BNSF Railway
| Burlington Northern Santa Fe, LLC
|
|
|---|---|
| legal form | LLC |
| founding | September 22, 1995 |
| Seat | Fort Worth , United States |
| management | Matthew K. Rose, President and CEO |
| Number of employees | 41,000 |
| sales | $ 21.4 billion |
| Branch | Railway company |
| Website | www.bnsf.com |
| As of December 31, 2017 | |

The BNSF Railway Company is a US Class 1 - railway company , based in Fort Worth , Texas . It is the second largest rail company in the country. The parent company of the BNSF Railway, Burlington Northern Santa Fe Corporation , has been wholly owned by Berkshire Hathaway since 2010 and was renamed Burlington Northern Santa Fe LLC .
history
The railway company was created by contract dated September 22, 1995 to January 1, 1996 from the merger of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway and the Burlington Northern Railroad . The company operates on one of the largest route networks in the USA with a route length of approx. 51,500 km, of which 37,000 km are owned and the remainder are track usage rights. In total, the BNSF maintains around 80,500 km of track with side tracks, second or third track and station facilities. With 8,000 locomotives and 77,000 freight wagons , 10.2 million wagonloads were transported in 2015 and a turnover of over 21 billion dollars. Operating profit was $ 4.9 billion.
In 1999, the BNSF and the Canadian National Railway began merger talks to form the North American Railway . Due to objections from other railway companies and the problems with the merger of Union Pacific Railroad with Southern Pacific Railroad and the division of the Conrail , the Surface Transportation Board imposed a 15-month moratorium . As a result, the merger talks were discontinued without result.
On January 24, 2005, the name of the railway company was changed from The Burlington Northern and Santa Fe Railway to its current name. In April 2007, the holding company Berkshire Hathaway paid $ 3.2 billion (€ 2.4 billion) for a stake in Burlington of more than 10 percent. On February 12, 2010, the complete takeover of the company by Berkshire Hathaway was completed.
In 2009, in cooperation with the United States Department of Defense , the company presented the world's first Hydrail pusher locomotive that is powered by hydrogen - via fuel cells .
Route network
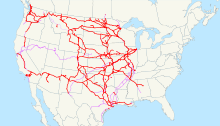
The company has routes in 28 US states and two Canadian provinces. The route network extends from Seattle in the northwest to Chicago . The most south-easterly point is Birmingham, Alabama . To the west, San Diego and Los Angeles are reached. There are also connections to San Francisco , Houston , Denver , Dallas and Kansas City . The Powder River Basin is also served by BNSF tracks.
Container terminals exist in Los Angeles (Hobart Yard) , in the Chicago metropolitan area ( Corwith Yard , Logistics Park Chicago, Cicero Yard) and in the Kansas City metropolitan area ( LPKC Intermodal Facility ) as well as in Willow Springs ( Illinois ), Fort Worth ( Texas ) and San Bernardino, California .
Marshalling yards are located in the metropolitan area of Kansas City ( Argentine Yard and Murray Yard) , Minneapolis ( Northtown Yard ) , Galesburg ( Galesburg Yard ) , Barstow ( Barstow Yard ) , Pasco ( Washington ), and Memphis (Tennessee) .
The most important passes over the continental divide used by the BNSF are the Marias Pass (1588 m), the Mullan Pass (1691 m) and the Campbell Pass (2208 m).
Corporate governance
Chief Executive Officer and President
- December 22, 1995 - December 2000: Robert D. Krebs (President until June 1999)
- June 1999 - December 31, 2013: Matthew K. Rose (President until October 31, 2010)
- since November 1, 2010: Carl R. Ice (also CEO since January 1, 2014)
Chairman
- December 22, 1995 - December 31, 1996: Daniel P. Davison
- January 1, 1997 - June 1999: Robert D. Krebs
- since December 2000: Matthew K. Rose
Company headquarters
The headquarters of the company and the parent company Burlington Northern Santa Fe LLC is in north Fort Worth . On the 155 hectare site there are several office buildings for all departments (marketing) of the company as well as the 1.85 hectare Network Operation Center. The NOC monitors traffic on the entire network of the railway company.
The Burlington Northern Incorporated had relocated their corporate headquarters to Fort Worth, to the headquarters of the railway company Burlington Northern Railroad , after the spin-off of Burlington Resources Inc. in 1988. The plan to build a central network monitoring system also made it possible to move the entire company management to this location. Construction work on the partially developed and developed site began in 1990 and was completed in 1998. After the merger of Burlington Northern and Santa Fe Pacific Corporation, it was decided that the new company would be Fort Worth. A total of around 4,000 employees work at this company location.
family tree
- Burlington Northern Santa Fe
The Burlington Northern Santa Fe was formed from the merger of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway (Santa Fe) with the Burlington Northern Railroad in 1995. The Santa Fe previously merged with Toledo, Peoria and Western Railroad and Kansas City, Mexico and Orient Railway .
In 1970, Burlington Northern was an amalgamation of the Great Northern Railway , Chicago, Burlington and Quincy Railroad , Spokane, Portland and Seattle Railroad and the Northern Pacific Railroad , which had worked closely for decades and also operated many of the American overland trains together, including the Empire Builder and the North Coast Limited . Both trains between Chicago and Seattle , some with through coaches to Portland . The Burlington Northern in turn took over the St. Louis - San Francisco Railway (Frisco) and the Alabama, Tennessee and Northern Railroad in the 1980s .
literature
- Lawrence H. Kaufman: Leaders Count. The Story of the BNSF Railway . Texas Monthly Press, Austin TX 2005, ISBN 0-9724495-2-3 .
- Annual Report of the BNSF 2004
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b BNSF 2017 Form 10-K Report , accessed on August 18, 2018
- ↑ Fact Sheet
- ^ Shareholders approve Burlington Northern Santa Fe Transaction with Berkshire Hathaway
- ↑ BNSF Railway and Vehicle Projects Demonstrate Experimental Hydrogen-Fuel-Cell Switch Locomotive ( Memento from June 21, 2011 in the Internet Archive ). BNSF Railway (June 29, 2009)
- ↑ Plan of the site
- ↑ Woodbine Development: Burlington Northern Santa Fe Corporate Campus Factsheet ( Memento from November 22, 2016 in the Internet Archive )