Abies beshanzuensis
| Abies beshanzuensis | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Abies beshanzuensis | ||||||||||||
| Wu. |
Abies beshanzuensis is a species ofthe pine family (Pinaceae). This endemic endemic speciesin Chinais only known from a single group of five trees.
description
Abies beshanzuensis grows as a straight-trunk tree and can reach heights of up to 30 meters and diameters of up to 80 centimeters at chest height . The branches go off horizontally from the trunk. The resinous buds are oval to conical in shape and yellow-brown in color. The needles are 1 to 4.2 centimeters long, 2.5 to 3.5 millimeters wide and have a notched needle point. They are arranged like a comb on the branches and are twisted at the needle base. The top of the needle is glossy dark green while the underside of the needle is paler. On the underside of the needle there are two white stomatal bands .
Young trees have smooth, light gray bark which later becomes scaly and tears open lengthways. The bark of the branches is light yellowish to brownish yellow. On some branches it turns gray-black after three or four years. After the needles fall off, round to oval scars remain.
The male cones are yellowish and stand on the branches of the branches. They grow to be between 2 and 2.5 centimeters. The female cones are fertilized in May. The upright cones are 7 to 11 inches long and 3.5 to 4.5 inches thick. They are cylindrically shaped and colored brown-yellow to light brown when ripe in October to November. The seed scales are 1.8 to 2.4 inches long and 2.5 to 3 inches wide. The egg-shaped and winged seeds are 6 to 9 millimeters long and 3 to 4 millimeters thick. With the wing they become 13 to 19 millimeters long.
Distribution and location
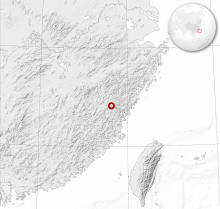
Abies beshanzuensis occurs only in the southwest of Zhejiang in the Baishanzu Shan . When the species was discovered in 1963, only seven specimens grew in its natural habitat. Three were taken to the Beijing Botanical Gardens , where they died after a short time. In 1988 the inventory only comprised three copies. In 1998 the natural population had grown back to five trees. The location of the last specimens is a single group of trees northeast of Qingyuan .
The species is a tree species of the maritime climate with warm summers and cold-wet winters. It occurs at altitudes of 1,500 to 1,700 meters. The annual precipitation is around 1,250 mm.
In the group of trees there are some broad-leaved deciduous trees such as maples ( Acer ), pseudo-chestnuts ( Castanopsis ), glossy beech ( Fagus lucida ), Lithocarpus hancei , Magnolia cylindrica and oaks ( Quercus ). In addition to the deciduous trees, there are also conifers such as the Chinese head yew ( Cephalotaxus sinensis ), the Chinese sickle fir ( Cryptomeria japonica var. Sinensis ), the Chinese yew ( Taxus sumatrana ) and the Taiwan hemlock ( Tsuga chinensis ).
Systematics
Abies Beshanzuensis is within the genus of the fir ( Abies ) of the section Momi and the lower section company e assigned. The species is equated by some authors with Delavay's fir ( Abies delavayi ). The closest related species seems to be the momi fir ( Abies firma ). Some authors consider Abies ziyuanensis to be a variety of Abies beshanzuensis .
Hazard and protection
Since there are only five trees left in its natural habitat, Abies beshanzuensis is listed as "critically endangered" on the IUCN Red List . The main risk factors are the spread of agriculture and forest fires in connection with the low reproduction rate.
Web links
- Liguo Fu, Nan Li, Thomas S. Elias, Robert R. Mill: Abies beshanzuensis . In: Wu Zheng-yi, Peter H. Raven (Ed.): Flora of China . Volume 4: Cycadaceae through Fagaceae . Science Press / Missouri Botanical Garden Press, Beijing / St. Louis 1999, ISBN 0-915279-70-3 , pp. 50 (English).
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g Christopher J. Earle: Abies beshanzuensis. In: The Gymnosperm Database. February 23, 2011, accessed October 31, 2011 .
- ↑ a b Abies beshanzuensis in the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2014.3. Posted by: Yang, Y., Zhang, D, Luscombe, D, Liao, W., Farjon, A., Katsuki, T., Xiang, Q. & Li, N., 2010. Retrieved January 14, 2015.
- ^ Liguo Fu, Nan Li, Thomas S. Elias, Robert R. Mill: Abies beshanzuensis var. Ziyuanensis . In: Wu Zheng-yi, Peter H. Raven (Ed.): Flora of China . Volume 4: Cycadaceae through Fagaceae . Science Press / Missouri Botanical Garden Press, Beijing / St. Louis 1999, ISBN 0-915279-70-3 , pp. 50 (English).