ASF virus
| ASF virus | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
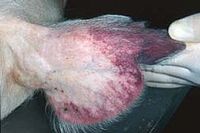
Ear of a pig infected by the ASF virus |
||||||||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Taxonomic characteristics | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||||||||
| African swine fever virus | ||||||||||||||||||
| Short name | ||||||||||||||||||
| ASFV | ||||||||||||||||||
| Left | ||||||||||||||||||
|
The ASF virus (derived from English A frican S wine F ever , also African swine fever virus ) is the causative agent of African swine fever .
The virus was previously assigned to the Iridoviridae family . In 1984 it was separated from this family in the international nomenclature and assigned as the only virus to the family of Asfarviridae (derived from African Swine Fever And Related Viruses).
Pathogen properties
The ASF virus is an enveloped, double-stranded DNA virus of which no other serological types or subtypes are known. It is a very heat- and pH- stable pathogen. The virus can survive even strongly acidic solutions (up to pH 4) or strongly basic compounds (up to pH 13). In meat products (. As salami or ham z) the pathogen remains up to four months, up to seven months in the bone marrow or carcasses infectious . Temperatures above 75 ° C and gamma radiation can inactivate the virus , but solar radiation and putrefaction processes have only a minor influence.
The virus multiplies in the cytoplasm of the host cells. It has a highly lipid- containing, outer virus envelope and is therefore susceptible to fat solvents. A particular virulence factor is that the virus causes antibodies to be formed in the body, but no antibodies that neutralize the virus are formed. Therefore, the production of a vaccine is not yet possible today.
Occurrence
The ASF virus occurs mainly in Africa ( Angola , Mozambique ). In addition, Sardinia in particular is considered to be enzootic . Occasional, worldwide disease outbreaks (Caribbean, South America, Mediterranean islands, Europe) have so far been eradicated.
The host range is domestic pigs , European wild boars , warthogs ( Phacochoerus aethiopicus ), bush pigs ( Potamochoerus porcus ) and leather ticks ( Ornithodorus spp. ). China has been affected since August 2018, Belgium since September 2018. At the end of January 2019, the focus of the occurrence of swine fever is in eastern central Europe and parts of south-eastern Europe. On January 22, 2020, the Federal Ministry of Food and Agriculture reported that an infected wild boar was found 12 km from the German border in the Polish part of the Lusatian Forest.
transmission
Within the wild pig populations, the virus is mainly transmitted through the act of sucking when a tick bites. The ASF virus multiplies in the ticks and persists within the tick for up to three years. In the domestic pig population, naso-oral transmission from pig to pig and ingestion via infected feed play a role.
meaning
The ASF virus, which causes African swine fever, is one of the most dangerous pathogens in pigs. Its occurrence leads to a rapidly spreading epidemic with great economic losses. The disease is therefore subject to special control measures in many countries. Within the EU there are uniform regulations for eradicating the disease, which are then implemented by the individual member states accordingly.
In order to contain this disease, the affected animals are culled .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e ICTV: ICTV Taxonomy history: African swine fever virus , EC 51, Berlin, Germany, July 2019; Email ratification March 2020 (MSL # 35)
- ↑ tierseucheninfo.niedersachsen.de African swine fever
- ↑ agro today: ASP: Only 12 km to Germany. In: agrarheute.com. January 22, 2020, accessed January 22, 2020 .
- ↑ African swine fever (ASP): BMEL asks for vigilance and prevention. In: bmel.de. September 13, 2018, accessed January 22, 2020 .