
- Operation Clambake - The Inner Secrets Of Scientology
- Research essay describing OT 3 as a drug induced hallucination posted to alt.religion.scientology on 3/29/96 by Prignillius
- The History Of Xenu, As Explained By L. Ron Hubbard In 8 Minutes
