Barium oxide
| Crystal structure | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
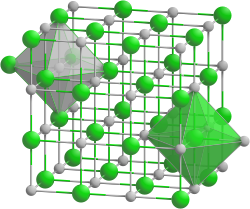
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| __ Ba 2+ __ O 2− | |||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal system |
cubic |
||||||||||||||||||
| Space group |
Fm 3 m (No. 225) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Coordination numbers |
Ba [6], O [6] |
||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Barium oxide | ||||||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | BaO | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless powder |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 153.32 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
5.72 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
1918 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
2000 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
Decomposes to barium hydroxide in water |
||||||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.9841 |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
0.5 mg m −3 (Ba) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Thermodynamic properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| ΔH f 0 |
−554 kJ mol −1 |
||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | |||||||||||||||||||
Barium oxide is the oxide of the alkaline earth metal barium . It has the formula BaO.
Barium oxide (barium earth) was first presented by Johan Gottlieb Gahn in 1774.
properties
Barium oxide is a colorless solid that melts at 1918 ° C. It reacts with water to form barium hydroxide with vigorous heat development .
It has a crystal structure of the sodium chloride type and reacts with humid air to form hydroxide; barium carbonate is formed with air containing CO 2 .
presentation
Technically, it is by heating a coal barium carbonate prepared solvent mixture at about 1030 ° C, in the laboratory by annealing of barium nitrate .
use
Barium oxide is used as an absorbent for carbon dioxide and as a drying agent as well as for the production of barium peroxide , barium hydroxide , organic barium salts , special glasses and oxide cathodes .
Barium oxide undergoes an equilibrium reaction in an oxygen atmosphere to form barium peroxide BaO 2 .
Between 500 and 600 ° C, BaO reacts to form barium peroxide. Above 600 ° C, the oxygen bound in the peroxide is released again. So BaO must not be heated too much. Since the equilibrium reaction to barium peroxide is associated with the release of heat ( exothermic reaction ) and a change in volume, the equilibrium shifts to the left with increasing temperature. You can therefore bind oxygen at a low temperature and release it again at a higher temperature.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Entry on barium oxide. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on July 15, 2014.
- ↑ a b c d e data sheet barium oxide at AlfaAesar, accessed on January 29, 2010 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Index of Refraction of Inorganic Crystals, pp. 10-245.
- ↑ a b Entry on barium oxide in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on July 23, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Not explicitly listed in Regulation (EC) No. 1272/2008 (CLP) , but with the indicated labeling it falls under the group entry barium salts, with the exception of barium sulphate, salts of 1-azo-2-hydroxynaphthalenyl aryl sulphonic acid, and of salts specified elsewhere in this Annex in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ PAETEC Formula Collection Edition 2003, p. 116.
- ↑ Georg Brauer (Ed.), With the collaboration of Marianne Baudler a . a .: Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry. 3rd, revised edition. Volume II, Ferdinand Enke, Stuttgart 1978, ISBN 3-432-87813-3 , p. 926.




