Acetoacetic ester
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Acetoacetic ester | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 6 H 10 O 3 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless liquid with a fruity odor |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 130.14 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.03 g cm −3 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−44 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
180 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
|
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
easily in water (116 g l −1 at 20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.4171 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
not yet classified |
|||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
Acetoacetic ester is a chemical compound from the group of carboxylic acid esters , more precisely the ethyl ester of 3-oxobutanoic acid (acetoacetic acid).
Extraction and presentation
Technical processes produce acetoacetic esters from ethanol and diketene . The synthesis is exothermic with a heat of reaction of −127 kJ mol −1 .
Another way is the Claisen condensation of the ethyl acetate . He was first portrayed by Johannes Wislicenus .
properties
Acetoacetic ester is a colorless, slightly oily liquid that boils at 180 ° C under normal pressure . The vapor pressure function results according to Antoine according to log 10 (P) = A− (B / (T + C)) (P in bar, T in K) with A = 5.16327, B = 2189.547 and C = −29.184 in the temperature range from 302 to 454 K. The heat of vaporization is 52.2 kJ · mol −1 . Acetoacetic ester shows pronounced keto-enol tautomerism ( 46% of the acetoacetic ester is present in n- hexane, 12% in ethanol and 0.4% in water as enol).
It is a C-H-acidic compound, pK s = 11, since the enolate anion strongly stabilized by resonance is.
The activated methylene group between the two carbonyl functions is very reactive and can be alkylated, acylated and halogenated. Acetoacetic ester derivatives functionalized in this way can be split into carboxylic acids with concentrated alkali and a ketone is formed with acids .
Acetoacetic ester forms flammable vapor-air mixtures at higher temperatures. The compound has a flash point of 65 ° C. The lower explosion limit (LEL) is 1.0% by volume (54 g / m 3 ). The ignition temperature is 350 ° C. The substance therefore falls into temperature class T2.
use
Acetoacetic ester is the starting material for organic syntheses such as the Hantzsch dihydropyridine synthesis and the Japp-Klingemann reaction due to its functional groups . It is also used as a solvent.
It was first synthesized by Johannes Wislicenus and used by him for organic syntheses.
Analytics
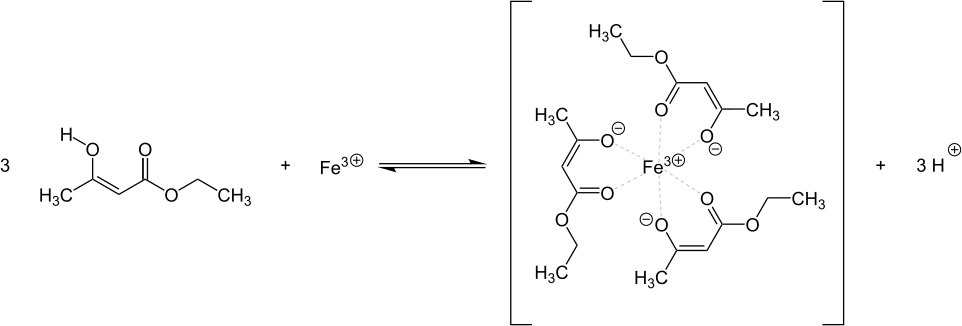
Iron (III) chloride solution turns an aqueous acetoacetic ester solution purple through complex formation:
The reaction is not very specific because other enolizable β-ketocarboxylic acids (such as salicylic acid ) and their esters show the same reaction.
Acetoacetic ester is used in building material analysis to determine free calcium oxide (CaO) in fly ash or cement (determination according to Franke).
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on ETHYL ACETOACETATE in the CosIng database of the EU Commission, accessed on February 16, 2020.
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p Entry on ethylacetoacetate in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on September 8, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-236.
- ↑ a b Entry on ethyl acetoacetate. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on July 19, 2019.
- ↑ Lopatin, EB; Popov, VV; Epshtein, NA; Mikhaleva, LM; Makarov, Yu.N .: Kinetic and thermochemical characteristics of diketene-based reactions in Khim.-Farm. Zh. 26, 76-78 (1992).
- ↑ Stull, DR: Vapor Pressure of Pure Substances - Organic Compounds in Ind. Eng. Chem. 39 (1947) 517-540, doi: 10.1021 / ie50448a022 .
- ↑ Stephenson, RM; Malanowski, S .: Handbook of the Thermodynamics of Organic Compounds 1987, doi: 10.1007 / 978-94-009-3173-2 .
- ↑ Jürgen Sauer: The Experiment: Keto-Enol-Tautomerism. In: Chemistry in Our Time. 3, 1969, pp. 25-26, doi: 10.1002 / ciuz.19690030106 .
- ^ A b c E. Brandes, W. Möller: Safety-related parameters - Volume 1: Flammable liquids and gases , Wirtschaftsverlag NW - Verlag für neue Wissenschaft GmbH, Bremerhaven 2003.
- ↑ Franke, L., Bentrup, H .: Influence of cracks on the resistance to driving rain of hydrophobized masonry and testing of the hydrophobability in building protection + building renovation 1991, 14, 98–101 and 117–121.
literature
- Hans Beyer, Wolfgang Walter: Textbook of Organic Chemistry , 23rd edition; S. Hirzel Verlag, Stuttgart - Leipzig 1998; ISBN 3-7776-0808-4 .