Strontium oxide
| Crystal structure | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
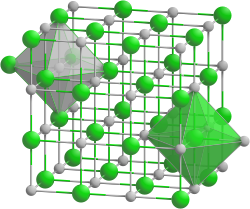
| __ Sr 2+ __ O 2− | |||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal system |
cubic |
||||||||||||||||||
| Space group |
Fm 3 m (No. 225) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Coordination numbers |
Sr [6], O [6] |
||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Strontium oxide | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
Ätzstrontian |
||||||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | SrO | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless or white |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 103.62 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
5.0 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
2460 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
3200 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
Decomposes in water |
||||||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.8710 |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | |||||||||||||||||||
Strontium oxide is the oxide of the alkaline earth metal strontium . In the pure state it is a white powder, in technical quality it is often colored gray by foreign admixtures, which are created, for example, by the oxidation of the very reactive strontium.
Extraction and presentation
Strontium oxide can be obtained from strontium carbonate , which is found in nature as the mineral strontianite . At 1268 ° C under normal atmospheric pressure , strontium carbonate breaks down into strontium oxide and carbon dioxide :
properties
Strontium oxide crystallizes in the sodium chloride structure. At high pressures of> 36 GPa a phase change to a cesium chloride structure is observed. This is accompanied by a volume reduction of 13%, the density of the crystal increases to over 7.1 g / cm 3 .
With water strontium oxide reacts with evolution of heat to strontium :
With the help of aluminum powder , strontium oxide can be reduced to strontium ( aluminothermics ):
use
Strontium oxide is used in the glass industry for the production of special glasses, for example the oxide is added to the glass of screen tubes to reduce radiation . In the past, strontium oxide was used in the production of beet sugar (Strontian process).
Furthermore, due to its high melting temperature and its low electron work function of 1.0 eV, it is used as a coating material on cathodes, for example made of tungsten. This makes it an oxide cathode . See work function . However, because it is water soluble, other materials are preferred in applications where the vacuum must be broken for maintenance work and humid atmospheric air can enter the system. Therefore, the use in practice is limited to systems that are continuously operated in a vacuum. In these permanently closed diodes, they allow glow emissions at as low as 800 ° K.
Individual evidence
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Inorganic Compounds, pp. 5-92.
- ↑ a b Yosiko Sato, Raymond Jeanloz: Phase Transition in SrO. In: Journal of Geophysical Research . 86, 1981, pp. 11773-11778, doi : 10.1029 / JB086iB12p11773 .
- ↑ a b c d e Entry on strontium oxide in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on July 23, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Index of Refraction of Inorganic Crystals, pp. 10-248.
- ^ H. Ost: Textbook of Technical Chemistry , published by Robert Oppenheim, Berlin, 1890, p. 369ff.



