1,3-dioxolane
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | 1,3-dioxolane | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 3 H 6 O 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
highly volatile, colorless liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 74.08 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.06 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−26.4 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
74 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
114 mbar (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
miscible with water |
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.401 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
Switzerland: 20 ml m −3 or 62 mg m −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| Thermodynamic properties | ||||||||||||||||
| ΔH f 0 |
−333.5 kJ / mol |
|||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
1,3-Dioxolane is a chemical compound from the group of oxygen heterocycles and is isomeric to 1,2-Dioxolane . The compound can also be viewed as a cyclic acetal .
Extraction and presentation
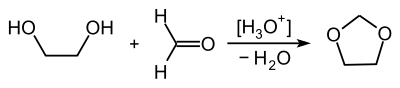
1,3-Dioxolane can be obtained by reacting ethylene glycol with formaldehyde :
properties
1,3-Dioxolane is a volatile, colorless liquid that can be mixed with water. The flash point (cc) is −5 ° C, the ignition temperature +245 ° C.
use
1,3-Dioxolane is used as a comonomer for the production of modified polyoxymethylenes . It serves as a substitute for dichloromethane in paint strippers .
Safety instructions / toxicology
In 2016, 1,3-dioxolane was included by the EU in the Community's ongoing action plan ( CoRAP ) in accordance with Regulation (EC) No. 1907/2006 (REACH) as part of substance evaluation . The effects of the substance on human health and the environment are re-evaluated and, if necessary, follow-up measures are initiated. The reasons for the uptake of 1,3-dioxolane were concerns about consumer use , exposure of sensitive population groups , high (aggregated) tonnage and widespread use, as well as the possible dangers of mutagenic and reproductive properties. The re-evaluation has been running since 2016 and is carried out by Germany .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j Entry for CAS no. 646-06-0 in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on May 2, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b entry on 1,3-dioxolane. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on November 12, 2014.
- ↑ Data sheet 1,3-Dioxolane, anhydrous, contains ~ 75 ppm BHT as inhibitor, 99.8% from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on February 14, 2013 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Entry on 1,3-dioxolane in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on August 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Schweizerische Unfallversicherungsanstalt (Suva): Limit values - current MAK and BAT values (search for 646-06-0 or 1,3-dioxolane ), accessed on November 2, 2015.
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Standard Thermodynamic Properties of Chemical Substances, pp. 5-24.
- ↑ by Karl-Heinz Lautenschläger, Werner Schröter, Andrea Wanninger: Pocket book of chemistry - Karl-Heinz Lautenschläger, Werner Schröter, Andrea Wanninger . Harri Deutsch Verlag, 2005, ISBN 978-3-8171-1760-4 , pp. 451 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Community rolling action plan ( CoRAP ) of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA): 1,3-dioxolane , accessed on March 26, 2019.