Barium selenide
| Crystal structure | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
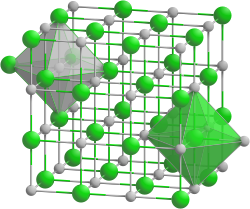
|
||||||||||||||||
| __ Ba 2+ __ Se 2− | ||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Barium selenide | |||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | Base | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white to pink solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 216.29 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
5.02 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
1780 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
2.268 |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
Barium selenide is an inorganic chemical compound of barium from the group of selenides . In addition to BaSe, at least three other selenides of barium are known: Ba 2 Se 3 , BaSe 2 and BaSe 3 .
Extraction and presentation
Barium selenide can be obtained by reducing barium selenate in a hydrogen stream.
It is also possible to display it by reacting barium oxide or barium carbonate with selenium at high temperatures.
properties
Barium selenide is a white solid. In air it turns reddish after a few minutes, after a few hours the powder is light brown. It decomposes with water and reacts with hydrochloric acid to form hydrogen selenide and separate red selenium . It has a crystal structure of the sodium chloride type with the space group Fm 3 m (space group no. 225) .
use
Barium selenide is used in semiconductors and photocells.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e Georg Brauer (Ed.), With the collaboration of Marianne Baudler u. a .: Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry. 3rd, revised edition. Volume II, Ferdinand Enke, Stuttgart 1978, ISBN 3-432-87813-3 , p. 949.
- ^ William M. Haynes: CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 94th Edition . CRC Press, 2016, ISBN 978-1-4665-7115-0 , pp. 50 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ A b R. Blachnik: Pocket book for chemists and physicists Volume 3: Elements, inorganic compounds and materials, minerals . Springer-Verlag, 2013, ISBN 978-3-642-58842-6 , pp. 330 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Harmonized classification and labeling of selenium compounds with the exception of cadmium sulphoselenide and those specified elsewhere in this Annex in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on March 18, 2017.
- ↑ Not explicitly listed in Regulation (EC) No. 1272/2008 (CLP) , but with the indicated labeling it falls under the group entries for barium salts, with the exception of barium sulphate, salts of 1-azo-2-hydroxynaphthalenyl aryl sulphonic acid , and of salts specified elsewhere in this Annex and selenium compounds with the exception of cadmium sulphoselenide and those specified elsewhere in this Annex in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on March 18, 2017. Manufacturers or distributors can use the expand harmonized classification and labeling .
- ^ A b Richard C. Ropp: Encyclopedia of the Alkaline Earth Compounds . Newnes, 2012, ISBN 0-444-59553-8 , pp. 177 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ H. Okamoto: The Ba-Se (barium-selenium) system. In: Journal of Phase Equilibria. 12, 1991, p. 467, doi : 10.1007 / BF02645971 .
- ^ Dale L. Perry: Handbook of Inorganic Compounds, Second Edition . CRC Press, 2016, ISBN 978-1-4398-1462-8 , pp. 56 ( limited preview in Google Book search).




