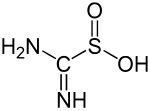
Aminoiminomethanesulfinic acid
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Aminoiminomethanesulfinic acid | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | CH 4 N 2 O 2 S | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
yellow odorless solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 108.12 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.68 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
100 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
123 ° C (decomposition) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Aminoiminomethanesulfinic acid is a chemical compound from the group of amidines and sulfinic acids .
Extraction and presentation
Aminoiminomethanesulfinic acid can be prepared by oxidation of thiourea with hydrogen peroxide are produced.
The first synthesis was carried out in 1910 by Edward de Barry Barnett.
structure
The exact structure of the compound has long been unclear. The two tautomeric structures thiourea dioxide and aminoiminomethanesulfinic acid can be formulated.
It was assumed that the stable thiourea dioxide is converted into the unstable aminoiminomethanesulfinic acid when heated, which decomposes under these conditions to urea and sulfoxylic acid as a reducing agent .
An X-ray structure analysis in 1962 led to the result that the compound is present in the solid as a zwitterion .
This result was also confirmed in 2014 for aqueous solutions of the compound using FTIR spectroscopy . Thiourea dioxide is therefore not applicable as a name for aminoiminomethanesulfinic acid.
properties
Aminoiminomethanesulfinic acid is a white to yellow odorless solid. The compound is particularly stable in acidic medium, while it is alkaline unstable. With it, let ketones to alcohols , quinones to hydroquinones , aromatic nitro compounds to amines , nitroso compounds to hydrazo compounds and azoxy - and azo compounds to amines and hydrazo compounds reduce. The reducing effect does not come from the compound itself, but from the sulfinate ion formed during hydrolysis .
Aminoiminomethanesulfinic acid has an orthorhombic crystal structure with the space group Pnmb (space group no. 53, position 2) .
use
Aminoiminomethanesulfinic acid is used as a redox activator in the manufacture of chlorinated rubber , as a reducing agent for vat dyes , as an accelerator for amino resins and in the production of polyacrylonitrile fibers. It is used to bleach paper, wool and silk due to its reducing ability.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Entry on aminoiminomethanesulfinic acid in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 8, 2018(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c Entry on formamidinesulfinic acid. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on July 1, 2015.
- ↑ D. Schubart: Sulfinic Acids and Derivatives. In: Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. , Wiley-VCH, Weinheim 2012. doi : 10.1002 / 14356007.a25_461 .
- ↑ James Frederick Shuan-Liang Apps: Synthesis and application of thiourea-S, S-dioxide derivatives. University of Warwick institutional repository, accessed July 1, 2015.
- ↑ Edward de Barry Barnett: VII. — The action of hydrogen dioxide on thiocarbamides . In: J. Chem. Soc., Trans. Volume 97 , 1910, pp. 63 , doi : 10.1039 / ct9109700063 .
- ↑ P. Krug: Thiourea Dioxide (Formamidinesulphinic Acid) A New Reducing Agent for Textile Printing . In: Journal of the Society of Dyers and Colourists . tape 69 , no. 13 December 1953, p. 606 , doi : 10.1111 / j.1478-4408.1953.tb02803.x .
- ^ A b R. AL Sullivan, A. Hargreaves: The crystal and molecular structure of thiourea dioxide. In: Acta Crystallographica. 15, 1962, p. 675, doi: 10.1107 / S0365110X62001851 .
- ↑ David Lewis, John Mama, Jamie Hawkes: An Investigation into the Structure and Chemical Properties of Formamidine Sulfinic Acid. In: Applied Spectroscopy. 68, 2014, p. 1327, doi : 10.1366 / 13-07306 .
- ^ Hermann Rath: Textbook of textile chemistry including textile-chemical technology . Springer-Verlag, 2013, ISBN 978-3-662-00064-9 , pp. 693 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Jürgen Bracht, P. Hartter, Christine Kropf, Peter Müller, Heidi Müller-Dolezal, Renate Stoltz, Hanna Söll: Houben-Weyl Methods of Organic Chemistry Vol. IV / 1d, 4th Edition Reduction II . Georg Thieme Verlag, 2014, ISBN 3-13-179714-2 , p. 567 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ C. Carr: Chemistry of the Textiles Industry . Springer Science & Business Media, 2012, ISBN 978-94-011-0595-8 , pp. 60 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ Henan Hongye Chemische Werke GmbH: Thiourea dioxide. accessed on July 1, 2015.
- ↑ Jürgen Blechschmidt: Pocket book of paper technology . Carl Hanser Verlag, 2013, ISBN 978-3-446-43701-2 , pp. 103 ( limited preview in Google Book search).







