Arsenic acid
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
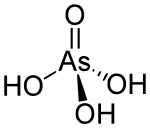
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Arsenic acid | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
Arsenic (V) acid |
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | H 3 AsO 4 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
transparent to white, odorless solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 141.94 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
2.50 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
35 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
120 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
55 h Pa (50 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
|
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
easily soluble in water |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Authorization procedure under REACH |
of particular concern : carcinogenic ( CMR ); subject to approval |
|||||||||||||||
| MAK |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Arsenic acid (arsenic (V) acid called) is of Diarsenic pentaoxide derived acid with the molecular formula H 3 AsO 4 . It is a three-proton, medium-strength acid and about as strong as phosphoric acid . The salts of arsenic acid are called arsenates .
Extraction and presentation
Arsenic acid is formed by dissolving arsenic pentoxide in water :
The equilibrium of this chemical reaction can be shifted to the left. By removing water, for example with phosphorus pentoxide , arsenic acid is converted back to arsenic pentoxide.
Another reaction for the preparation of arsenic acid is the oxidation of arsenic or arsenic (III) oxide with the help of concentrated nitric acid . The hemihydrate is formed:
The dihydrate (H 3 AsO 4 · 2H 2 O) is only accessible via crystallization for several days at −30 ° C.
properties
Solid arsenic acid removes water very quickly from the air and forms hydrates : H 3 AsO 4 · ½H 2 O or H 3 AsO 4 · 2H 2 O at −30 ° C. When heated to 100 ° C, As 2 O 5 · 1.66H 2 O is formed, above 300 ° C all water is released.
A saturated aqueous solution is approximately 80%.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j Entry for CAS no. 7778-39-4 in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 8, 2013(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Dissociation Constants of Inorganic Acids and Bases, pp. 8-40.
- ↑ Not explicitly listed in Regulation (EC) No. 1272/2008 (CLP) , but with the specified labeling it falls under the group entry arsenic acid and its salts, unless specifically listed in this appendix in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) , accessed on January 9, 2017. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Entry in the SVHC list of the European Chemicals Agency , accessed on July 17, 2014.
- ↑ Entry in the register of substances subject to authorization of the European Chemicals Agency , accessed on July 17, 2014.
- ↑ Swiss Accident Insurance Fund (Suva): Limit values - current MAK and BAT values (search for 7778-39-4 or arsenic acid ), accessed on October 24, 2016.
- ↑ G. Brauer (Ed.), Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry 2nd ed., Vol. 1, Academic Press 1963, p. 601.






