4-octine
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
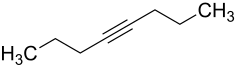
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | 4-octine | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 8 H 14 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 110.20 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
0.7509 g cm −3 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−103 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
131.6 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
47 hPa (38 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
almost insoluble in water |
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.4248 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
4-Octyne is a chemical compound from the alkynes group . It has the basic structure of octane with a C≡C triple bond at the 4-position.
4-octyne ( dipropylethyne ) belongs to the symmetrical alkynes with 5-decyne ( dibutylethyne ), 3-hexyne ( diethylethyne ) and 2-butyne ( dimethylethyne ).
presentation
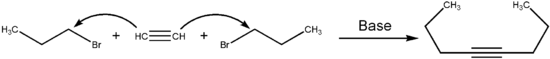
One way of synthesizing 4-octyne is to react acetylene with two parts of 1-bromopropane . Acetylene is deprotonated with a base . The resulting anion is then substituted on 1-bromopropane. The second carbon atom of the resulting alkyne is then deprotonated and the same reaction takes place on the second side. The reaction can be carried out in liquid ammonia at −70 ° C with sodium amide as the base.
Another synthetic route consists in the elimination of 4,5-dibromooctane. Sodium amide can again serve as the base for this purpose. The reaction is carried out at −70 ° C in liquid ammonia.
properties
4-Octyne is a colorless compound that is liquid at room temperature and boils at 131.6 ° C.
use
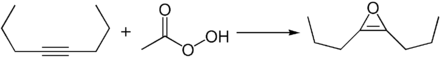
A number of typical reactions of alkynes can be carried out at the triple bond of 4-octyne. For example, 2,3-di- n- propyl oxiren can be produced by reaction with peroxycarboxylic acids , for example peracetic acid .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e 4-Octin data sheet (PDF) from Merck , accessed April 2, 2017.
- ↑ a b c d e David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-406.
- ↑ E. Otsa, LS Kudrjawzewa, OG Eisen, EM Piotrowskaja: Thermodynamic investigations on n-alkane / n-alkyne systems , in: MONTHS. Chem. , 1980 , 111 , pp. 607-617; doi: 10.1007 / BF00903314 .
- ↑ H. Seifert: Olefinsynthesen in the C 6 - to C 11 series , in: MONTHS. Chem. , 1948 , 79 , pp. 198-215; doi : 10.1007 / BF00899394 .
- ↑ HN Miller, KW Greenlee, JM Derfer, CE Boord: Mono- and Di-Alkylacetylenes from vicinal Dihalides and Sodium Amide in liquid Ammonia , in: J. Org. Chem. , 1954 , 19 , pp. 1882-1888; doi : 10.1021 / jo01377a003 .
- ↑ MS Sheela, K. Sreekumar: Epoxidation and Oxidation Reactions Using Divinyl Benzene Crosslinked Polystyrene Supported t-Butyl Hydroperoxide , in: Indian J. Chem. Sect. B , 2006 , 45 , pp. 943-950; doi : 10.1002 / chin.200633058 .
- ↑ V. Franzen: The constitution of the compound C 10 H 18 O obtained from dibutylacetylene and peracetic acid , in: Chem. Ber. , 1954 , 87 , pp. 1478-1488; doi : 10.1002 / cber.19540871015 .
Web links
- Entry for 4-Octin . In: P. J. Linstrom, W. G. Mallard (Eds.): NIST Chemistry WebBook, NIST Standard Reference Database Number 69 . National Institute of Standards and Technology , Gaithersburg MD .
- www.chemicalbook.com: 1 H NMR